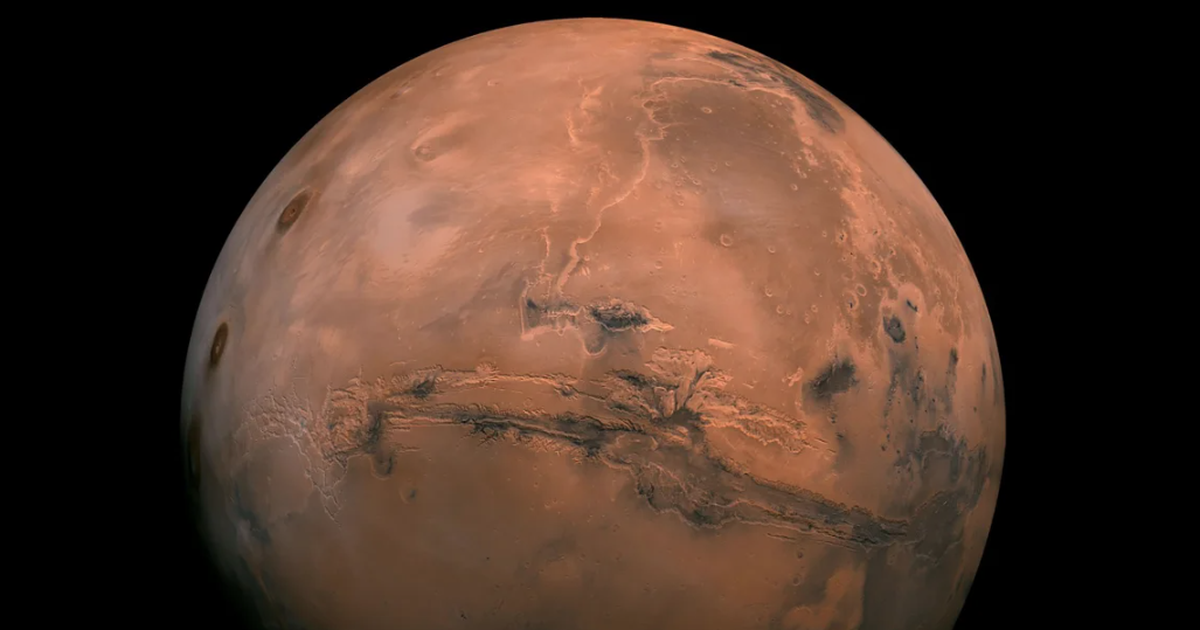
(NLDO) - The new photo has provided a clear look at how the "Mars spider in the Inca City" formed.
In the photo released by NASA, taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) spacecraft, the red color of the cold southernmost land on Mars appears with strange black spots, looking as if something dark has just erupted from below.
According to NASA, these strange, fan-like features on the surface of Mars are geysers of gas and dust, which only appear in the area around the planet's south pole and only in the spring.
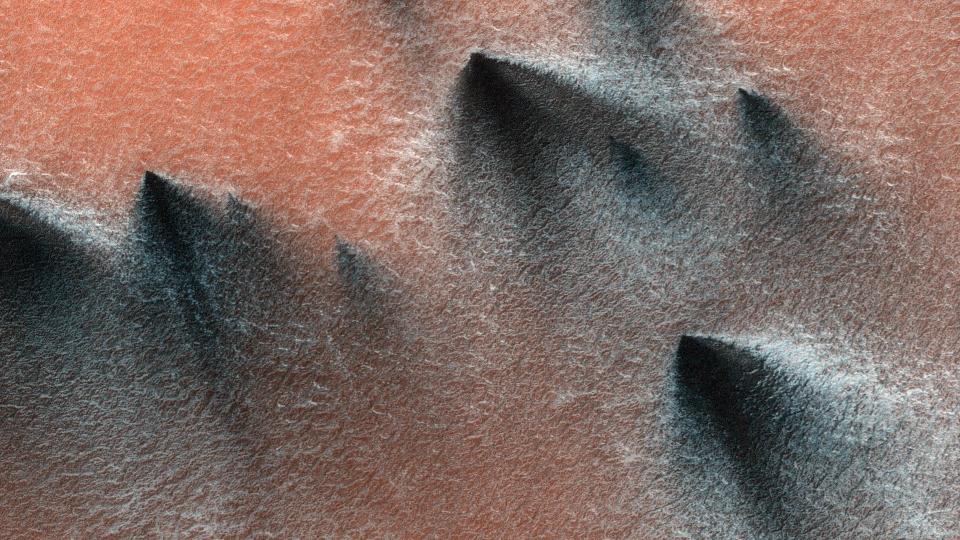

Dark streaks created by spring eruptions of gas and dust in the area around the south pole of Mars - Photo: NASA
In winter, on the red planet, carbon dioxide ice accumulates near the surface.
This ice is transparent and sunlight that passes through it is absorbed at the bottom of the ice. As the sun rises higher in the sky and spring begins, the carbon dioxide ice begins to warm, turning into vapor from below, much like cometary material sublimates.
This vapor quickly seeks out weak points in the ice, punches through them, and erupts upward, carrying with it a great deal of dust.
These eruptions sometimes leave behind streaks of dust that radiate in many directions within the ice, resembling the legs of spiders, giving the appearance the nickname "Mars spiders".
Last spring, the European Space Agency (ESA) also attracted attention when it released a photo of a swarm of "Mars spiders", which looked even more mysterious when gathered in an area called "Inca City", also an area near the planet's South Pole.
The name "Inca City" comes from the fact that natural structures in the area accidentally created an image that resembled the ruins of a giant city when photographed by spacecraft from above.
Mars also has four seasons like Earth, thanks to its orbital tilt of 25.2 degrees, which is quite close to Earth's 23.5 degrees.
The tilted axis allows different parts of the planet to receive different amounts of light as it orbits the Sun.
However, the red planet takes 687 days to orbit the Sun, so the seasons are twice as long as on Earth. The planet's orbit is a much longer ellipse than Earth's, so the temperature differences between seasons are also more severe.
According to the ESA, Mars is closest to the Sun during the southern hemisphere summer, making that season shorter and hotter than the northern hemisphere summer.
In contrast, winter in the Southern Hemisphere occurs when Mars is moving slowest and furthest from the sun, making winters longer and colder than winters in the Northern Hemisphere.
This has contributed to the creation of the unique "Mars spider" structure, something we do not see on Earth.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/tau-vu-tru-nasa-chup-duoc-nhen-sao-hoa-tai-xuat-196250211103336316.htm



![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper announces the project "Love Vietnam so much"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/362f882012d3432783fc92fab1b3e980)
![[Photo] Closing of the 4th Summit of the Partnership for Green Growth and the Global Goals](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/c0a0df9852c84e58be0a8b939189c85a)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives French Ambassador to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/49224f0f12e84b66a73b17eb251f7278)
![[Photo] Promoting friendship, solidarity and cooperation between the armies and people of the two countries](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0c4d087864f14092aed77252590b6bae)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with outstanding workers in the oil and gas industry](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/1d0de4026b75434ab34279624db7ee4a)























![[Photo] Welcoming ceremony for Chinese Defense Minister and delegation for friendship exchange](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/fadd533046594e5cacbb28de4c4d5655)



























![[Video] Viettel officially puts into operation the largest submarine optical cable line in Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/f19008c6010c4a538cc422cb791ca0a1)





































Comment (0)