Why do we need to control our diet?
According to an expert on artificial kidneys, most patients on periodic artificial kidney dialysis will have no urine or only a very small amount, because the kidneys have failed and lost function. Therefore, between dialysis treatments (cyclic artificial kidney dialysis), the patient's body will accumulate waste products and excess fluids. Artificial kidneys will help remove waste products and excess fluids from the body but will not completely replace them like normal kidneys.

Foods high in potassium
Through the practice of caring for and monitoring the health of patients, Bachelor of Nursing Dang Thi Bich Hao, Department of Nephrology and Dialysis - National Children's Hospital (Hanoi), noted that periodic artificial kidney is usually performed 3-4 times/week, each cycle lasts 3-4 hours, depending on the patient. Therefore, to reduce the accumulation of waste and excess fluid, controlling the nutritional regimen is very necessary.
Note on nutritional intake
Energy intake should be appropriate to weight and age. Of which, protein should be 1.2 - 1.4 grams/kg/day. Meals should be rich in calcium; sufficient in vitamins and other trace elements. Should be low in water, low in salt, low in potassium, low in phosphorus.
Prioritize foods rich in animal protein: meat, fish, eggs, milk. Limit foods rich in plant protein: beans, peas, sesame.
It is important to provide enough energy for the body to prevent malnutrition. Starch is the main source of energy for the body, accounting for 50 - 60% of the total energy intake.
Add cooking oil (soybean oil, sunflower oil, canola oil) when preparing dishes to increase energy.
Limit fatty meat, offal, butter, coconut oil, etc. to reduce the risk of lipid metabolism disorders.
Low phosphorus diet, avoid fruits high in potassium
According to the Department of Nephrology and Dialysis - National Children's Hospital, if there is a lot of phosphorus in the blood, it can weaken bones, make them more fragile, cause joint pain, and cause itchy skin. Therefore, people on dialysis need to limit foods rich in phosphorus such as oats, cereals, dairy products, beans, chocolate, processed and canned foods, and offal.
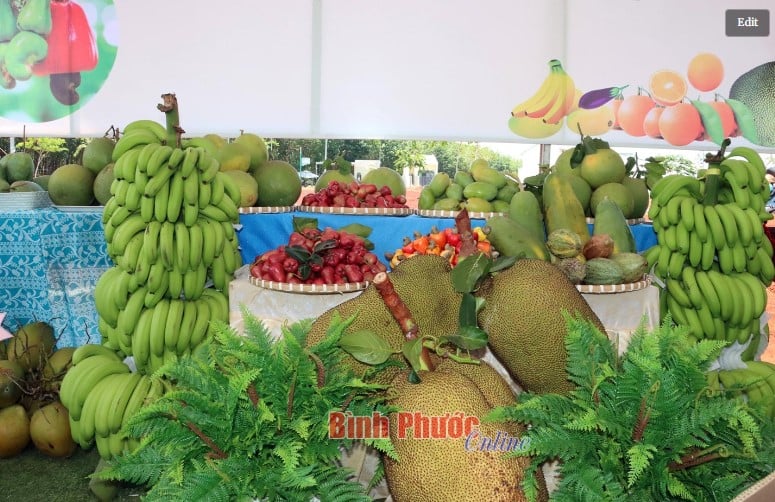
People on dialysis need a low potassium diet. High blood potassium levels can lead to heart rhythm disturbances and can lead to cardiac arrest. Therefore, people on dialysis should avoid foods high in potassium such as bananas, plantains, grapes, oranges, jackfruit, dried longans, dried lychees, whole grains, bread, biscuits, nuts, coconut water, canned fruit and vegetable juices, tea, coffee, and cocoa.
Potassium can be reduced during vegetable preparation before cooking by soaking, chopping, and boiling in a full pot of water.
In addition, it is necessary to follow a low-salt diet: limit salt added to food; avoid using salt, fish sauce, sauces; reduce canned, packaged products, fast food. Prioritize using fresh foods. Eating too much salt can increase the risk of high blood pressure, stroke, cardiovascular disease, making the body thirsty and drink more water.
Water overload can cause problems such as high blood pressure, difficulty breathing due to pleural effusion; chest pain, angina, headache; swelling of hands, feet, and whole body.
If the patient vomits, has a fever, has diarrhea, etc., the amount of water intake must be increased depending on the amount of fluid lost.
To control daily water intake, prepare a water bottle with the amount of water consumed each day.
Drink water from a smaller glass. Suck on sour candies or lemon to moisten your mouth when it feels dry.
Limit salt intake to limit water intake and control blood sugar levels.
(Source: Department of Nephrology and Dialysis - National Children's Hospital)
Source link




![[Photo] Opening of the 11th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/f9e717b67de343d7b687cb419c0829a2)
![[Photo] April Festival in Can Tho City](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/bf5ae82870e648fabfbcc93a25b481ea)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh commends forces supporting Myanmar in overcoming earthquake consequences](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/e844656d18bd433f913182fbc2f35ec2)
























![[Photo] Reliving the heroic memories of the nation in the program "Hanoi - Will and belief in victory"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19ce7bfadf0a4a9d8e892f36f288e221)



























































Comment (0)