Some studies have shown that kitchen sponges can harbor a lot of bacteria. Bacteria can contaminate any surface the sponge touches. These bacteria increase the risk of food-related illnesses, such as food poisoning, according to the health website Healthline (USA).
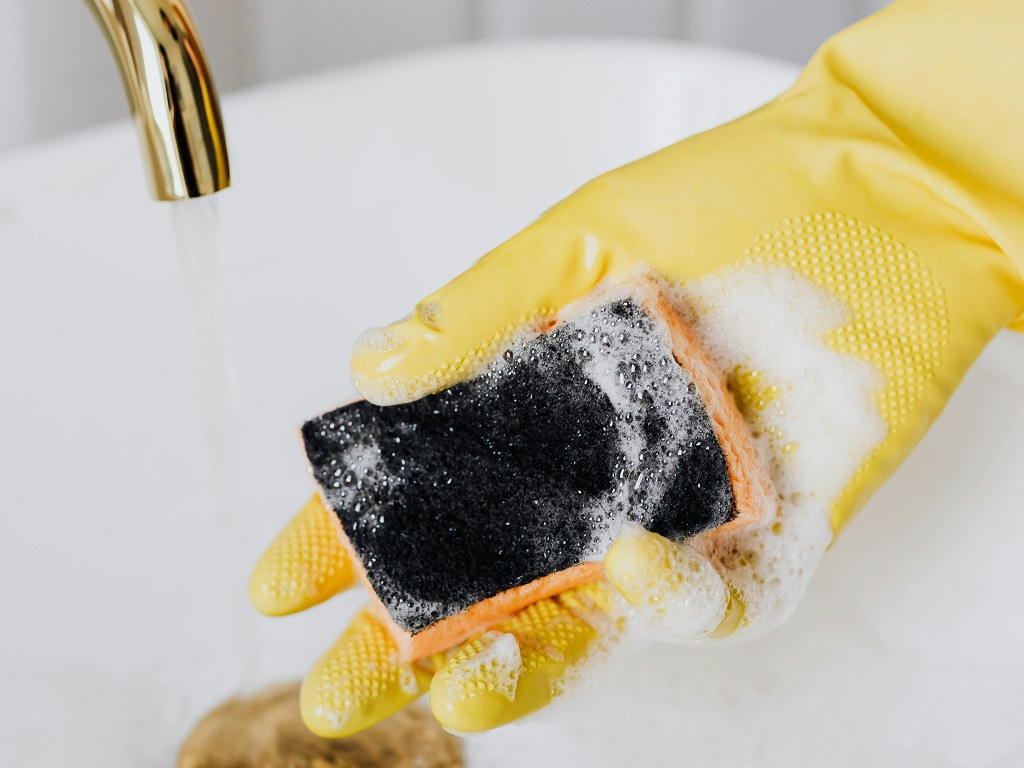

Dishwashing sponges can be a breeding ground for disease-causing bacteria.
Sponges are often used to wash pots, basins, bowls, or plates containing food... This makes sponges susceptible to Salmonella bacteria, which causes diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea, or vomiting.
A test by biomedical engineers at Duke University (USA) showed that sponges have a porous and moist structure, making them an ideal environment for bacteria to grow. Kitchen sponges are capable of cultivating more bacteria than the bacterial culture dishes commonly used in laboratories. Harmful bacteria on sponges can cause a range of health problems, from mild gastritis to serious conditions such as pneumonia.
Pathogenic bacteria that can be found in sponges include campylobacter, enterobacter cloacae, E. coli, Klebsiella, moraxella osloensis, Salmonella or staphylococcus. Enterobacter cloacae are part of the natural flora of the intestinal tract. However, in people with weakened immune systems, they can develop and cause serious infections such as pneumonia and meningitis.
How to reduce bacteria in sponges
To minimize the health risks from sponges, the first thing to do is not to use the same sponge for everything. The sponge used for washing dishes should be different from the sponge used for cleaning items that have come in contact with raw meat.
Sponges should be aired and kept dry after each use, as a moist environment encourages bacteria to grow. If you have a microwave, place your sponge in the microwave for about 2 minutes. This can significantly reduce the amount of bacteria in your sponge, according to Healthline .
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/mieng-bot-bien-rua-chen-chua-nhieu-vi-khuan-lam-sao-de-tranh-mac-benh-185240917131852316.htm


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to discuss tax solutions for Vietnam's import and export goods](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19b9ed81ca2940b79fb8a0b9ccef539a)
![[Photo] Phuc Tho mulberry season – Sweet fruit from green agriculture](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/1710a51d63c84a5a92de1b9b4caaf3e5)





























![[Photo] Unique folk games at Chuong Village Festival](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/cff805a06fdd443b9474c017f98075a4)






























































Comment (0)