Several new European and American rockets will launch next year, as the aerospace industry faces a shortage of launch vehicles due to the growing number of satellites.
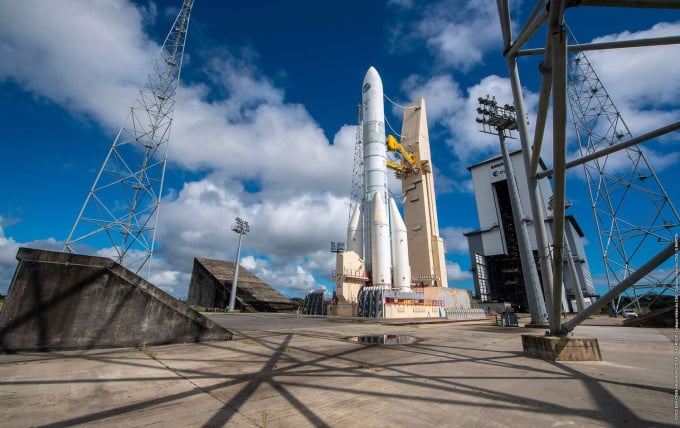

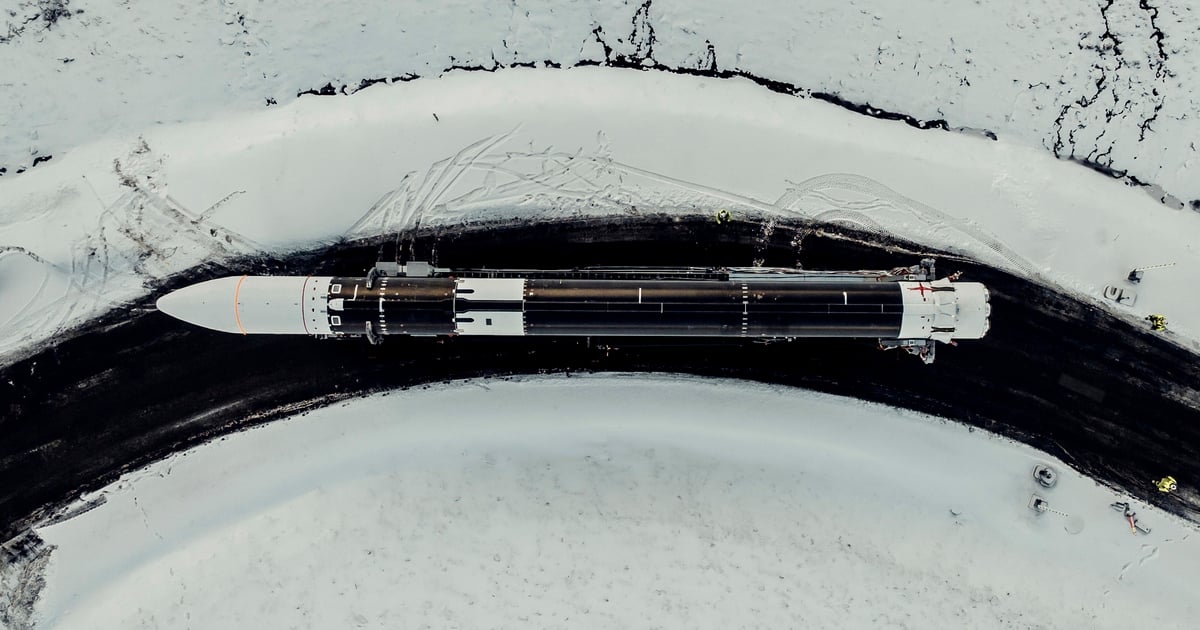
The Ariane 6 rocket at the European Spaceport launch site in Kourou, French Guiana, June 22. Photo: AFP
Ariane 6
The Ariane 6 rocket is being developed by ArianeGroup, a French company, for the European Space Agency (ESA). The rocket is scheduled to make its maiden flight between June 15 and July 31, 2024, after a four-year delay due to Covid-19 and other difficulties. The project was launched in 2014 as Europe's answer to the strong development of the Falcon 9, a rocket manufactured by the US company SpaceX. Based on the Ariane 5, the Ariane 6 will be half the price of its predecessor thanks to new manufacturing methods.
Ariane 6 currently has 28 launches planned. There are two versions of the rocket, the more powerful one capable of carrying 11.5 tons of cargo to geostationary orbit and 21.6 tons of cargo to low Earth orbit. Once Ariane 6 is operational, the challenge for ArianeGroup will be to increase production. "Going from producing two rockets a year to nine rockets a year is a huge industrial challenge," said CEO Martin Sion.
Vega C
Grounded since December 2022 after the failure of its first commercial flight, the Vega C rocket, manufactured by Italian aerospace company Avio, is scheduled to launch again in the fourth quarter of next year. The incident occurred due to a damaged rocket engine nozzle, forcing experts to redesign it. The Vega C rocket is about 35 meters tall with a takeoff mass of 210 tons.
The lack of small rockets has forced ESA to rely on the US' SpaceX to launch some of Europe's scientific and GPS satellites. If successful, the Vega C would help to overcome this problem.
Vulcan Centaur
United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin, is developing the Vulcan Centaur rocket to replace the aging Atlas V and Delta IV launch vehicles. After its first flights, ULA will begin recovering and reusing the rocket’s first stage. Reusability and other improvements make the Vulcan Centaur much more affordable than its predecessors, according to Tory Bruno, CEO of ULA.
The Vulcan Centaur can carry 27.2 tons of cargo into low Earth orbit, about the same as the Falcon 9 rocket. The first launch of the Vulcan Centaur is scheduled for early January 2024. On this mission, a private lunar lander could become the first American craft to land on the Moon since the end of the Apollo program. On its second mission, the rocket will launch the new Dream Chaser spacecraft from the US company Sierra Space into space in the second quarter of 2024. This mini-shuttle will be responsible for resupplying the International Space Station (ISS).
Starship
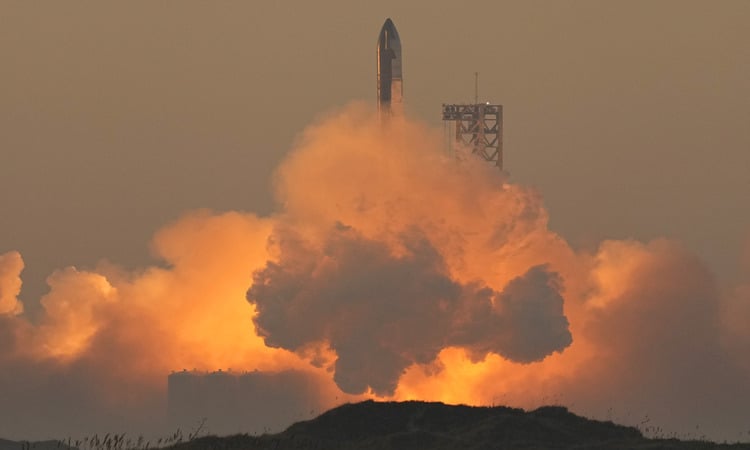
SpaceX will continue testing the massive Starship launch system in 2024. The first two flights after the rocket was fully assembled ended with an explosion. SpaceX said the explosions in the early stages of the rocket’s development were well received and helped it make design choices more quickly. On the second flight in November 2023, the rocket’s two stages successfully separated before exploding, causing no major damage to the launch pad.
Starship launch system explodes during second test flight in November 2023. Video: WSJ
Starship is the largest and most powerful launch vehicle ever built, standing at about 400 feet tall. NASA is closely monitoring the development of Starship. The agency has signed a contract to use a version of Starship as a lunar lander for the Artemis missions.
SpaceX founder Elon Musk predicts that Starship could launch again in a few weeks. However, the next launch will not take place until the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) approves it.
New Glenn
Blue Origin, the US-based company of billionaire Jeff Bezos, has already taken tourists to the edge of space on short flights on its suborbital rocket New Shepard. But the company is also developing a larger rocket, the New Glenn, which will stand 320 feet tall and carry 45 tons of cargo into low Earth orbit. That’s more than twice the size of the Falcon 9, but still smaller than SpaceX’s 63.8-ton Falcon Heavy.
“We’re aiming to launch in 2024,” a Blue Origin spokesperson said of New Glenn. One of the rocket’s first flights will help NASA’s EscaPADE spacecraft study the Martian magnetosphere. New Glenn is also part of the lunar landing system NASA ordered for its Artemis 5 mission.
Thu Thao (According to AFP )
Source link






![[Photo] Third meeting of the Organizing Subcommittee serving the 14th National Party Congress](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/3f342a185e714df58aad8c0fc08e4af2)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Russian Ambassador to Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/b486192404d54058b15165174ea36c4e)



























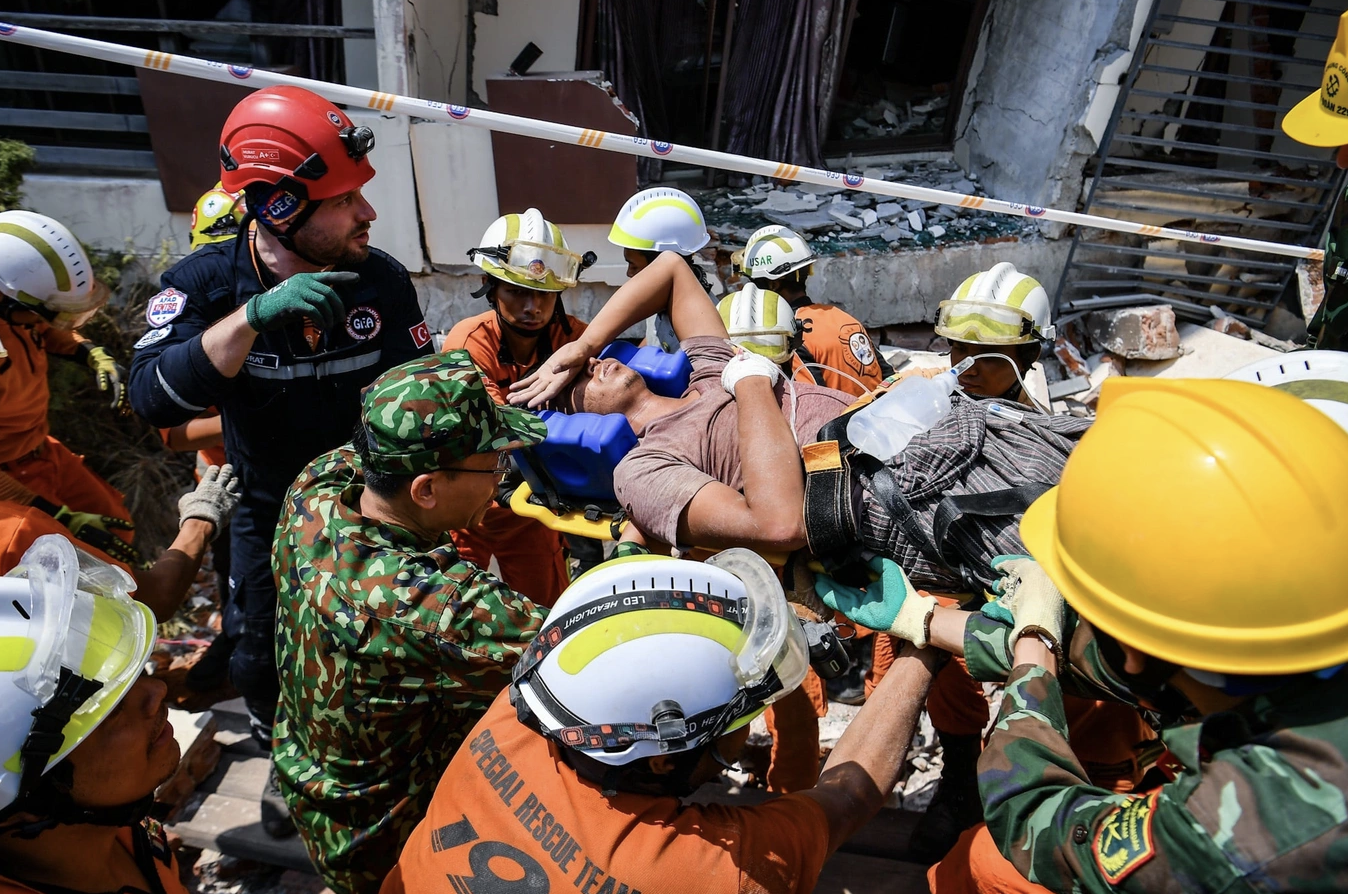
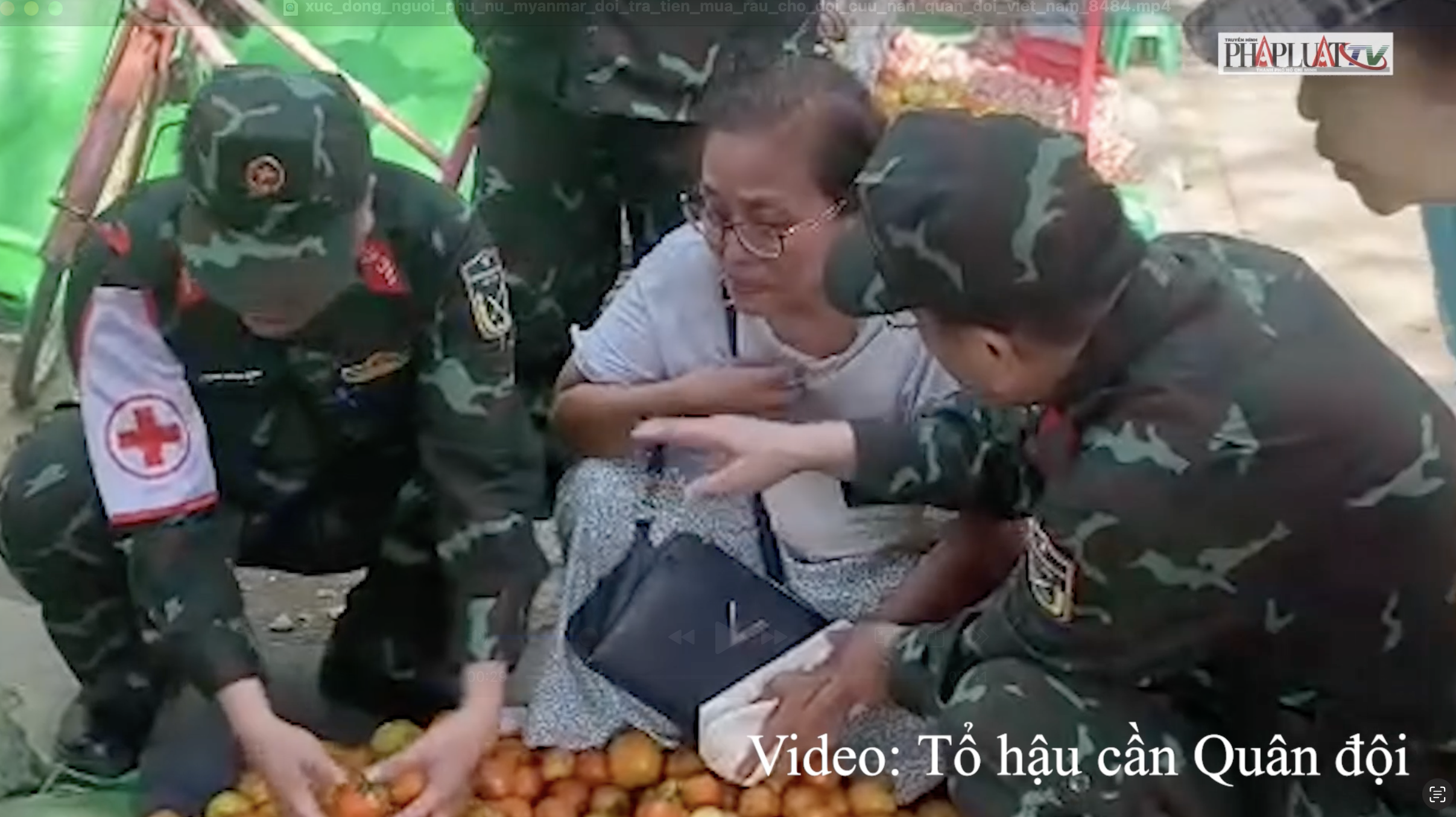
![[Photo] Relatives of victims of the earthquake in Myanmar were moved and grateful to the rescue team of the Vietnamese Ministry of National Defense.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/aa6a37e9b59543dfb0ddc7f44162a7a7)



































































Comment (0)