People who drink a lot of alcohol, eat a lot of foods rich in purines, elderly men, and people with chronic diseases are at high risk of gout in the wrist.
Gout is a type of arthritis that usually affects the big toe. However, it can affect any joint, including the wrist. When it occurs in more than one joint at a time, it is called polyarthritis. People with the following factors are at higher risk of developing gout in the wrist.
Drinking too much alcohol : Alcoholic beverages contain high levels of purines, which create uric acid that leads to gout. In addition to increasing the risk of gout in the wrist, alcohol also makes gout flare-ups more likely.
Consuming foods high in purines : You are at higher risk of gout if you regularly eat foods that produce uric acid, such as red meat, sugary drinks, and seafood. Excess uric acid can build up as crystals in tissues, causing kidney stones and gout.
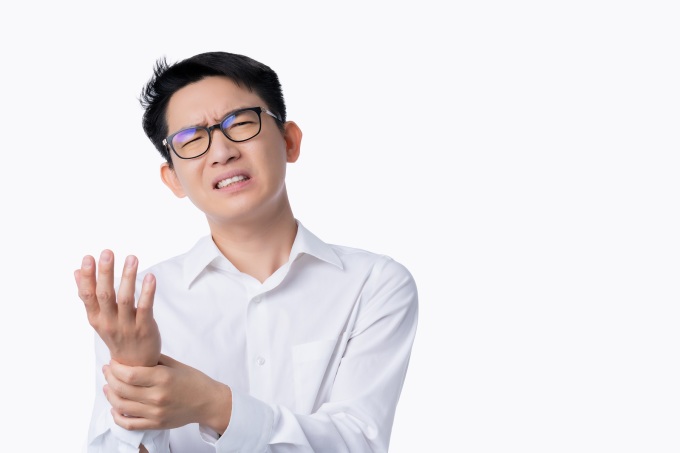

Gout in the wrist affects the ability to move the hand. Photo: Freepik
Family history : If grandparents and parents have gout, the risk of their children and grandchildren getting the disease is often higher. First, it is partly due to genetics. Second, because people live together in a family, their eating and living habits will be similar. This increases the risk of getting the disease.
Chronic diseases : The risk of gout in the wrist increases when people have diseases such as psoriasis, kidney disease, diabetes and high blood pressure. In addition, inflammatory arthritis conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and wrist injuries also increase the risk of gout in the wrist.
Men : Men under 65 are four times more likely to develop gout than women. This ratio is also true for gout in the wrist.
Increasing age : The risk of gouty wrist occurs in everyone, of all ages. However, for the elderly, the joints are more vulnerable, the risk of gouty wrist also increases.
Gout in the wrist is not as common as gout in the big toe. Symptoms come on quickly and become severe over a short period of time, and can affect the hand and wrist simultaneously. Clinical symptoms of gout in the wrist or hand may include: swelling of the wrist or hand, heat, redness, and pain in the affected joint, stiffness of the wrist, limited movement due to pain and swelling, pain, fever due to inflammation, headache, and malaise.
Untreated gout can cause permanent joint damage, affecting mobility. Early diagnosis and treatment is the best way to avoid irreversible damage to the wrist. Additional tests to confirm a diagnosis of gout in the wrist include a uric acid blood test, joint aspiration, imaging studies, etc.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the goal of gout treatment is to control pain and prevent future attacks. People can reduce symptoms by making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, stopping alcohol consumption, choosing activities that are gentle on the joints, including walking, swimming, and cycling, exercising the wrists, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding overexertion of the wrists.
Anh Chi (According to Very Well Health )
Source link


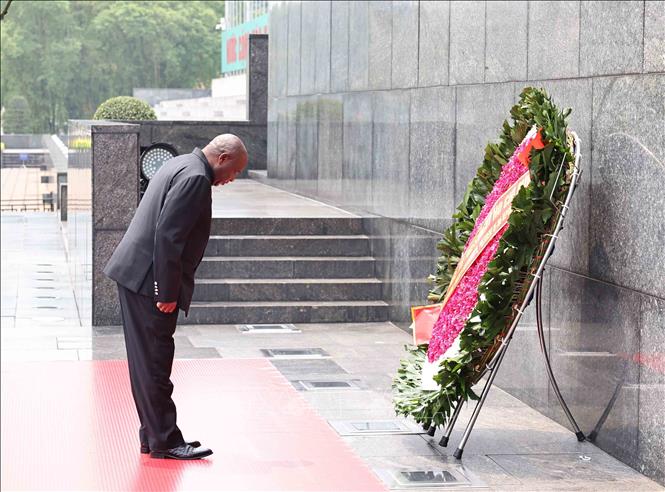
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong presides over the official welcoming ceremony for Burundian President Évariste Ndayishimiye](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/4/63ceadc486ff4138abe2e88e93c81c91)
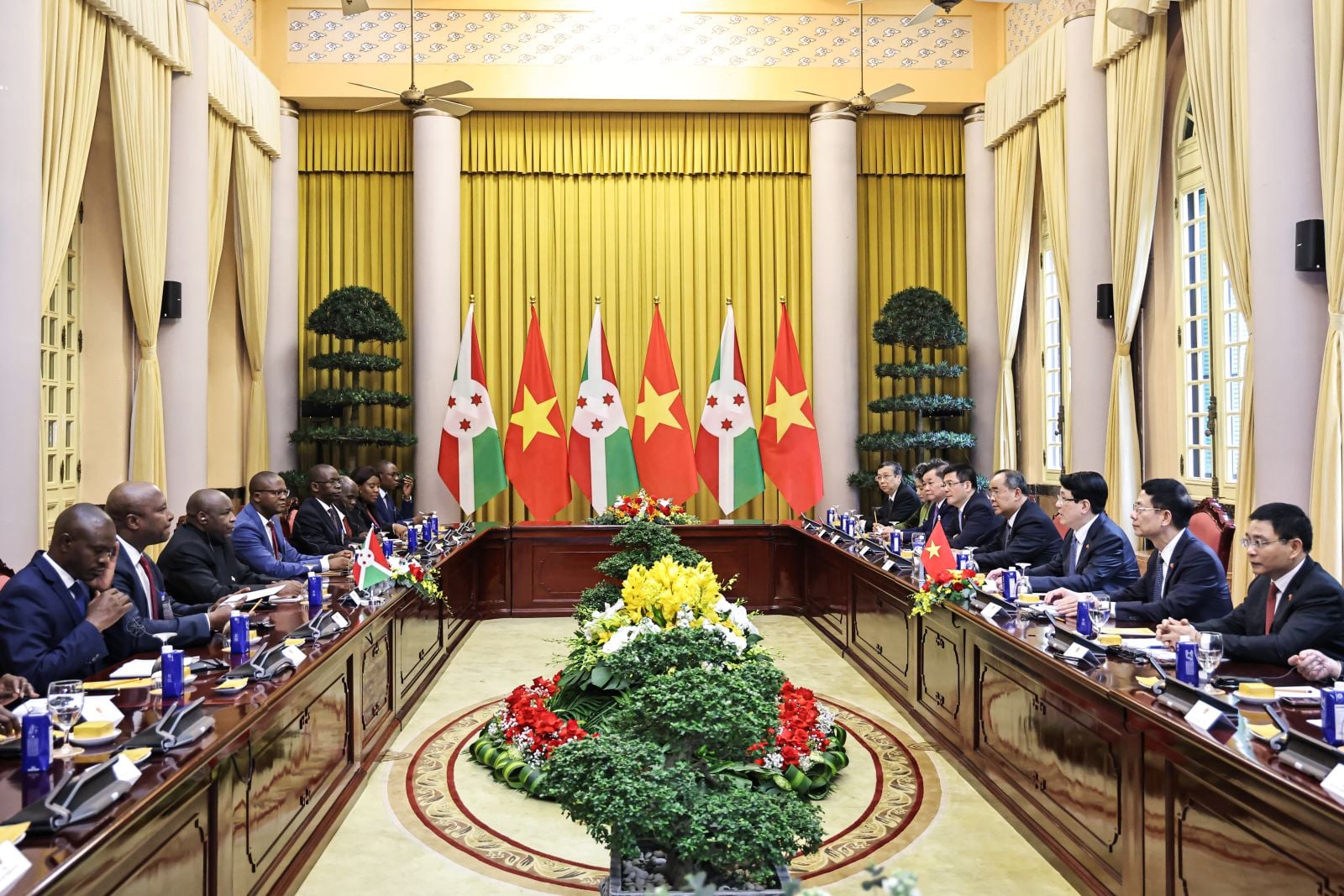
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with President of the Republic of Burundi Evariste Ndayishimiye](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/4/979010f4c7634f6a82b8e01821170586)
![[Photo] Parade rehearsal on the training ground in preparation for the April 30 celebration in Ho Chi Minh City](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/4/e5645ddf85f647e6a25164d11de71592)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives President of the Republic of Burundi Évariste Ndayishimiye](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/4/d6df4662ecde41ef9bf55f1648343454)
![[Photo] Workshop "Future for the Rising Generation" continues the profound value and strong message from the article of General Secretary To Lam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/4/ec974c5d9e8e44f2b01384038e183115)


















































































Comment (0)