A team of astronomers at Harvard University discovered a cluster of super-fast stars, including one that set a record with a speed of 8,226,967 km/h.
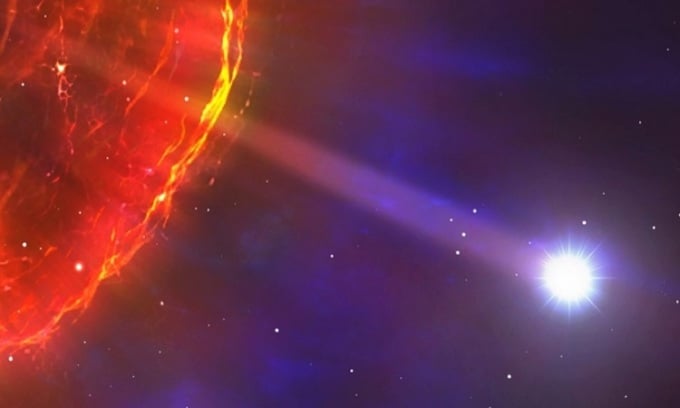

Simulation of a white dwarf ejected from a supernova explosion. Photo: Mark Garlick/Science Photo Library
Astronomers have discovered the fastest runaway star ever seen in the Milky Way. It's rocketing at incredible speeds from a massive explosion. The white dwarf, J0927, hurtles through space at 5,000,000 mph (8,226,967 km/h). Called a hypervelocity star because its speed will allow it to one day completely escape the Milky Way's gravity, J0927 is traveling with three other fast-moving stars. They are thought to be the result of a Type Ia supernova, one of the most violent explosions in the universe. The team, led by Kareem El-Badry of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, published the discovery on the arXiv database, Live Science reported on June 15.
A Type Ia supernova occurs when two stars, one of which is a white dwarf, fall into orbit around each other. The process causes the white dwarf to strip hydrogen from the star it orbits, creating a reaction that leads to a massive thermonuclear explosion. But a simple stellar explosion isn’t enough to eject the star at such speeds. Astronomers suspect the hypervelocity was caused by a special type of Type Ia supernova called a D6 supernova.
In the D6 supernova, two white dwarfs orbit each other, one of which strips the remaining helium from the surface of its sister star. This creates so much energy on the surface of the cannibalistic white dwarf that it triggers another fusion reaction, sending shock waves deep into the core and causing the star to explode.
Although such powerful supernovae are common, evidence of them and the white dwarfs they eject remains elusive. To find some candidates, El-Badry and his colleagues turned to the Gaia star catalog, a project that aims to create the most detailed star map of the Milky Way. From the Gaia data, the team discovered white dwarfs. By looking more closely at their chemical composition (mostly oxygen and carbon), they confirmed that the runaway white dwarfs were the result of explosions that stripped them of helium and hydrogen.
Measurements of the white dwarf revealed that J0927 is the fastest runaway white dwarf ever observed in the Milky Way, beating the previous record of 7,919,904 km/h held by the star D6-1. The team estimates that D6 supernovae could account for half of all Type Ia supernovae. But to be sure, they’ll need to find more runaway stars flying through space.
An Khang (According to Live Science )
Source link


![[Photo] Looking back at the impressive moments of the Vietnamese rescue team in Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/5623ca902a934e19b604c718265249d0)


![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)





![[Podcast] News on March 24, 2025](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/f5fa1c3a9ae14d4590ac6965d233586b)
![[Podcast] News on March 25, 2025](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/735b3003484942af8e83cbb3041a6c0c)
![[Podcast] News on March 26, 2025](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/c3d9c3c48b624fd9af79c13ff9e5c97a)
![[Podcast] News on March 27, 2025](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/de589137cda7441eb0e41ee218b477e8)















![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)



























































Comment (0)