'I saw information online that diabetics should not eat porridge. Is this true? Thank you, doctor.' (M. Long, in Ho Chi Minh City).
Specialist Doctor 1 Cao Thi Lan Huong, Cardiovascular - Diabetes Healthcare System 315 (HCMC), answers: Before answering the question of whether diabetics can eat porridge, we need to clearly understand the information about the glycemic index of this dish.
Specifically, the glycemic index of porridge (GI) usually ranges from 78 - 99.3 (high group), while the glycemic load (GL) of this dish usually ranges from 10.3 - 18.3 (high group), depending on the rice variety and the ratio of rice to water used to cook the porridge.
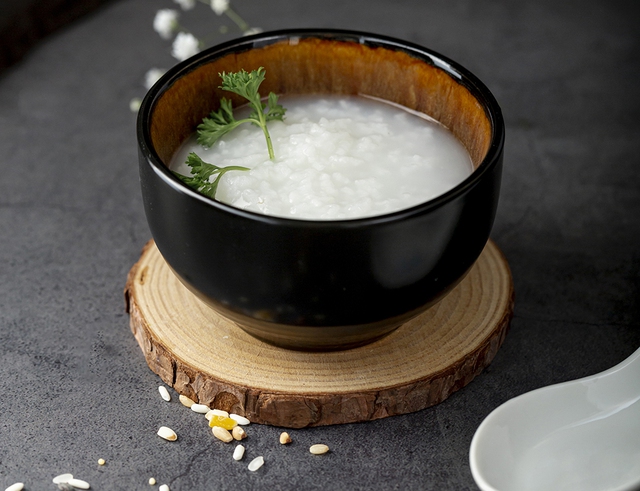

Porridge (cooked from white rice) can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, but the increase is usually low to moderate.
In which, GI and GL are two important quantities, respectively reflecting the speed and level of blood sugar increase after 2 hours of eating porridge.
With the above indicators, porridge (cooked from white rice) can increase blood sugar quickly, but the increase is usually at a low-average level (not high) if consumed in moderation.
The reason the glycemic index of porridge is high is because this dish is made from white rice - a food that is rich in carbohydrates but low in fiber.
In addition, in terms of nutritional value, the protein, fat, vitamin and mineral content in porridge is not much.
According to Dr. Cao Thi Lan Huong, diabetics can eat porridge but need to pay attention to the type of rice, the amount consumed and the method of preparation. Because, as mentioned, porridge has the effect of increasing blood sugar after consumption.
The more water (thinner) the porridge is cooked with, the lower the glycemic load of the diet, and therefore, the patient can be allowed to eat more porridge than if the porridge was cooked thickly.
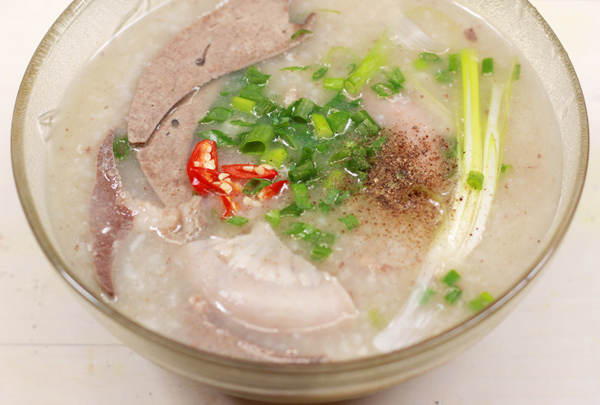

Diabetics should limit eating porridge and instant porridge because they often contain a lot of saturated fat, cholesterol, sodium, preservatives...
How to eat porridge more safely for diabetics
Prioritize brown rice. White rice often has a high glycemic index, so it should be carefully considered before using. Instead, you can choose brown rice because it contains more fiber and has a lower glycemic index than white rice, supporting the process of controlling blood sugar smoothly.
Limit the use of spices. Diabetics should limit the use of salt, sugar, seasoning powder, MSG, etc. when eating porridge because they can affect blood sugar, blood pressure and promote the onset of cardiovascular complications.
Instead, you should prioritize natural spices such as onions, garlic, ginger, etc. to enhance flavor and have less negative effects on health.
Combine with foods rich in fiber and protein. White porridge lacks fiber and protein. Therefore, to fully meet the body's nutritional needs, patients should combine porridge with foods rich in fiber (beans, cereals, green vegetables) and protein, especially lean protein (skinless chicken, fatty fish, other seafood).
Monitor your blood sugar before and after eating porridge. As mentioned, porridge has the risk of causing high or low blood sugar after meals, depending on the amount consumed. Therefore, measuring your blood sugar regularly, especially before and after eating porridge, will help you monitor your body's reaction to this dish, thereby taking timely measures to adjust when detecting signs of abnormal blood sugar.
Porridge dishes should be limited. To ensure health, you should limit eating porridge and instant porridge because they often contain a lot of saturated fat, cholesterol, sodium, preservatives, etc. which are not good for the cardiovascular system as well as overall health.
Readers can ask questions for the column. Doctor 24/7 by entering comments below the article or sending via email: [email protected] .
Questions will be forwarded to doctors, experts... to answer for readers.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/bac-si-24-7-nguoi-benh-tieu-duong-luu-y-gi-khi-an-chao-185241206102008634.htm



![[Photo] Phuc Tho mulberry season – Sweet fruit from green agriculture](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/1710a51d63c84a5a92de1b9b4caaf3e5)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to discuss tax solutions for Vietnam's import and export goods](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19b9ed81ca2940b79fb8a0b9ccef539a)

























![[Photo] Unique folk games at Chuong Village Festival](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/cff805a06fdd443b9474c017f98075a4)































































Comment (0)