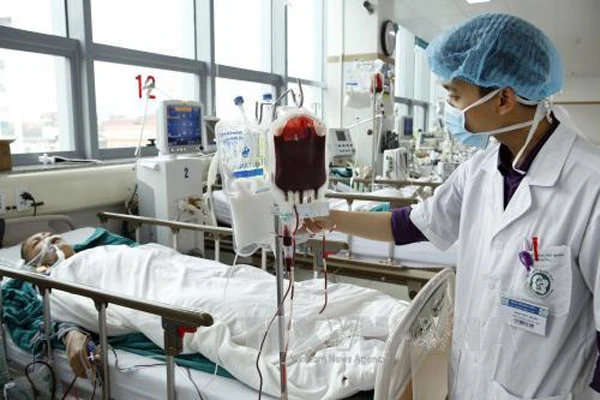
Syphilis, if not treated promptly and properly, can cause many dangerous complications such as meningitis, cardiovascular disease, and even blindness.
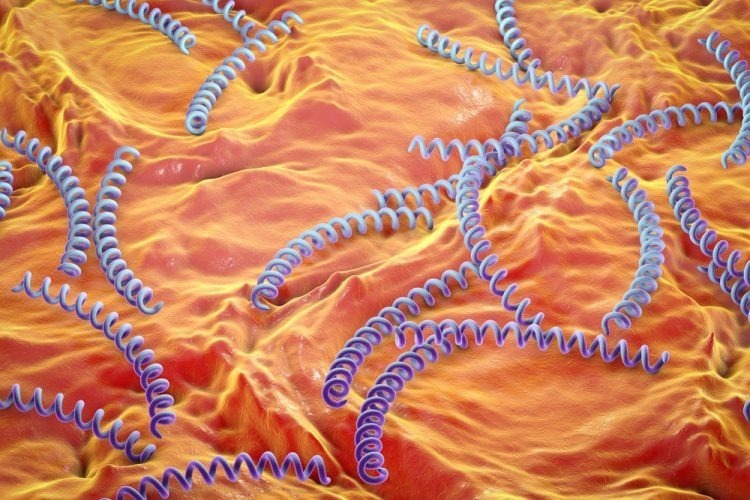
According to Dr. Nguyen Thi Kim Dung, Dermatology - Dermatology Aesthetics, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. The disease is spread through vaginal, anal, oral sex or indirectly through contaminated objects, objects, scratches on the skin, mucous membranes. In addition, the disease is also transmitted through blood or from mother to child during pregnancy.
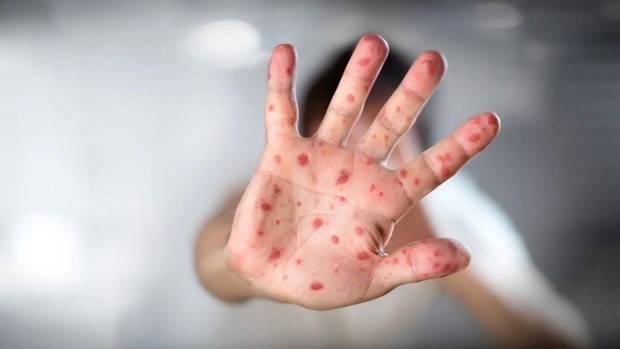
Like other sexually transmitted diseases, syphilis is difficult to diagnose because people often do not have any symptoms for many years. If syphilis is left untreated for too long, it can cause serious complications such as:
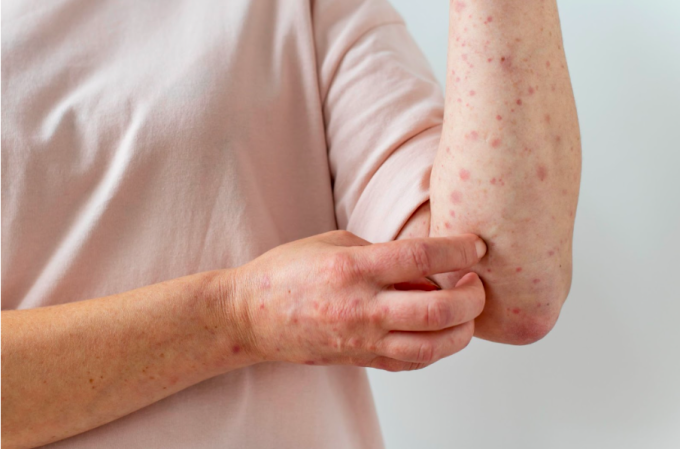
Small bumps or tumors: Called sebaceous cysts, these bumps can develop on the skin, bones, liver, or any other organ in a person with late-stage syphilis.
Neurological problems : Headache, meningitis, decreased vision, even blindness, dementia, loss of pain sensation, sexual dysfunction in men, uncontrolled bladder, cardiovascular...
HIV infection : People with sexually transmitted syphilis or other genital ulcers are 2-5 times more likely to be infected with HIV. Syphilis ulcers bleed easily, allowing the HIV virus to easily penetrate.
Complications during pregnancy and childbirth : Depending on the stage of the disease, syphilis will have a certain impact on the pregnant mother: damage to the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs, muscles, bones... In addition, when Treponema pallidum bacteria invade, the fetus is at risk of arteritis leading to death. In case of birth, the child will have congenital syphilis with complications such as blindness, deafness, meningitis...
Syphilis can be cured if detected and treated early. Photo: Freepik
In its early stages, syphilis can be cured with medication. Therefore, one option for doctors is to give the patient penicillin, an antibiotic that kills the bacteria that cause syphilis and is usually effective in most stages. If the patient is allergic to penicillin, the doctor will recommend a different antibiotic or penicillin desensitization.
If you are diagnosed with primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis (less than one year old), the recommended treatment is a single injection of penicillin. For people who have had syphilis for more than one year, your doctor may consider a booster dose. Penicillin is also the only treatment recommended for pregnant women with syphilis.
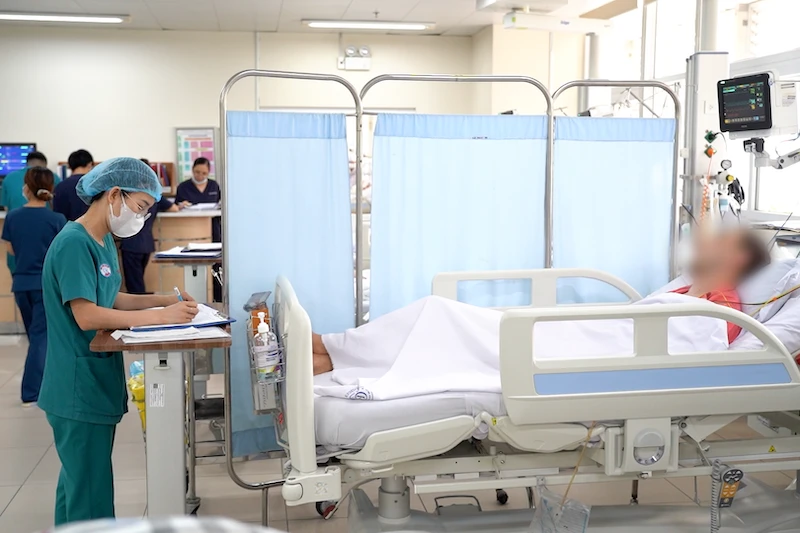
Dr. Nguyen Thi Kim Dung added that on the first day of treatment, the patient may experience a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction with symptoms including fever, chills, nausea, and headache. This reaction usually does not last longer. After treating syphilis with medication, the patient needs to pay attention to regular check-ups and blood tests to ensure that they are responding to the usual dose of Penicillin. Avoid having sex with your partner until treatment is complete and blood tests show that the infection has been cured. It is necessary to inform your partner so that they can be tested and treated early. Test for HIV infection.
As soon as you discover that you are at risk of syphilis, you should quickly see a dermatologist for early diagnosis and treatment. If you delay your visit until syphilis symptoms become obvious, the condition may be severe and difficult to cure completely.
Nguyen Van
Source link





![[Photo] April Festival in Can Tho City](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/bf5ae82870e648fabfbcc93a25b481ea)
![[Photo] Opening of the 11th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/f9e717b67de343d7b687cb419c0829a2)
![[Photo] Unique folk games at Chuong Village Festival](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/cff805a06fdd443b9474c017f98075a4)

















































































Comment (0)