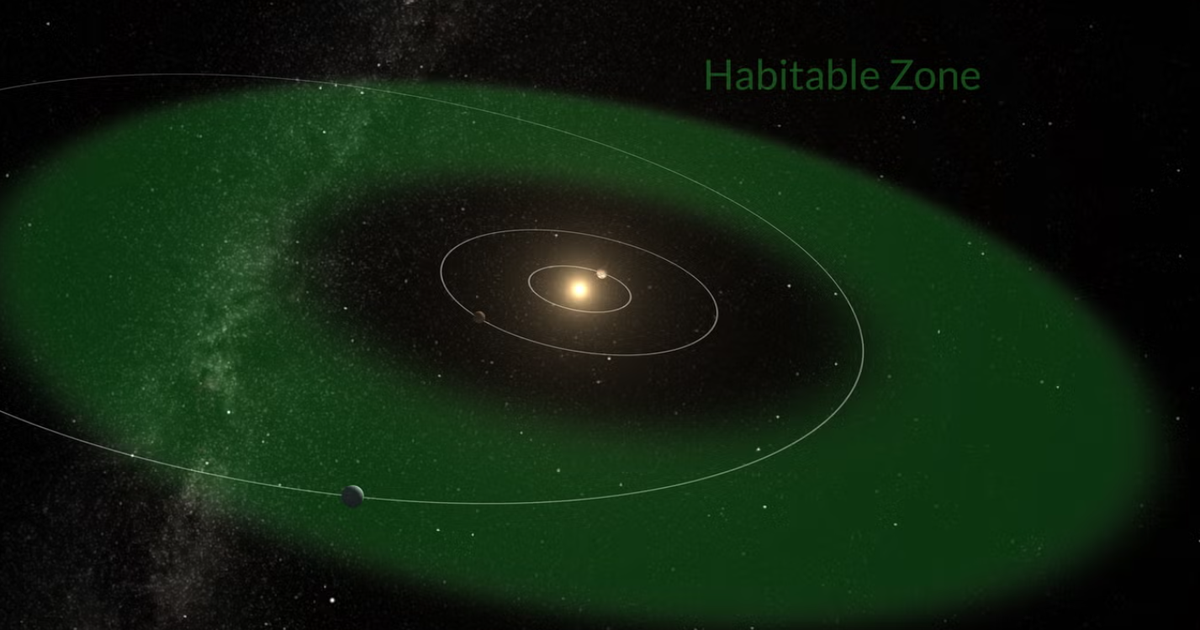
Astronomers have discovered a super-Earth in the habitable zone, orbiting a star 137 light years from the Solar System.
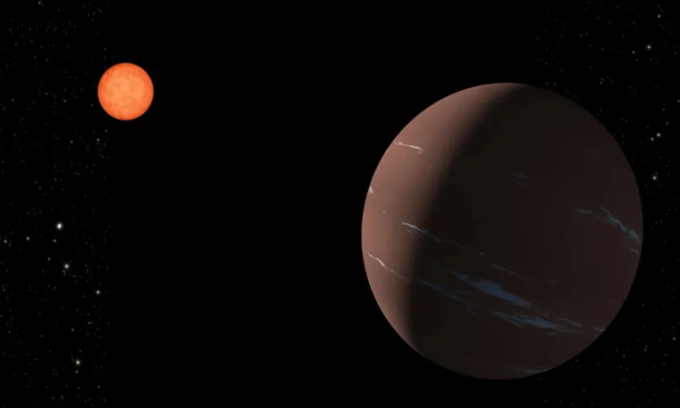

Super-Earth TOI-715b orbits a red dwarf star. Photo: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The exoplanet, called TOI-715b, orbits a cool red dwarf star that is smaller than the Sun. Astronomers discovered the planet using NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). They detailed their findings in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, CNN reported on February 10.
The team determined that the planet, estimated to be 1.5 times the size of Earth, takes just over 19 days to complete one orbit around its host star. It is close enough to its star to exist in the habitable zone, the distance from the star that provides the planet with the right temperature for liquid water to exist on its surface.
The habitable zone is usually calculated based on factors such as the size, temperature and mass of the star, as well as the reflectivity of the planet's surface. However, there can be large uncertainties associated with these factors, leading to questions about whether the planet is truly in the habitable zone, according to lead author Dr Georgina Dransfield of the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Birmingham, UK. Astronomers believe that TOI-715b lies in a narrower, more optimal region of the star called the preserved habitable zone, which is less affected by the margin of error.
Since its launch in 2018, TESS has helped astronomers discover a number of planets around relatively nearby stars that are suitable for follow-up with ground-based and space-based observatories. The telescope can detect dips in starlight, revealing planets as they pass across their surfaces. TOI-715b is close to its star and has a fast orbit, meaning the planet frequently passes in front of it. The exoplanet is an ideal candidate for observation with the future Webb Space Telescope, which observes the universe in infrared light and can peer inside planetary atmospheres.
As the planet passes in front of its host star and filters out the starlight, Webb will be able to look for evidence of an atmosphere, and even determine the planet’s atmospheric composition. If the Earth-sized planet is confirmed, it will become the smallest planet in the habitable zone that TESS has found.
Red dwarfs are the most common type of star in the Milky Way. Some red dwarfs harbor small, rocky planets, like the recently discovered TRAPPIST system, which contains seven planets located just 40 light years away. TOI-715b’s star has only flashed twice in the past two years and is not very active, suggesting it is an old star, Dransfield said.
In the future, astronomers hope to search for planets orbiting stars more similar to the Sun. Upcoming missions such as the European Space Agency’s PLATO mission, which will carry 26 cameras and search for Earth-like planets in the habitable zone of their host star, are scheduled to launch in 2026.
An Khang (According to IFL Science )
Source link


![[Photo] Warm meeting between the two First Ladies of the Prime Ministers of Vietnam and Ethiopia with visually impaired students of Nguyen Dinh Chieu School](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/b1a43ba73eb94fea89034e458154f7ae)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives Kenyan Defense Minister Soipan Tuya](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0e7a5185e8144d73af91e67e03567f41)
![[Photo] Promoting friendship, solidarity and cooperation between the armies and people of the two countries](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0c4d087864f14092aed77252590b6bae)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives French Ambassador to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/49224f0f12e84b66a73b17eb251f7278)
![[Photo] Welcoming ceremony for Chinese Defense Minister and delegation for friendship exchange](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/fadd533046594e5cacbb28de4c4d5655)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and Ethiopian Prime Minister visit Tran Quoc Pagoda](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/18ba6e1e73f94a618f5b5e9c1bd364a8)



















































![[Video] Viettel officially puts into operation the largest submarine optical cable line in Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/f19008c6010c4a538cc422cb791ca0a1)





































Comment (0)