Speaking at the opening of the workshop, Dr. Nguyen Trong Khoa - Deputy Director of the Department of Medical Examination and Treatment Management, Ministry of Health said that cardiovascular - renal - metabolic diseases are issues that need special attention.
Currently, the number of diabetic patients in the world is up to 537 million people. Heart failure patients are over 60 million people and especially chronic kidney patients are over 850 million people.
The combination of cardiovascular, renal and metabolic diseases is becoming a major challenge in modern medicine. These diseases not only increase the burden of disease on the health system but also seriously affect the quality of life of patients and their families, especially the elderly who have many diseases at the same time needing care and treatment.
According to Dr. Nguyen Trong Khoa, in recent years, the Ministry of Health has been making efforts to promote programs to prevent, control and manage non-communicable diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, kidney and urinary diseases and metabolic disorders. However, the current reality requires the health sector to have a more comprehensive and multi-dimensional approach, especially interdisciplinary coordination between cardiovascular, kidney and endocrinology specialties.
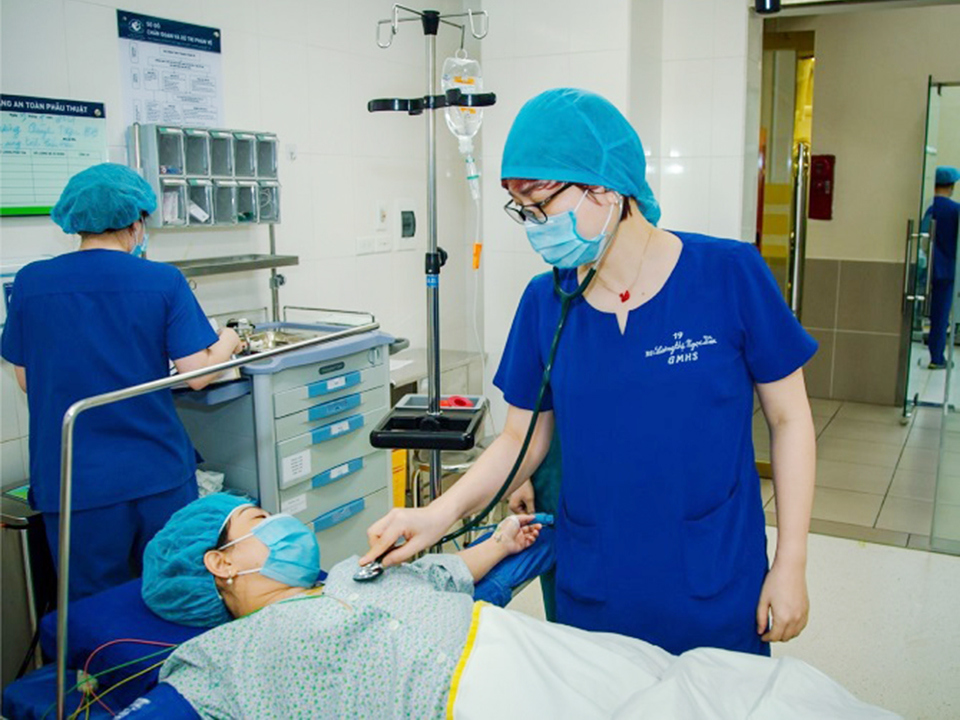
Dr. Duong Huy Lieu - Chairman of the Association of Health Economics also said that cardiovascular - renal - metabolic diseases are often co-morbid and "mutually promote each other", making the patient's prognosis worse. The disease creates an additional burden on diagnosis, treatment as well as on the health system if not screened, detected, treated and managed comprehensively in all three aspects.
According to Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Thi Thu Hoai - Deputy Director of Vietnam Heart Institute, cardiovascular - kidney - metabolic diseases often seriously reduce the patient's life expectancy, especially if they coexist.
Diabetes and hypertension are responsible for more than 80% of end-stage renal disease worldwide. Cardiovascular disease affects 40% of diabetic patients, and at least 30% of diabetic patients have cardiovascular disease.
In Vietnam, 55% of type 2 diabetes patients have complications, the cost of treating complications accounts for 70% of the total cost of treating diabetes patients, and among the complications, treatment of cardiovascular complications accounts for the largest cost.
Associate Professor, Dr. Vu Thi Thanh Huyen - Head of the Department of Endocrinology and Musculoskeletal, Central Geriatric Hospital said that primary care physicians play an important role in early screening for chronic kidney disease and improving care for people with diabetes, heart failure or cardiovascular disease.
Early screening of high-risk patients and subsequent diagnostic decisions optimize renal and cardiovascular disease management. Collaboration with primary care physicians (clinicians) can help prevent diabetes, heart failure, and cardiovascular disease from becoming isolated problems.
At the workshop, experts also suggested that management agencies and clinical facilities need to have plans and solutions to work together to build a management and treatment program for patients with heart, kidney and metabolism diseases .
Source: https://kinhtedothi.vn/quan-ly-dieu-tri-phoi-hop-benh-tim-mach-than-chuyen-hoa.html





![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to discuss tax solutions for Vietnam's import and export goods](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19b9ed81ca2940b79fb8a0b9ccef539a)
![[Photo] Phuc Tho mulberry season – Sweet fruit from green agriculture](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/1710a51d63c84a5a92de1b9b4caaf3e5)











































































![[Photo] Silk ribbons connect the harvest season](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/8c416981570441889721443f115dc7f6)











Comment (0)