Japan is preparing to beam solar energy from space to Earth next year, in the form of microwaves.
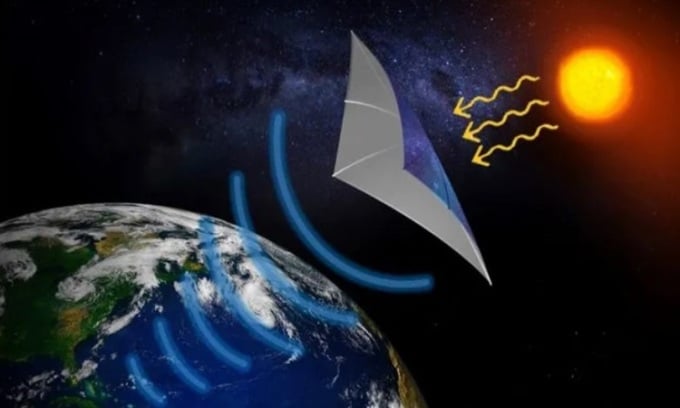

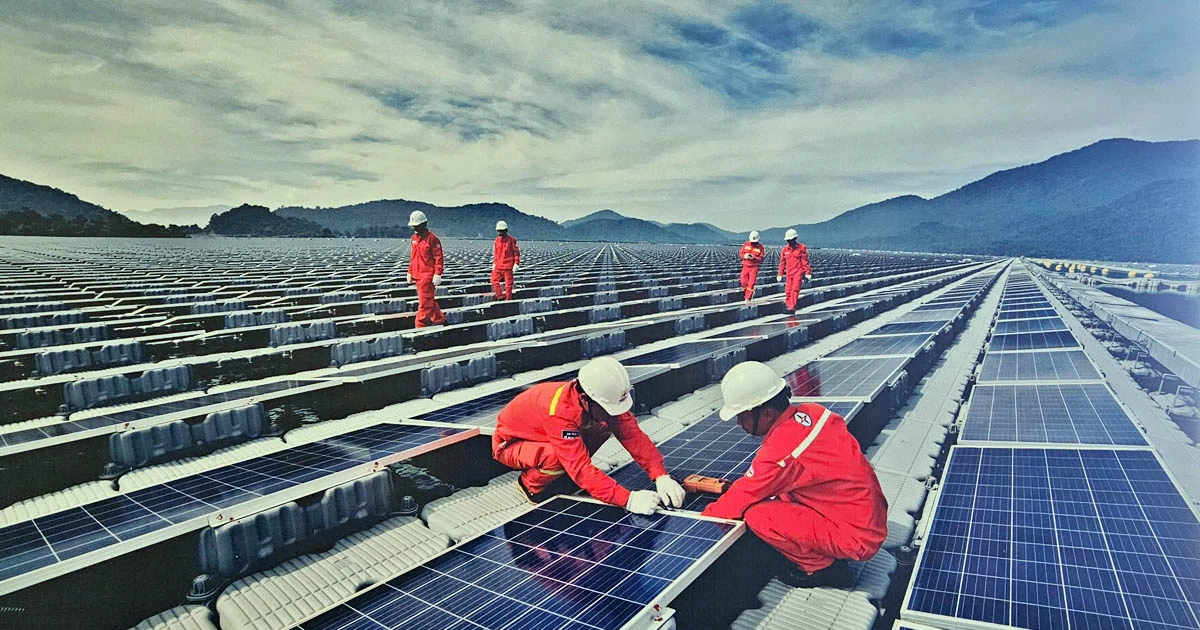
Simulation of a solar power generation system in space. Photo: AFRL
Japan is preparing to beam solar energy from space to Earth next year, two years after US engineers achieved a similar feat. The development marks a major step toward a space-based solar power station that could help the world cut fossil fuels in the fight against climate change, Space reported on April 19.
Speaking at the International Space Energy Conference this week, Koichi Ijichi, an adviser at the Japan Space Systems research institute, outlined a path to testing a small solar power plant in space that would transmit power wirelessly from low orbit to Earth. He said it would be a small satellite, about 180 kilograms (400 pounds), transmitting about a kilowatt of power from an altitude of 400 kilometers (250 miles). A kilowatt is about the amount of electricity needed to run a household appliance like a small dishwasher for about an hour, depending on its size. So the experiment is not yet on a scale suitable for commercial use.
The spacecraft will use a 2-square-meter solar cell to charge its battery. The stored energy will then be converted into microwaves and transmitted to receiving antennas on Earth. Because the spacecraft is traveling so fast, about 28,000 kilometers per hour, the antennas need to be spread out over 40 kilometers, with each antenna spaced 5 kilometers apart, to be able to transmit enough energy. According to Ijichi, the transmission takes only a few minutes, but when the battery runs out of power, it will take several days to fully charge.
The mission, part of the OHISAMA (meaning Sun in Japanese) project, is scheduled to launch in 2025. Researchers have already tested wireless transmission of solar power from a stationary source on the ground. They plan to conduct transmissions from an aircraft in December this year. The aircraft will be equipped with solar cells similar to those used on spacecraft and will transmit power over a distance of 5-7 km.
The idea of generating solar power in space was first described in 1968 by former Apollo engineer Peter Glaser. Unlike most renewable energy technologies on Earth, solar power in space is available all the time because it is not dependent on the weather or time of day. Currently, nuclear power plants and coal or natural gas plants are used to meet demand when the wind stops blowing or the sun goes down. Recent technological advances may help solve some of the problem in the future. But researchers have yet to find a way to ensure a continuous, carbon-free supply of electricity by the middle of the 21st century.
Advances in autonomous technology and wireless power transmission, especially the advent of the giant Starship rocket, could make space solar power a reality. Last year, a satellite built by Caltech engineers on the Space Solar Power Demonstrator mission transmitted solar power from space for the first time. The mission ends in January 2024. However, according to a NASA report, the energy required to build, launch, and assemble the orbital power station makes the electricity the facility produces too expensive, more than 12 times higher than wind and solar power on Earth.
An Khang (According to Space )
Source link




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Chairman of Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China (COMAC)](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/93ca0d1f537f48d3a8b2c9fe3c1e63ea)























































































Comment (0)