In an increasingly competitive global economy with strict requirements on quality, production costs, and delivery times, the textile and apparel industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Automation is no longer an option, but a vital factor to maintain and enhance competitiveness. Major textile and apparel exporting countries such as Bangladesh, India, and China have taken strong steps in applying automation technology to production, helping to improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance resilience to market fluctuations.
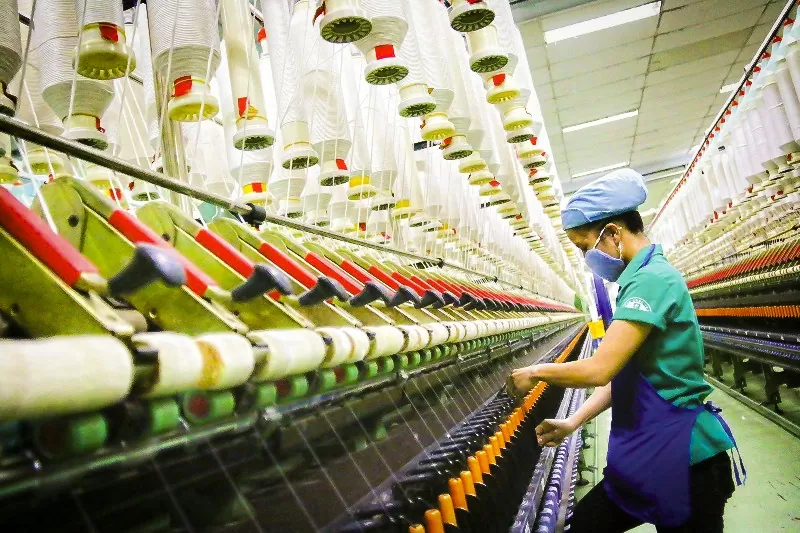 |
| Automation is no longer an option, but a vital factor to maintain and enhance competitiveness in the textile industry. Illustration photo |
Bangladesh: Investing in technology to boost productivity, improve quality
Bangladesh, with the textile industry being one of the major economic drivers, has witnessed a major change in the manufacturing process thanks to the adoption of automation technology. In recent years, Bangladeshi textile companies have started to adopt automation systems in processes such as fabric cutting, weaving and sewing. This has helped reduce dependence on manual labor, reduce errors and increase production speed.
Bangladesh has focused on basic automation, with machines such as automatic fabric cutters, weaving machines and sewing machines, which not only increases productivity but also improves product quality – an increasingly demanding requirement from international brands such as H&M, Zara and Guess, which are major partners of factories here.
A prime example is the implementation of “Nidle” – a real-time productivity monitoring system, integrated into each sewing machine. This device displays production progress directly on the screen, using a color code from red (behind schedule) to green (on target), thereby creating pressure to boost labor productivity. This is part of a “smart manufacturing” strategy that combines digital monitoring with semi-automated machines – semi-automated devices that perform tasks such as attaching pockets and attaching buttons with minimal human guidance. By applying technology like Nidle and other automated systems, many factories have recorded a 7–10% increase in production in a short period of time.
India: Digital Transformation and Manufacturing Process Optimization
The Indian market, one of the textile powerhouses, has implemented a strong automation strategy to optimize production processes and improve labor efficiency. Large enterprises such as Arvind Ltd and Vardhman Textiles have invested in automated production lines from yarn to weaving, dyeing and sewing.
According to data from The Textile Magazine, from 2022, Arvind Ltd has announced plans to invest INR 300–400 crore over the next 2-3 years, focusing on products such as leisure fabrics, man-made fibers and advanced materials, to take advantage of incentives from the government's PLI scheme. Notably, at the Bharat Tex 2025 event, Vardman Textiles showcased the latest advances in spinning, fabric and apparel solutions, including advanced dyeing techniques that significantly reduce the use of water and chemicals.
In addition, recognizing the importance of human resources in operating and maintaining automated systems, India has focused on training skilled human resources. These training programs are widely implemented in universities and vocational training centers, helping to prepare a highly skilled workforce for the textile industry.
According to information from ATDC India, Apparel Training & Design Centre (ATDC) is one of the largest vocational training networks in India with about 100 centers in major garment industrial clusters. ATDC has trained more than 313,500 students, providing employment opportunities for disadvantaged social groups.
Many training institutes like Technological Institute of Textile & Sciences (TIT&S) in Haryana and Government College of Engineering & Textile Technology in Berhampore offer in-depth training programmes in textile technology, combining theory and practice, to meet the growing demands of the industry.
China: Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
China, the world’s second largest economy, is leading the way in applying automation and smart manufacturing technology to the textile industry. From automated sewing lines to intelligent management systems, China has successfully integrated high technology into every stage of production, helping to optimize costs and labor productivity.
One of the key strategies China has adopted is “smart manufacturing,” where textile factories are connected to automated monitoring and management systems. Data collected from the production process is analyzed and used to optimize processes and predict problems before they occur. China has also pioneered the use of automated robots in high-precision processes such as sewing and quality control.
According to Textspace Today, the Chinese government has been pushing hard to adopt automation and smart manufacturing through its “Made in China 2025” initiative, aiming to enhance its manufacturing capabilities and global competitiveness. According to data from the International Federation of Robotics, China’s robot density reached 392 robots per 10,000 manufacturing workers in 2023, far exceeding the global average of 141.
Companies like Sewingtech have developed 3D automated sewing technology, which allows for the automation of sewing fabric panels of various shapes with high precision, minimizing errors and increasing production efficiency (according to chinadaily hk)
In addition, textile factories in China are also applying artificial intelligence (AI) to improve quality control, reduce waste and increase productivity. AI helps detect errors early in the production process, thereby minimizing defective products and optimizing production processes. However, the application of automation and AI also poses the challenge of retraining the workforce to adapt to new technology. Many training programs have been implemented to improve workers' skills, helping them operate and maintain automated systems effectively.
Difficulties of Vietnam's textile industry in investing in automation
Vietnam’s textile and garment industry is facing major challenges when deciding to invest in automation. Although the industry has great potential, there are still many significant challenges, especially in technology transformation and innovation of production processes.
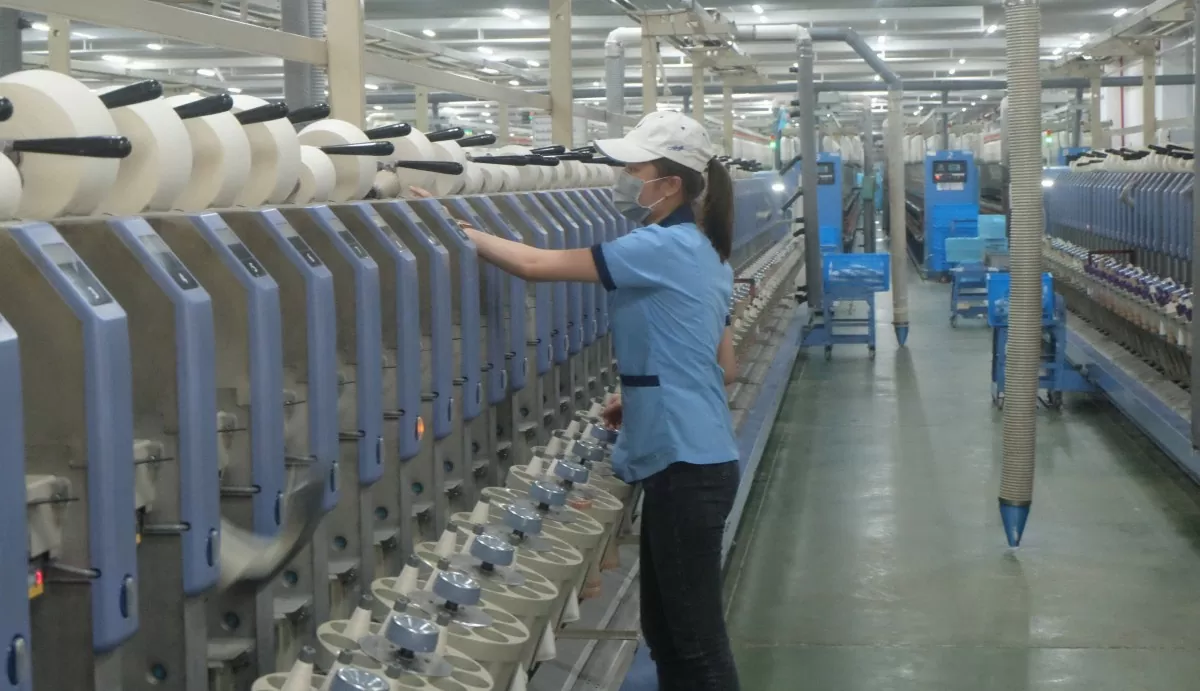 |
| The textile and garment industry is making efforts to transform digitally to increase labor productivity. Illustrative photo |
High investment costs : Investing in automation requires a large amount of capital, which is difficult for small and medium enterprises, which make up the majority of the Vietnamese textile and garment industry. Investing in automation technology, although necessary, still faces barriers in terms of cost and financial capacity.
Shortage of high-quality human resources : The transition to automation requires a highly skilled workforce. However, currently, the majority of workers in the Vietnamese textile and garment industry are not equipped with the necessary technological skills to operate and maintain automated systems.
Internal resistance : A significant number of businesses still maintain manual production habits and are hesitant about technological changes. Convincing managers and workers to participate in the digital transformation process is a big challenge.
Open lessons for Vietnam
To overcome these difficulties, the Vietnamese textile industry needs to:
First , increase investment in basic automation technology : Vietnamese textile and garment enterprises, especially small and medium enterprises, should start by investing in basic automation technology. The application of simple but effective automatic machines will help increase labor productivity and improve product quality without requiring too much initial investment. Vietnam needs to actively encourage textile and garment enterprises to start with small but influential steps, especially in stages such as fabric cutting, sewing, and production supervision.
Second , digital transformation and production optimization : Vietnam needs to focus on digital transformation in the textile and garment industry, not only in the production process but also in management and supervision. Enterprises need to invest in production management software, work progress tracking systems and automation systems to optimize processes. At the same time, training highly skilled human resources is very important. The government and enterprises need to coordinate to develop vocational training programs to equip textile and garment workers with advanced technological skills.
Third , training and developing human resources: Developing highly skilled human resources is an important factor to maintain and develop automation technology. The government and businesses need to coordinate to organize specialized training programs for textile and garment workers.
Fourth , apply smart manufacturing and advanced automation : Vietnam needs to move towards applying smart manufacturing in the textile and garment industry. In particular, the use of automated robots and artificial intelligence in stages requiring high precision such as sewing and quality inspection will help improve product quality, minimize errors and optimize processes. However, to do this, Vietnam needs a long-term strategy for developing high technology and training qualified human resources to operate and maintain automated systems.
| Vietnam needs to develop a comprehensive automation strategy, from upgrading infrastructure, innovating technology, to training a workforce with appropriate skills. Only then can the Vietnamese textile and garment industry maintain its competitive position and thrive in the era of Industry 4.0. |
Source: https://congthuong.vn/tu-dong-hoa-nganh-det-may-viet-nam-dang-o-dau-383257.html


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives French Ambassador to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/49224f0f12e84b66a73b17eb251f7278)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with outstanding workers in the oil and gas industry](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/1d0de4026b75434ab34279624db7ee4a)
![[Photo] Closing of the 4th Summit of the Partnership for Green Growth and the Global Goals](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/c0a0df9852c84e58be0a8b939189c85a)
![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper announces the project "Love Vietnam so much"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/362f882012d3432783fc92fab1b3e980)
![[Photo] Promoting friendship, solidarity and cooperation between the armies and people of the two countries](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0c4d087864f14092aed77252590b6bae)















![[Photo] Welcoming ceremony for Chinese Defense Minister and delegation for friendship exchange](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/fadd533046594e5cacbb28de4c4d5655)




























![[Video] Viettel officially puts into operation the largest submarine optical cable line in Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/f19008c6010c4a538cc422cb791ca0a1)






































Comment (0)