Compared to today's computers, ENIAC was a giant computer with an area of 150 m2 and a total weight of about 27 tons, using 18,000 light bulbs, 6,000 switches, 7,000 resistors, 10,000 capacitors... It consumed 140 kW of power and could perform 5,000 additions/second.
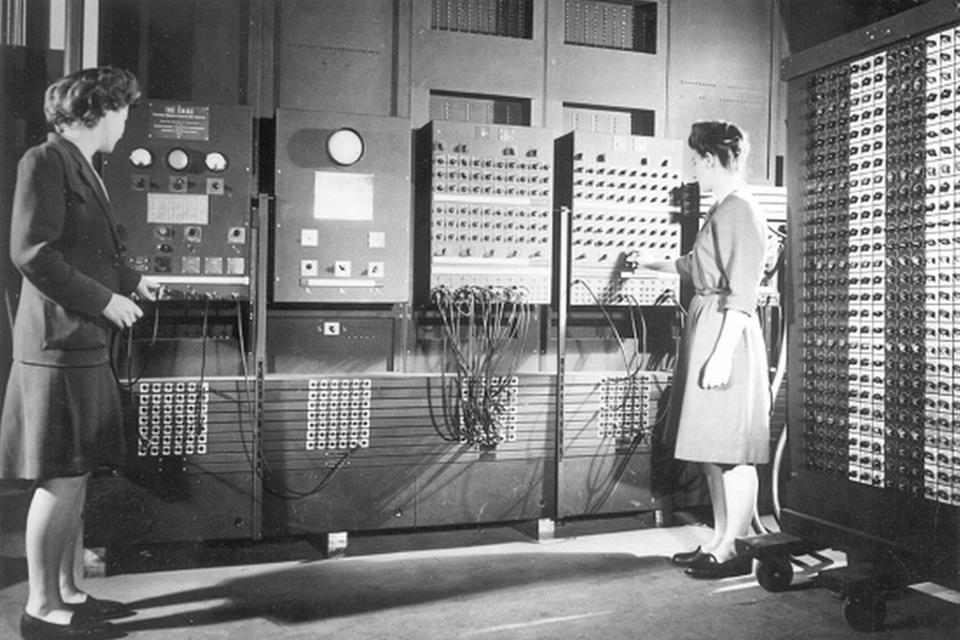
The original purpose of ENIAC was to serve World War II.
ENIAC was originally planned for World War II, but because World War II ended before it was built, the machine was later repurposed for hydrogen bomb research.
When ENIAC was announced, it was hailed by the press of the time as a "giant brain" because its calculation speed was a thousand times faster than an electromechanical machine - a leap forward that no machine had ever achieved before.
Its general mathematical and programming capabilities excited scientists and industrialists at the time.
It is worth mentioning that when we talk about programmers today, we often think of men, but at that time the position of programmer was usually held by women. The six female operators representing the "ENIAC Women's Team" were the first group of women in the world to participate in the development of computer programs.
Source link



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Mr. Jefferey Perlman, CEO of Warburg Pincus Group (USA)](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/18/c37781eeb50342f09d8fe6841db2426c)























































































Comment (0)