Hypoglycemia, if not treated promptly, can cause dangerous complications such as brain damage, increased risk of injury from falls, and cognitive impairment.
What is hypoglycemia?
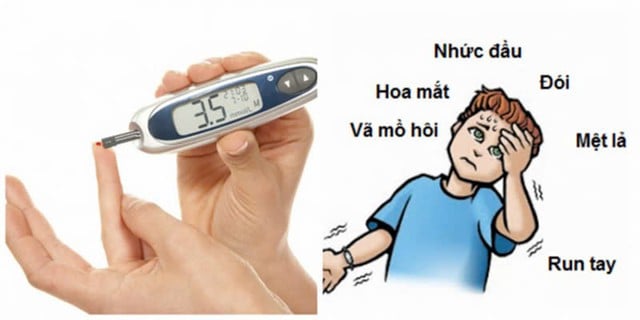
Hypoglycemia is a condition that occurs when blood sugar levels are too low, below 3.9 mmol/l ( blood sugar causes).
Hypoglycemia can be caused by many things, such as taking too much insulin or other diabetes medications, not eating enough or waiting too long between meals, exercising without eating enough, not eating enough carbohydrates, an unhealthy diet, or drinking too much alcohol causing hormonal imbalances.

Illustrative image
Signs of hypoglycemia
When experiencing hypoglycemia, patients often exhibit symptoms such as: Central nervous system disorders causing manifestations such as blurred vision, double vision, headache, confusion, memory loss, seizures, coma...
Autonomic nervous system disorders make the patient anxious, restless, sweaty, have trembling hands and feet, rapid heartbeat, vomiting/nausea, feeling hungry...
At this point, blood glucose levels will be below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/l). - Clinical symptoms will improve when the patient receives glucose supplementation.
Who is at risk of hypoglycemia?
- People who are susceptible to hypoglycemia include the elderly, those unable to care for themselves, those who frequently experience digestive disorders (vomiting, inability to eat), patients with acute illnesses leading to poor appetite, and patients with severe liver or kidney disease or undergoing dialysis.
- People with a history of severe hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia unawareness, hypoglycemia after exercise or hypoglycemia during sleep.
- Even healthy people can experience hypoglycemia when they exercise too much without supplementing food before exercise.
- Hypoglycemia due to overly aggressive treatment (low blood glucose target or low HbA1c). In elderly individuals who are constantly trying to maintain blood glucose levels.
What to do when blood sugar suddenly drops?
If the patient experiences mild hypoglycemia but remains conscious, they should immediately drink sugary water or other sugary foods and drinks, followed by porridge, milk, fruit, or pastries.
Patients need to quickly stop using oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin when they see signs of hypoglycemia.
In severe cases, when the patient is in a coma, unconscious, and unable to swallow, giving them oral medication will cause aspiration into the respiratory tract. The patient should be immediately taken to the hospital for intravenous administration of a 20-30% hypertonic glucose solution (40-60ml).
Next, switch to intravenous infusion of 5-10% glucose solution to avoid the risk of recurrent hypoglycemia. Glucose infusion will continue until the patient fully recovers and is able to eat and drink on their own.
Illustrative image
Ways to prevent hypoglycemia
Patients should proactively prevent hypoglycemia and control their daily blood sugar levels to protect their health with some simple measures such as:
- Build a scientific diet, before exercising you need to eat enough carbohydrates before exercising and have a snack during exercise if necessary.
- You need to eat extra meals as soon as your blood sugar shows signs of being low or when new signs of illness appear.
- Check blood sugar regularly and follow treatment as directed by your doctor. Do not take medication without a prescription or stop taking medication when symptoms improve.
- Always carry sugar or sugary products like candy, cookies, or chocolate in your bag or backpack so you can use them immediately in case of hypoglycemia.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/ha-duong-huyet-nguy-hiem-the-nao-day-la-cach-phong-benh-tot-nhat-172250318152942234.htm


![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)


















































Comment (0)