According to the World Health Organization 2019 statistics, the average life expectancy of women globally is 74.2, while men is 69.8. Women also have a higher healthy life expectancy. The majority of people who live to be 100 years old or older are women.
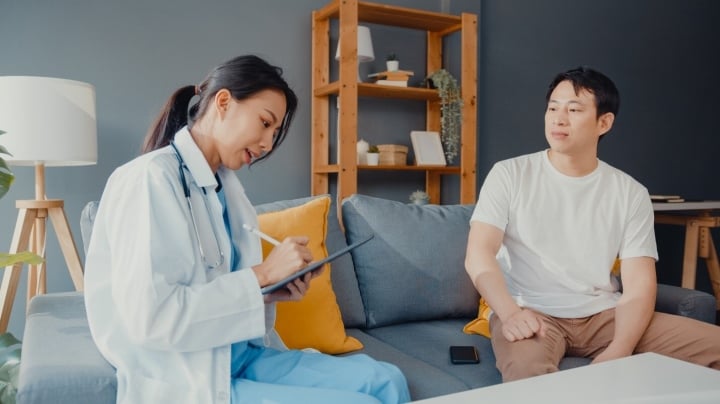

The average life expectancy of women is always higher than that of men.
Chromosomes, hormones and heart health
Women carry two XX chromosomes, a small body structure while men only have one X and Y chromosome, which makes them susceptible to disease. This means that women keep two copies of every gene they have, while men only keep one. If a gene becomes faulty or malfunctions with age, women have another one to fall back on. Men do not, so they are at higher risk of diseases like cancer.
In the UK, it is estimated that men are 40% more likely to die from cancer and 16% more likely to develop the disease than women. Higher levels of oestrogen (the female sex hormone) and the presence of a second X chromosome means that women have more fat under the skin while men have more fat around their organs (visceral fat). Visceral fat is a risk factor for heart disease.
According to Ranker, the reason why men are at higher risk of flu-related deaths and complications from serious respiratory illnesses is largely because estrogen in women boosts the immune system while testosterone in men suppresses immunity. Testosterone has been shown to increase the risk of heart disease, infections, and cancer.

Women always know how to take care of their health and beauty.
Women's survival is partly due to their chromosome structure. Scientists believe that women tend to live longer than men because their double X chromosome protects them against disease as cells begin to malfunction with age.
Body size
Men are generally taller and have more cells in their bodies. The more cells, the more likely something will develop a harmful mutation.
Additionally, a woman's menstrual cycle may have unexpected benefits. It requires an exercise regimen that helps eliminate the risk of cardiovascular disease. The "running woman's heart" hypothesis suggests that the increased heart rate in women during the second half of the menstrual cycle is as beneficial as moderate exercise.
Mental health
Although depression does not affect men more than women, statistics in the UK show that men are more likely to commit suicide. The male suicide rate is 15 per 100,000 people. The figure for women is 5. Men aged 45 to 49 have a suicide rate of 24 per 100,000 people.

Even the suicide rate in men is higher than in women.
Of course, both men and women are capable of feeling stressed. When we are stressed, our bodies release adrenaline, which increases our heart rate and blood pressure. However, stress is more likely to lead to unhealthy habits in men than in women, such as excessive drinking and smoking. Women, on the other hand, are more likely to develop healthy coping mechanisms for stress than men. For example, women are more likely to seek mental health support or practice yoga.
Men – especially young men – are more likely to engage in behaviours that can lead to serious illness and death. These range from unhealthy choices such as smoking and behaviours after drinking too much to traffic accidents caused by dangerous driving. In fact, young men account for 73% of all road traffic deaths.
Additionally, women are nurturers. A healthy mother’s body is essential to the survival of her offspring. Women’s bodies have evolved to withstand and recover from the physical stresses of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as the demands of breastfeeding. Coupled with a maternal mentality, women are more resilient to stressful situations than men. And so for women, that strength can translate into a longer, healthier life.
Tuyet Anh (Source: Synthesis)
Useful
Emotion
Creative
Unique
Wrath
Source





![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)

![[Photo] Looking back at the impressive moments of the Vietnamese rescue team in Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/5623ca902a934e19b604c718265249d0)






















![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)































































Comment (0)