China, Egypt, and Mesopotamia are generally considered the most enduring civilizations, although there is much debate about how to determine this.
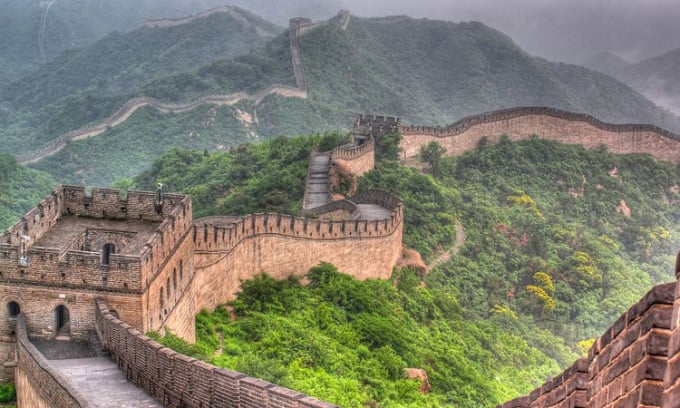

The Great Wall, a massive structure built in China more than 2,000 years ago. Photo: Britannica
World history has seen many civilizations rise and fall, some lasting only a few decades, others standing strong for centuries. However, finding out which civilization has lasted the longest is not simple, IFL Science reported on August 7.
The main problem here is that modern historians have not been able to agree on a number of important issues that will help answer this question. For example, what is the definition of civilization, how to measure its beginning and end, and whether or not periods of civilization ruled by outside powers should count. Here are some of the cultures that are considered to have lasted the longest in history, although the actual assessment is complicated.
China
China has the world’s oldest surviving written language. Experts estimate that it has been in use for around 6,000 years. Surprisingly, some of the characters used today on artifacts, such as oracle bones or oracle bones used for divination, are at least 3,000 years old. No other culture has such continuity.
However, there is still much debate about whether modern China can be considered a continuation of ancient civilization. If so, China is more than 5,000 years old. A decade-long study by the State Administration of Cultural Heritage supports this. But not all historians agree. First, this assessment has important political value because it helps legitimize the structure of modern China. Second, it is too vast and composed of many different ethnic groups to be considered a homogeneous group with the same culture and traditions.
Egypt
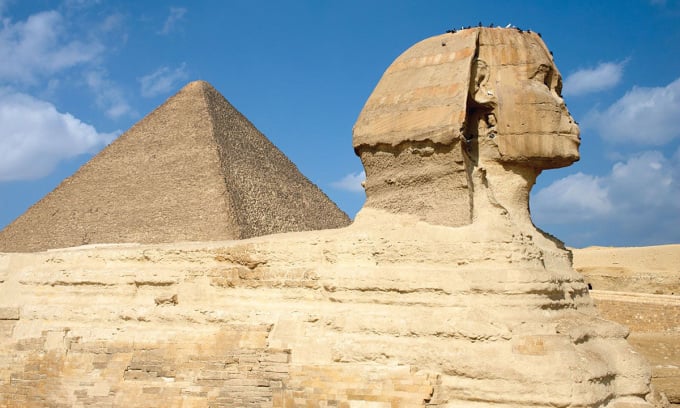

The Sphinx and the Pyramid of Cheops, two of the symbols of ancient Egypt. Photo: Maksym Gorpenyuk/Shutterstock
Another prominent contender for the title of “longest-lived civilization” might be Ancient Egypt. Egypt was a vast kingdom in the ancient world, first unified around 3100 BC and lasting until 332 BC, when it was conquered by the Macedonians. Despite this political change, the language remained the same, and Egyptian hieroglyphs continued to be used until the 5th century, 3,500 years after their creation. As a result, the actual longevity of Ancient Egyptian civilization is also debated.
Some view ancient Egyptian religion as a testament to the longevity of the civilization, but it was not a static cultural expression. The religion and its adherents changed over time, eventually being replaced by Christianity in the 1st century.
Mesopotamia
The region in Southwest Asia that developed around the Tigris and Euphrates river systems is considered the cradle of civilization. The name Mesopotamia comes from the ancient Greek, meaning "land between the rivers." It is where some of the most important advances in early human history occurred, including the invention of the wheel, sailing, maps, writing, and mathematics.
Humans first settled here during the Paleolithic period, taking advantage of the fertile land around the river. Around 12,000 years ago, people brought the land into the Agricultural Revolution. Then, around 5,000 to 6,000 years ago, the urban revolution took place, with larger cities emerging from many small villages. The first city was Uruk, which existed around 3200 BC. Experts believe that Uruk was founded by the Sumerians, who are also credited with creating the first written language.
The history of Mesopotamia is deep and complex, having seen many changes in rulership, including the Akkadian Empire, the Gutians, the Ur-Namma, the Babylonians, the Hittites, the Assyrians, and the Persian Empire. In 332 BC, Alexander the Great conquered the region. After his death, the region became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Overall, Mesopotamia can be considered to have a history as long as that of ancient Egypt, but it is difficult to determine whether it is a continuous period or a collection of different changes and cultures.
Thu Thao (According to IFL Science )



![[Photo] Special relics at the Vietnam Military History Museum associated with the heroic April 30th](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/a49d65b17b804e398de42bc2caba8368)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Japanese Ambassador to Vietnam Ito Naoki](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/3a5d233bc09d4928ac9bfed97674be98)

![[Photo] Moment of love: Myanmar people are moved to thank Vietnamese soldiers](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/9b2e07196eb14aa5aacb1bc9e067ae6f)























































































Comment (0)