Pathology - Revolution in Advanced Disease Diagnosis
To diagnose cancer early, in addition to paraclinical tests, pathology is considered a revolution in diagnosing cancer diseases right at the germinal stage.
A year ago, the patient had a mass in the armpit area. She went to many places for examination and was diagnosed with reactive lymphadenitis, so she did not receive any treatment. Worried that the mass was getting bigger, the woman went to the doctor. The imaging results continued to monitor for abscess lymphadenitis. However, thanks to the pathology results - the "gold" standard in diagnosis, the patient was stunned when she discovered a rare type of tumor.
 |
| To diagnose cancer early, in addition to paraclinical tests, pathology is considered a revolution in diagnosing cancer diseases right at the germinal stage. |
Patient NQA (33 years old, Bac Ninh) came to Medlatec General Hospital for examination because he felt a mass in his left armpit. According to the patient, a mass appeared in his left armpit 1 year ago, and after examination in many places, he was diagnosed with reactive lymphadenitis and did not receive any treatment. This time, worried about the mass gradually growing to the size of a lemon, painful, red, and leaking pink fluid, the patient came to Medlatec General Hospital for examination.
Given that history, the patient was assigned to perform the necessary tests and diagnostic imaging techniques. The test results showed an increased 2-hour blood sedimentation rate and high CRP levels (suggesting that the body had an acute inflammatory condition).
Ultrasound of the left axillary soft tissue: Image of the left axillary soft tissue abscess. Left axillary lymph nodes, monitoring reactive lymph nodes. MRI and chest CT with contrast injection both provide images to monitor abscess inflammation.
MSc. Dang Van Quan, Department of Surgery, Medlatec General Hospital, said that with the assessment of an abscess, the patient was punctured into the tumor and drained, revealing bloody fluid.
At the same time, to accurately assess whether the mass was abnormal or not, the medical team quickly consulted, ordered an MRI, and then a biopsy for diagnostic pathology.
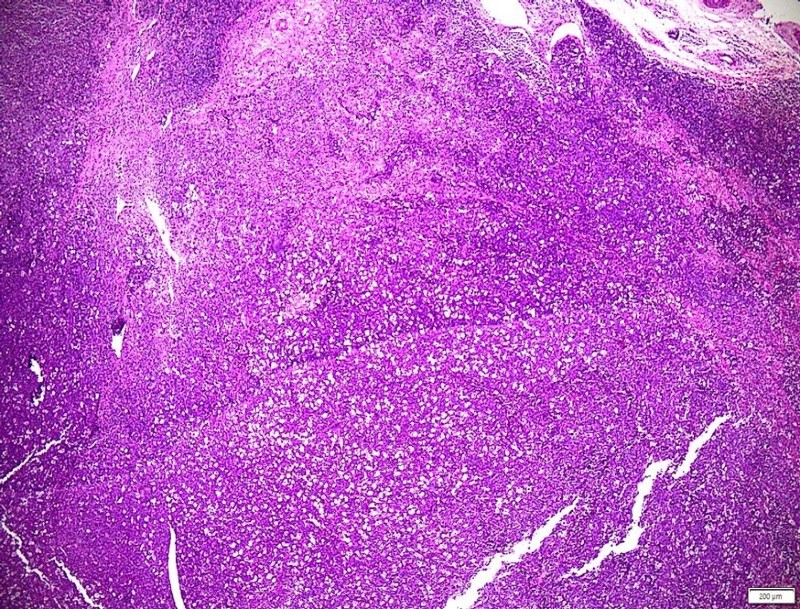
Histopathological results: The tumor has a diffuse structure, with malignant characteristics: Lymphoid cells, large size, alkaline, with nuclei, many mitotic nuclei; many macrophages in the tumor tissue, so the diagnosis: Malignant tumor, leading to non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Based on the morphological characteristics of HE cells, there are 3 types considered: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL); Burkitt lymphoma; Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Therefore, to accurately determine the nature of the tumor, the patient was advised to do an in-depth test, which was immunohistochemical staining. The results showed positive LCA, strong and diffuse positive CD30, and positive ALK.
The results of the two "gold" standards, histopathology and immunohistochemistry, were consistent with the diagnosis of anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK positive.
After that, the patient was transferred to a hospital for treatment of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. At this hospital, before treatment, the patient requested the tumor from the MEDLATEC Testing Center for pathological anatomy and the results were the same as at Medlatec.
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK positive is a malignant tumor of T cells, with characteristic cell morphology, CD30 expression, ALK positive. This disease is common in children and young adults, usually in stage III-IV, with B symptoms.
The common location is lymph nodes; it can also be found outside the lymph nodes such as soft tissue, bone, and skin. MSc. Thai Thi Hong Nhung, Medlatec Pathology Center shared that in the case of patient NQA, if only based on clinical examination and imaging diagnostic techniques, it would be thought of as an abscess and performing normal drainage would miss the dangerous disease.
However, during the drainage process, the medical team quickly removed all the necrotic tissue and surrounding lymph nodes for pathological anatomy.
It is thanks to this "gold" standard that helps detect the type of lymphoma, thereby further evaluating the stage criteria and prognostic factors to have an accurate treatment regimen for the patient.
According to statistics, each year, Vietnam records 200,000 new cancer cases and 82,000 cancer deaths. The cancer mortality rate in Vietnam is 73.5%, while the world rate is 59.7% and developing countries rate is 67.9%.
Because most cancers progress silently, without obvious symptoms, or non-specific signs, patients are subjective.
When symptoms appear, medical examination is often detected at a late stage, metastasis, causing high treatment costs, even threatening the patient's life. Therefore, cancer is currently the top health concern of people around the world, including Vietnam.
With the advances of modern medicine, many modern diagnostic methods and techniques have been developed to help detect, diagnose early and treat diseases in general, and cancer in particular.
MSc. Thai Thi Hong Nhung said that early diagnosis of cancer requires relying on the results of blood and urine tests, imaging (X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MRI) and cytology and histopathology. In particular, pathology is considered a revolution in diagnosing cancer diseases right at the germinal stage.
Because pathology is a method of diagnosing diseases based on the analysis of tissue and cell samples of organs in the body that are biopsied during endoscopy, needle biopsy or during surgery and analyzed by a Pathologist under a microscope. The results after analysis will accurately determine the nature of the lesion or tumor.
Commonly used pathological tests today include histopathological tests, cytological tests, immunohistochemical tests, and immediate biopsy tests.
Pathology results provide medical evidence for damage/disease. According to experts, pathology provides the following particularly important values:
Pathology is the gold standard for definitive diagnosis of disease/lesion; pathology results are mandatory for oncological diseases;
Pathological diagnosis guides the diagnosis in some non-tumor diseases (inflammation, tuberculosis, infection...); is legal evidence for both tumor and non-tumor lesions; is a microscopic diagnosis to compare the consistency with the clinical diagnosis; at the same time guides treatment, monitoring, prognosis; has decisive significance for targeted treatment of some oncological diseases.
Pathologists recommend that all organs with physical damage (changes in cells and tissues) need to be sent for pathology to determine the nature of the damage and have medical evidence.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/giai-phau-benh---cuoc-cach-mang-trong-chan-doan-benh-chuyen-sau-d227092.html







































Comment (0)