- Dong Nai provides inclusive education and career guidance for autistic children
- Binh Phuoc: Investors signed to implement a 55-hectare complex project next to the most beautiful ecological lake in Chon Thanh
According to MSc. Dr. Nguyen Mai Huong - Deputy Head of the Department of Psychiatry (National Children's Hospital), delayed language development in children is a condition of delay in achieving language development milestones, including receptive language and expressive language. Children may have difficulty understanding speech, responding to other people's speech, slow speech, inability to combine words into sentences, limited vocabulary, awkward sentence expression... Normally, a child is considered to have delayed speech when by the age of 2 he or she still cannot say about 50 single words or cannot say compound words (2-word sentences).
Language delay in children accounts for about 20%. Most children will catch up by age 4 if they receive early and active intervention. However, some children still have language difficulties after age 4, so they still need long-term intervention.
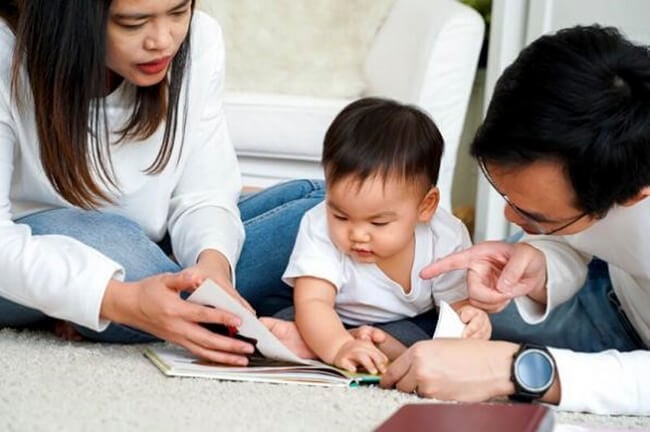

Children need hearing tests in cases of abnormal language development.
Some risk factors for language delay: Boys are affected about 3 times more than girls; Family members with language delay (parents, siblings); Premature babies, low birth weight babies, and birth complications.
Symptoms of children with delayed language development
Language delay can appear alone in children, or as one of many symptoms of other communication and developmental disorders. Therefore, parents need to pay attention to detect other accompanying abnormalities, including abnormalities of the jaw and face, and the speech apparatus.
Hearing comprehension: The child is less responsive to sounds, or does not understand speech or commands. The child needs to have his or her hearing tested in cases of abnormal language development.
Poor communication and social interaction skills: Little response to calls, reduced eye contact, indifference, less play with peers, not knowing how to show off or share concerns, no gestures such as pointing, waving, nodding/shaking head...
Unusual behaviors: hand movements, unusual waving, tiptoeing, spinning, excessive absorption in an object or event…
Excessive activity, difficulty sitting still, difficulty maintaining attention for more than a few minutes. Frequent, intense, unprovoked tantrums.
What should parents do when their children have slow language development?
Early detection of signs of delayed language and communication development in children will bring better treatment opportunities. Therefore, when parents see that their children have the above abnormalities, they should promptly take their children to reputable medical facilities for examination: To comprehensively assess the child's developmental skills, detect the causes or factors affecting the child's language, and perform the necessary psychological tests.
The Department of Psychiatry – National Children’s Hospital is the leading unit in mental health care for children in Vietnam. Children with language delay will be examined by a multidisciplinary team, including doctors, clinical psychologists, special education teachers, experienced speech therapists, with deep expertise, enthusiasm, and love for children. Parents of children will be guided and advised specifically on intervention activities and support for children at home.
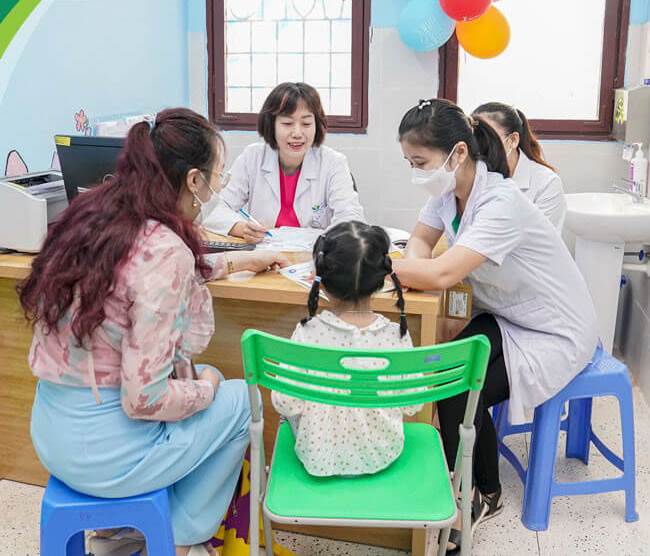

Children with speech delay are examined by a team of doctors, clinical psychologists, special education teachers, and speech therapists at the Department of Psychiatry - National Children's Hospital.
Children with speech delay are examined by a team of doctors, clinical psychologists, special education teachers, and speech therapists at the Department of Psychiatry - National Children's Hospital. Currently, to meet the needs of examination and intervention for developmental disorders and mental disorders in children, the Department of Psychiatry - National Children's Hospital has implemented weekly medical examinations on Saturdays.
At the same time, to reduce costs and procedures during the examination process, from July 2023, the Department of Psychiatry has implemented examination packages in cases of children suspected of autism or suspected hyperactivity.
Some guidelines for language development in children
Playing with children is the best way to help them learn language. Through interactive play activities with parents or other children, children will imitate pronunciation, express their wishes, understand other people's requests, etc. While playing, parents should try to do the following:
Express verbally what your child is doing, what he or she is interested in, or what you are doing, what you are interested in, to provide a rich verbal environment for your child. Try to follow the principles of speaking slowly, speaking clearly, speaking in short sentences, and speaking with emphasis. For example: “push the car”, “open the door”…
Model the words you expect your child to say. For example, “open,” “mommy get,” etc. Praise any attempt at saying them, no matter how unclear.
Limit imperatives. Too many imperatives or questions will confuse your child and cause him to refuse to speak. For example, instead of asking “say ‘flower’,” say “look, flower.”
Offer choices, and wait for your child to respond to the choice with a gesture or sound. For example: “Would you like a banana or an orange? Banana. Orange.”
Read or talk to your child regularly, as part of your daily activities.
Source link


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives CEO of Standard Chartered Group](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/125507ba412d4ebfb091fa7ddb936b3b)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Belarus Anatoly Sivak](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/79cdb685820a45868602e2fa576977a0)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Russian Ambassador to Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/b486192404d54058b15165174ea36c4e)





























































































Comment (0)