Vitamin D deficiency can manifest in many ways such as fatigue, back pain, muscle pain, hair loss, slow wound healing or depression symptoms...
Frequent illness or infection
One of the most important roles of vitamin D is supporting the immune system, helping the body fight off viruses and bacteria that cause disease. Vitamin D interacts directly with the cells responsible for fighting infections. If you often get sick, especially with colds or the flu, a vitamin D deficiency may be a contributing factor.
Research published in PubMed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) has shown a link between vitamin D deficiency and respiratory infections such as colds, bronchitis and pneumonia. Some studies have also found that taking about 4,000 IU of vitamin D per day can reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Tired
Research published in the US National Institutes of Health shows a link between vitamin D deficiency and symptoms of fatigue. Additionally, children with low vitamin D levels are associated with poor sleep quality, shorter sleep duration, and later bedtimes.
Supplementing with this vitamin may reduce severe fatigue in people who are deficient.
Bone and back pain
Bone pain and lower back pain can be warning signs of low vitamin D levels. Vitamin D helps maintain bone health by improving the body's ability to absorb calcium.
It has been hypothesized that people with arthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic pain often have lower levels of vitamin D than those without the condition. However, more specific research is needed to confirm this.
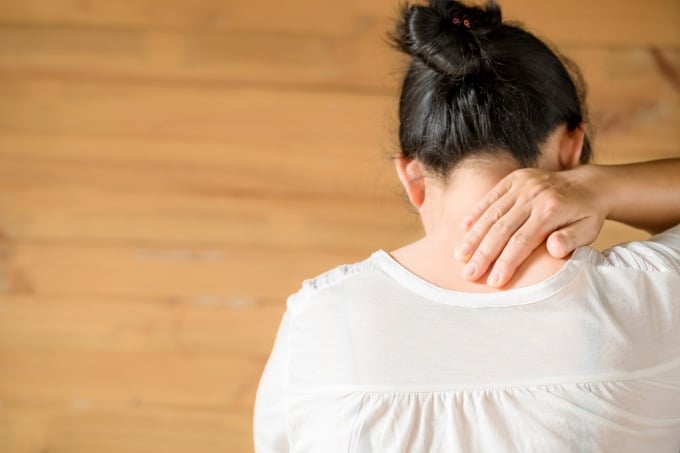

Bone pain can be a warning sign of low vitamin D levels in the body. Photo: Freepik
Osteoporosis
As mentioned, vitamin D plays an important role in calcium absorption and bone metabolism. Therefore, supplementing vitamin D and calcium at the same time will help the body absorb it to the maximum.
Low bone mineral density is a sign that bones have lost calcium and other minerals. This puts older adults, especially women, at higher risk of fractures. A study of more than 1,100 middle-aged or postmenopausal women found a strong link between low vitamin D levels and low bone mineral density.
High-dose vitamin D supplements may not improve bone density in vitamin D-deficient women but may be a good strategy to preserve bone mass and reduce the risk of fractures, researchers say.
Hair loss
Stress is a common cause of hair loss, but severe hair loss can be caused by illness or nutritional deficiencies. Hair loss in women has been linked to low vitamin D levels.
Research in people with hair loss and low vitamin D levels suggests a link between the two conditions. In another study in 48 people with hair loss, applying any synthetic form of vitamin D to their hair for 12 weeks significantly improved hair regrowth.
Muscle pain
The cause of muscle pain is often difficult to determine, however vitamin D deficiency is one potential cause.
Vitamin D receptors are found in nerve cells called nociceptors. Deficiency of this vitamin may also be involved in the body's transmission of pain signals, contributing to chronic pain. Some studies have also noted that high-dose vitamin D supplements may reduce various types of pain in people who are deficient in this vitamin.
Anxiety, depression
One review found that levels of calcidiol (a form of vitamin D) were lower in people with anxiety or depression.
Separate studies in pregnant women have shown that adequate vitamin D intake can help reduce symptoms of anxiety, improve sleep quality, and even prevent postpartum depression. Some reviews have found that vitamin D supplementation can also help reduce symptoms of depression.
Slow wound healing
Slow wound healing after surgery or injury may be a sign that your vitamin D levels are too low. In fact, results from a test-tube study showed that vitamin D increased the production of compounds important for forming new skin, similar to part of the wound-healing process.
Vitamin D deficiency is usually treated with supplements, dietary sources, and conscious exposure to sunlight. Foods rich in the vitamin include: fatty fish, egg yolks, cereals, yogurt... Oral supplements are a common treatment for vitamin D deficiency, but consult your doctor for dosage recommendations.
Due to the negative effects of too much exposure to UV rays, if you want to absorb vitamin D from sunlight, you need to apply appropriate sunscreen.
Bao Bao (According to Healthline )
Source link


![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper announces the project "Love Vietnam so much"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/362f882012d3432783fc92fab1b3e980)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives French Ambassador to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/49224f0f12e84b66a73b17eb251f7278)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with outstanding workers in the oil and gas industry](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/1d0de4026b75434ab34279624db7ee4a)

![[Photo] Closing of the 4th Summit of the Partnership for Green Growth and the Global Goals](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/c0a0df9852c84e58be0a8b939189c85a)
![[Photo] Promoting friendship, solidarity and cooperation between the armies and people of the two countries](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0c4d087864f14092aed77252590b6bae)

























![[Photo] Welcoming ceremony for Chinese Defense Minister and delegation for friendship exchange](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/fadd533046594e5cacbb28de4c4d5655)



























![[Video] Viettel officially puts into operation the largest submarine optical cable line in Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/f19008c6010c4a538cc422cb791ca0a1)





































Comment (0)