At 7:34 p.m. on August 23 (Hanoi time), India's unmanned spacecraft Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed on the south pole of the Moon after a 41-day flight. This mission helped India become the first country in the world to land a spacecraft on the south pole of the Moon, a place where humans have never set foot.
One of the big questions being asked is why it took India's Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft 41 days to land on the Moon.
For comparison, Russia's Luna-25 spacecraft took only 6 days to enter lunar orbit, China's Chang'e 2 spacecraft took only 4 days to reach the Moon in a mission carried out in 2010. NASA's Apollo-11 spacecraft also took only 4 days to do the same, and had the appearance of 3 astronauts landing on the Moon.
Even the Soviet Union's Luna-1 spacecraft took only 36 hours to reach the Moon's orbit, during a mission carried out in 1959.
The reason for the big difference in mission time is because Chandrayaan-3 uses the Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM-3) rocket system, which has a much weaker launch force than the above vehicles, in order to save on the mission budget.
To compensate for the technological limitations, Chandrayaan-3 had to use an ingenious method that relied on the gravity of the Moon and Earth to reach its destination. The spacecraft had to fly 4.5 times around the Earth and many times around the Moon to stabilize the necessary speed, before performing the landing phase. That is why the mission duration was extended to 40 days.
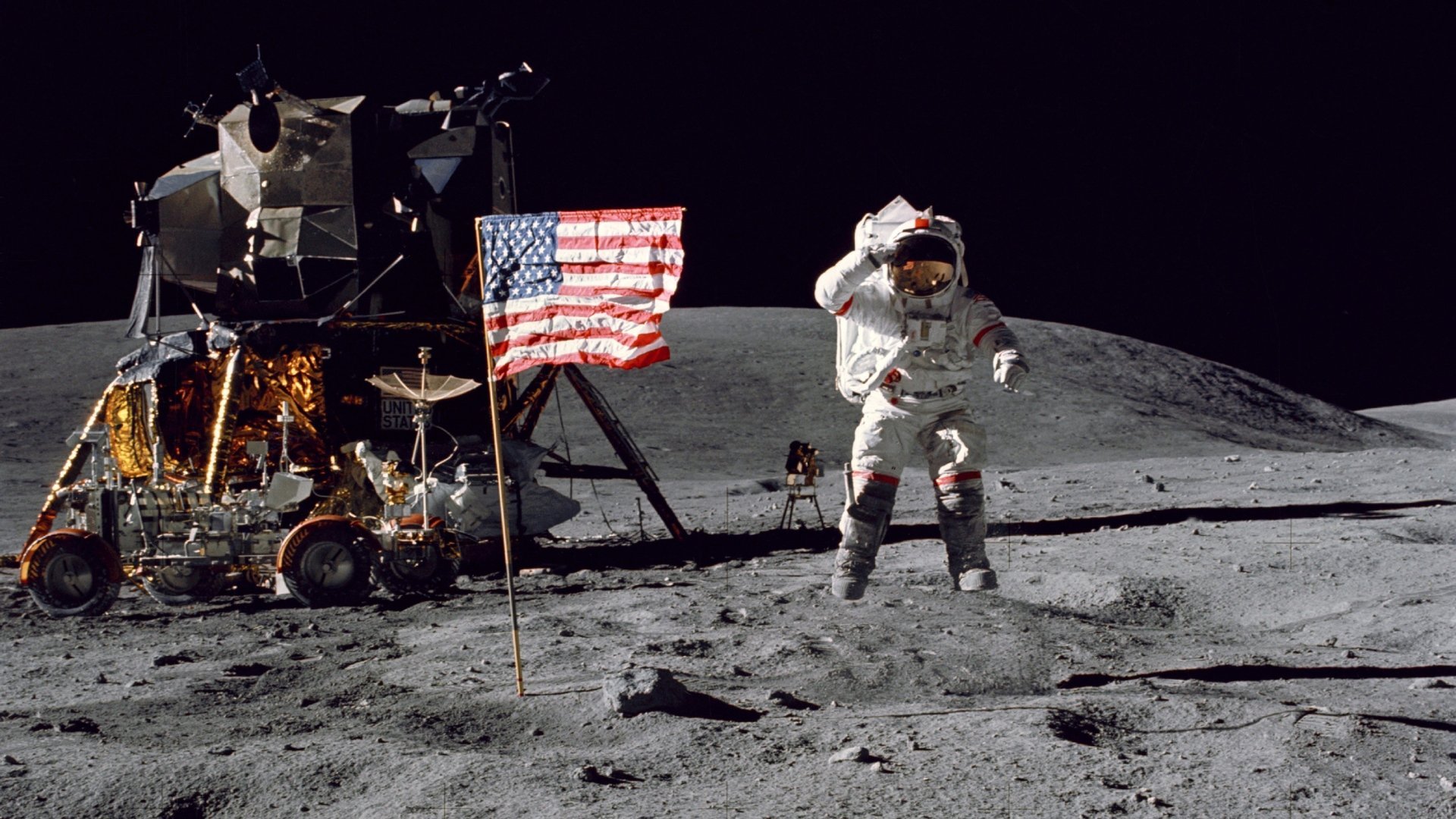

Astronaut Neil Armstrong next to the American flag on the Moon during the Apollo-11 mission. (Photo: NASA)
How to fly to the moon?
The Moon is approximately 384,400 km from Earth. This is a huge distance, if you could drive a car at 100 km/h to the Moon, it would take you more than 4,000 hours or about 166 days to reach Earth's satellite - equivalent to 5 months of non-stop driving.
Of course, we can't drive cars to the Moon. Humans have to rely on spaceships to travel into space, and this is the only way we can get to the Moon.
These spacecraft are specially designed to travel in the vacuum of space and withstand the harsh conditions of the journey.
There are different methods of flying to the Moon on a spacecraft including Lunar Rendezvous Orbit, Earth Rendezvous Orbit, and direct flight.
Of the three options above, the Lunar Rendezvous Orbit is the most popular and is used by Russia, the US and China in their lunar missions.
Lunar Orbital Rendezvous (LOR), or Lunar Orbital Approach, was a concept in the US Apollo Program in which a main spacecraft and a smaller lander were sent into lunar orbit.
The lander will then separate and land on the lunar surface, while the main ship will remain in lunar orbit. After the landing mission is complete, the lander will return to lunar orbit, and dock with the main ship. After the crew moves from the lander to the main ship, the lander will separate. The main ship will then return the astronauts to Earth.
LOR itself is also divided into many different flight modes depending on the rocket system, manned or unmanned spacecraft.
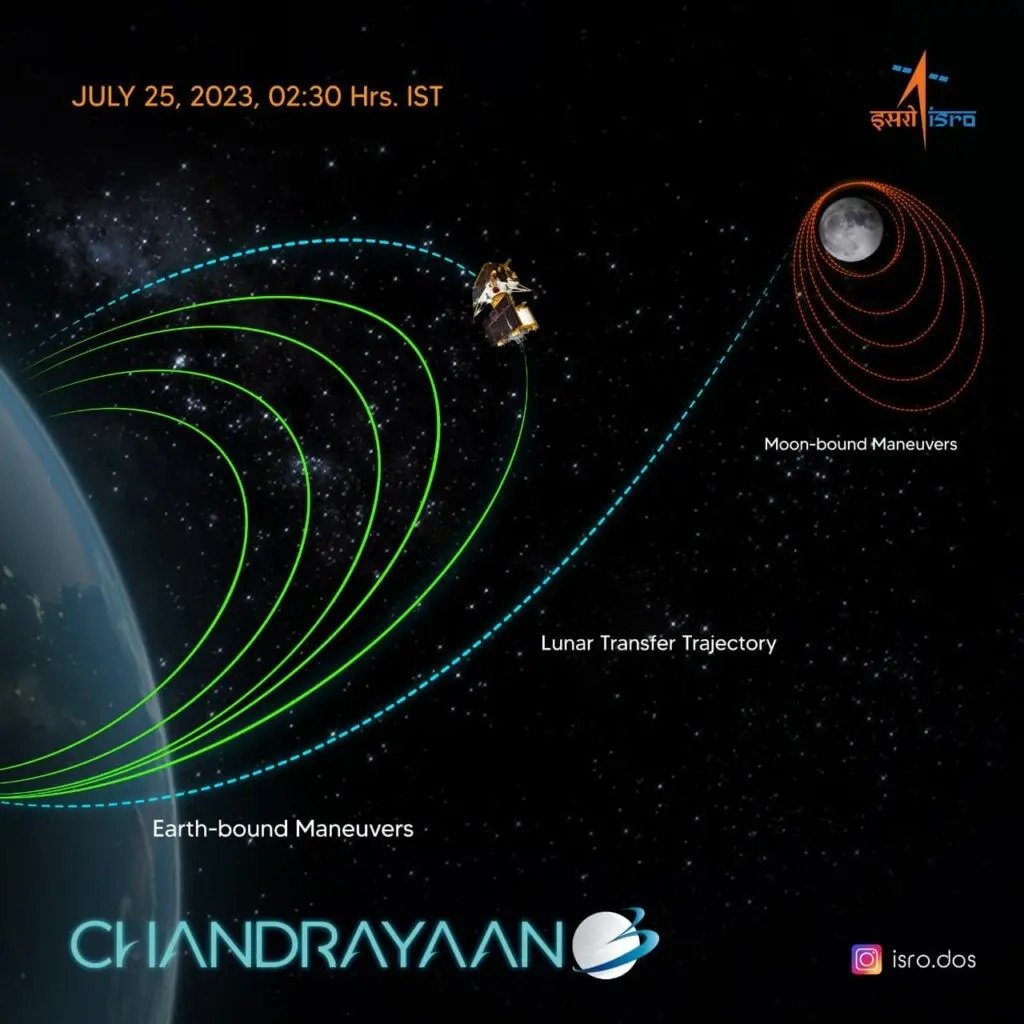
The trajectory of India's Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft during its 41-day journey to the Moon. (Photo: ISRO)
Direct flight is considered a cross between the LOR flight modes, essentially building a rocket that can fly directly from Earth to the Moon, then fly back on the same rocket.
The last way to fly to the Moon that was ever attempted by humans was the Earth Orbital Rendezvous (EORR), a method used by NASA before the Apollo program.
The highlight of the EOR approach is to launch several different spacecraft components into Earth orbit, where they can be assembled into a larger spacecraft. This larger spacecraft would then fly to the Moon and land there, then lift off and return to Earth.
How long does it take to fly to the moon?
The average speed of the lunar exploration spacecraft is about 38,000 km/h (10 times the speed of sound).
The time it takes for a spacecraft to travel to the Moon depends on a number of factors, such as the type of spacecraft, its speed, and the orbit it follows. On average, it takes a spacecraft about 3 to 4 days to travel from Earth to the Moon at a speed of about 5,300 km/h. This includes the time it takes for the spacecraft to escape Earth's gravity, travel through space, and enter the gravitational pull of the Moon's orbit.

Depending on the mission, the time it takes for a spacecraft to fly to the Moon varies, but on average it will be 3 to 4 days.
The trajectory or path a spacecraft takes also affects the time it takes to reach the Moon. Spacecraft often follow a curved path, called a transfer trajectory, to reach the Moon. This allows them to use the gravity of both the Earth and the Moon to save fuel and travel more efficiently. The exact trajectory depends on the mission requirements and the specific goals of the space mission.
In recent years, interest in lunar exploration has increased again, with plans for future missions to return humans to the Moon and even establish a permanent human presence on the lunar surface.
These missions will likely involve advanced spacecraft and technology, and scientists and engineers are constantly working to develop new ways to make the journey to the Moon faster and more efficient.
As technology continues to advance, we may see even faster time travel in the future, opening up new possibilities for exploration of the Moon and beyond.
Source



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Japanese Ambassador to Vietnam Ito Naoki](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/3a5d233bc09d4928ac9bfed97674be98)

![[Photo] Moment of love: Myanmar people are moved to thank Vietnamese soldiers](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/9b2e07196eb14aa5aacb1bc9e067ae6f)
![[Photo] Special relics at the Vietnam Military History Museum associated with the heroic April 30th](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/a49d65b17b804e398de42bc2caba8368)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting after US announces reciprocal tariffs](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/ee90a2786c0a45d7868de039cef4a712)






















































































Comment (0)