Although cerebral hemorrhage in young people is not a common condition, it is extremely dangerous and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Although cerebral hemorrhage in young people is not a common condition, it is extremely dangerous and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
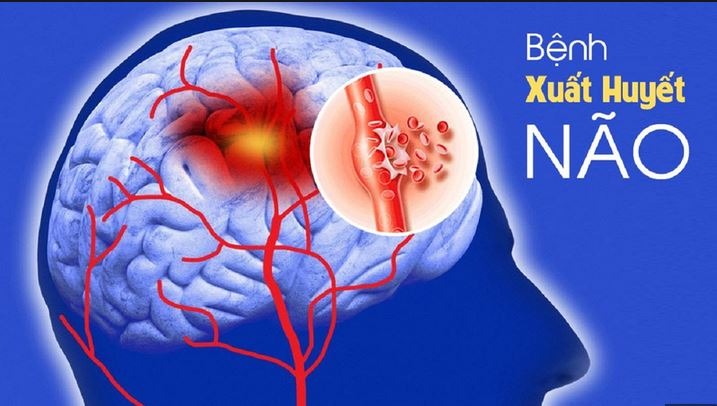
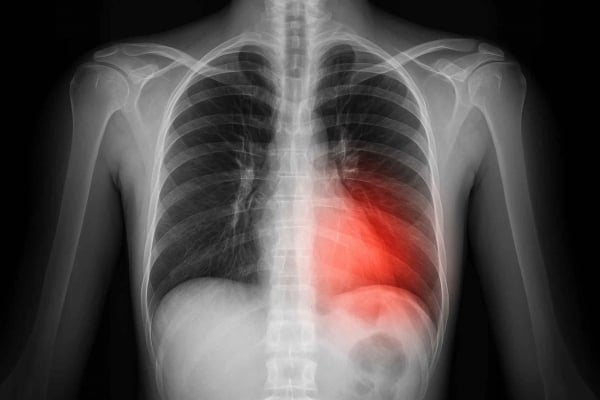
This is a type of hemorrhagic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or suddenly ruptures, leading to bleeding in the brain.
This disease can cause many serious complications, and if treated properly in the acute stage, the patient's chances of recovery are higher.
 |
| Although cerebral hemorrhage in young people is not a common condition, it is extremely dangerous and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. |
This condition, although rare, poses a serious threat to the health and life of the sufferer, especially if not recognized and intervened early.
Cerebral hemorrhage in young people can occur for many different reasons, of which high blood pressure is identified as the leading risk factor. Research shows that about 51.1% of cerebral hemorrhage cases in young people are related to high blood pressure.
High blood pressure increases the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage by 2 to 6 times. Other factors that can cause intracerebral hemorrhage include ruptured aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations, bleeding in brain tumors, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, amyloid angiopathy, traumatic brain injury, and depressed skull fractures.
In addition to the above causes, other risk factors should also be noted, including the use of anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs, chronic kidney disease, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, obesity, and low LDL cholesterol levels.
Symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can vary depending on the location and extent of bleeding in the brain.
Signs often appear suddenly and may progress rapidly, and include sudden, severe headache, sensitivity to light, weakness in one arm or leg, or on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, nausea or vomiting, seizures, especially without a history of previous seizures, decreased alertness or feeling drowsy, vision changes (such as double vision or drooping eyelids), stiff neck, difficulty breathing, unusual changes in heart rate, numbness or tingling in the limbs, loss of balance, or dizziness.
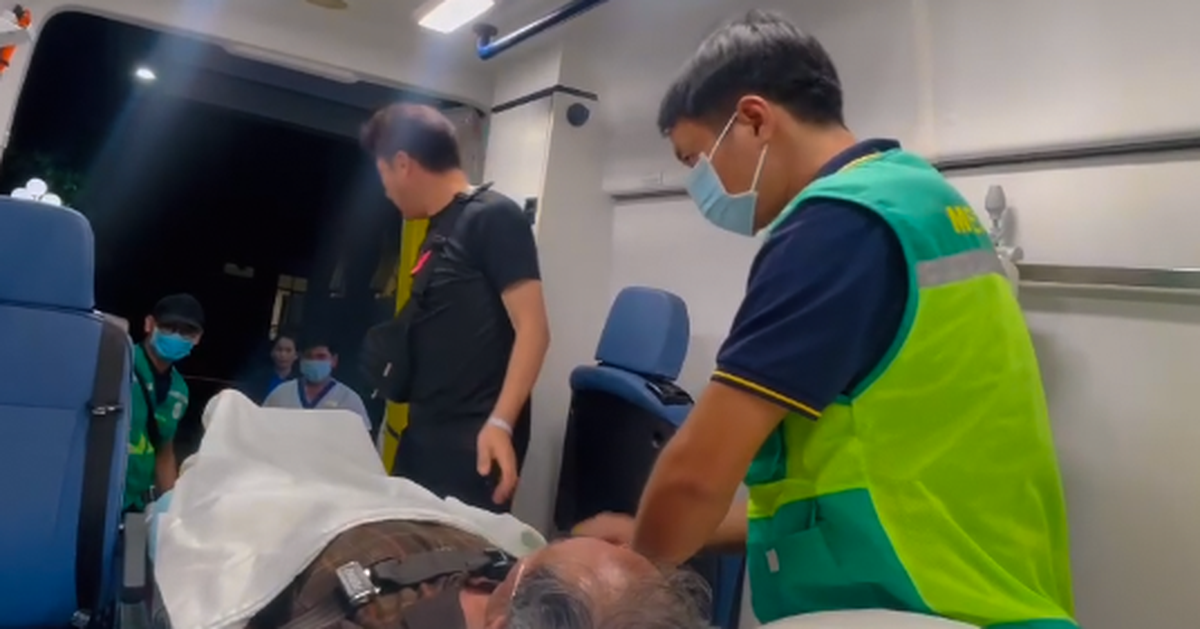
Although these symptoms can be easily confused with other diseases, if the patient shows the above signs, they should be taken to a medical facility immediately for timely diagnosis and intervention.
According to Dr. Dang Bao Ngoc, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, if not promptly treated, cerebral hemorrhage can lead to many dangerous complications, including expansion of the hematoma, edema around the hematoma, widespread hemorrhage in the ventricles, hydrocephalus, seizures, hyperglycemia, hypertension, fever and infection.
Some studies have shown that within 48 hours of a brain hemorrhage, about 33% of patients show signs of neurological impairment. The 30-day mortality rate can be as high as 47% if emergency treatment is not timely and effective.
To accurately diagnose cerebral hemorrhage, the doctor will rely on clinical symptoms and test results.
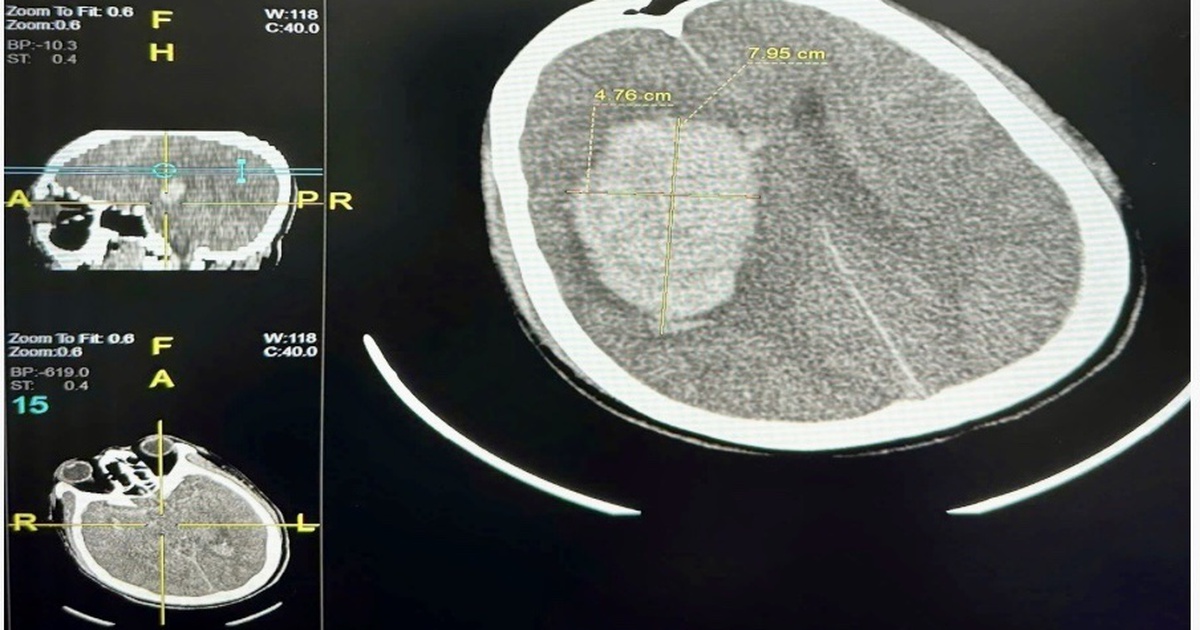
Common diagnostic methods include computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which help determine the presence of blood in the brain and distinguish a cerebral hemorrhage from an ischemic stroke.
Blood tests, assessing related factors such as blood sugar, platelets and clotting time; DSA or CT/MRI angiography of blood vessels, helping to detect abnormalities in the brain's blood vessels such as aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations.
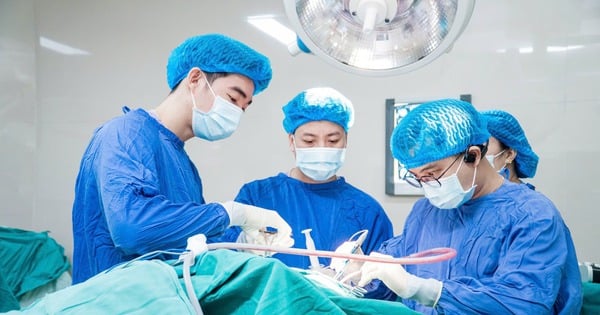
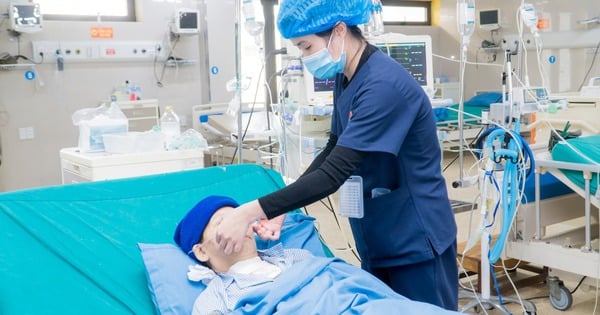
Once diagnosed, a patient with a brain hemorrhage will need emergency medical care. Brain surgery is a common procedure, helping to remove the accumulated blood and reduce pressure in the skull.
If the brain hemorrhage causes hydrocephalus, the doctor will place a shunt to relieve pressure in the brain. The patient will also be monitored and treated for other risk factors to prevent recurrence.
Although it is not possible to completely prevent all causes of cerebral hemorrhage, the following measures can help reduce the risk of the disease: control blood pressure and perform regular blood pressure screenings, exercise regularly to maintain cardiovascular health, reduce blood cholesterol and maintain a healthy weight.
Limit alcohol consumption, quit smoking, eat a healthy diet and control blood sugar if you have diabetes, wear protective equipment (such as helmets, seat belts) to protect the brain from injury, and have regular health check-ups to detect risk factors early.
Cerebral hemorrhage in young people is a serious disease, but if detected and treated promptly, the chance of recovery and minimizing complications will be very high. Therefore, early recognition of symptoms and timely emergency care play an extremely important role in saving the patient's life.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/canh-bao-gia-tang-ca-mac-xuat-huet-nao-o-nguoi-tre-d230467.html

























![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)




























































Comment (0)