Ms. Mai Huong (Vinh City, Nghe An Province) asked: Doctor, should children use sunscreen when going out?
Master, Doctor Tran Thu Nguyet, Vietnam Institute of Applied Medicine, answered as follows: Adults often think that children do not need to use sunscreen, just need to cover carefully and avoid exposing children to sunlight. However, the American Academy of Pediatrics affirms that it is necessary to use a small amount of sunscreen containing 15 +++ SPF (sun protection factor) for areas such as: Face, back of hands of infants and young children if children have to be exposed to sunlight.
The reason why you should use sunscreen for children is that their skin is easily damaged by ultraviolet rays in sunlight. In addition to the seven-color spectrum, sunlight also contains ultraviolet rays with 3 types: UVA, UVB and UVC. Ultraviolet rays, especially on hot sunny days with high intensity (UV index from 6 or higher), will cause many harmful effects on children's skin. The skin of adults has high elasticity thanks to the strong collagen fiber system. However, the collagen fibers in children's skin are very small, so the elasticity and ability to resist sunlight are many times lower than that of adults. Therefore, children's fragile, sensitive skin also needs sun protection.
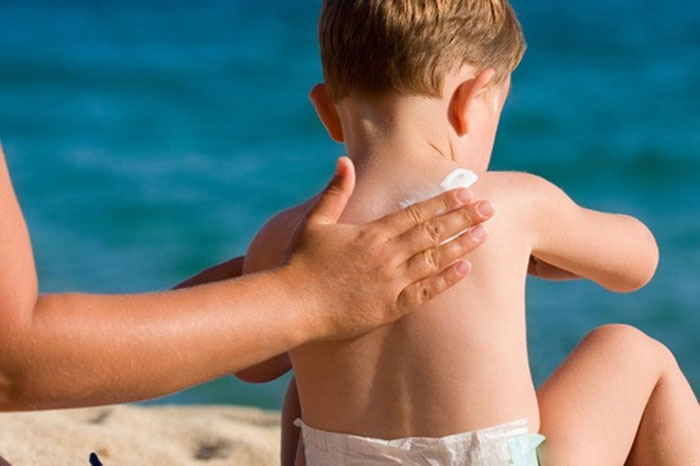 |
| Illustration photo: Vinmec Hospital |
Sun damage to the skin is most common in children when going to the beach, swimming pool or suddenly going out in strong sunlight, with different manifestations. Mild sunburn causes redness, burning sensation on the skin surface. Severe sunburn easily causes skin damage and can be treated as a severe burn. The child's skin blisters, feels painful and uncomfortable, a few days later the skin turns dark brown, scaly and peels off like snake skin. Or the child has polymorphic light rash: The disease often starts in the summer, due to frequent exposure to sunlight. Symptoms of the disease are rashes, redness, blisters, even blisters on exposed skin such as the face, neck, collar triangle, arms, forearms and back of hands, back of feet...
Sunlight can also trigger and aggravate skin diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, melasma, polymorphous light eruption... If exposed to strong sunlight regularly, young skin will age due to ultraviolet rays, with many freckles, age spots, roughness, and wrinkles appearing like in adulthood. More dangerously, all three types of ultraviolet rays UVA, UVB, and UVC damage the skin, increase the aging process, damage DNA, create many free radicals, cause increased proliferation of inflammatory cells in the dermis, and in the long term cause skin cancer.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends: Sunscreen should only be used on areas of the baby's skin that are exposed to sunlight when not covered by clothing. Using this sunscreen is to avoid the dangers of "overdose" of sunlight. The best sunscreen for children must meet the following requirements: Have an SPF of 15+++; provide protection against both UVA and UVB rays; choose a sunscreen with the words "broad spectrum" on the label. Prioritize choosing physical sunscreens, containing titanium dioxide, zinc dioxide to protect against both UVA and UVB rays and the probability of causing skin allergies is lower than chemical sunscreens; difficult to wash off with water; less likely to cause allergies, no fragrance and easy to use for babies such as gel, spray, spray...
To avoid allergies, parents should test sunscreen on thin areas of skin on their own body. If there are no signs of allergies or unusual reactions, try a small amount on the child's arms or legs first. Apply sunscreen about 30 minutes before going out, paying attention to apply evenly to sensitive areas that are most exposed to sunlight such as the nose, ears, cheeks and shoulders. Do not apply to the child's eyes or mouth. For young children, only apply enough cream to protect areas exposed to sunlight when not covered by clothing. Reapply after 2-3 hours or more often, especially when the child sweats, swims or plays in the water a lot; do not let the child stay in the sun for more than 2 hours... Parents should consult a doctor before using sunscreen if the child has a very sensitive skin or is having skin problems such as itching, blisters, rashes. Because people with sensitive skin are susceptible to skin irritation, dermatitis and infection. Children should be taken to the doctor if these symptoms appear after being in the sun: Blistering in the sunburn; the redness of the skin gets worse; swelling in the face; fever, chills, fatigue; headache (children who cannot speak often cry a lot and put their hands on their heads); thirst, very dry mouth, no tears when crying; decreased urination.
Health-related questions should be sent to the “Your Doctor” section, Economic-Social-Internal Affairs Editorial Department, People’s Army Newspaper, 8 Ly Nam De, Hang Ma, Hoan Kiem, Hanoi. Email: [email protected], [email protected]. Phone: 0243.8456735. |
*Please visit the Health section to see related news and articles.
Source





























![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)

























































Comment (0)