Children should sunbathe to increase vitamin D, eat foods rich in vitamin K, calcium, and magnesium for strong bones and physical development.
Weak bones increase the risk of future injuries, making children susceptible to bone fractures and osteoporosis. A balanced diet and healthy lifestyle help children have strong bones.
Vitamin D
The easiest way to prevent bone-related disease is to supplement with vitamin D. Infants and young children grow rapidly and are susceptible to vitamin D deficiency if they do not get enough sunlight or do not get enough through their diet. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that exclusively breastfed infants receive 400 IU of vitamin D daily, starting in the first few days of life.
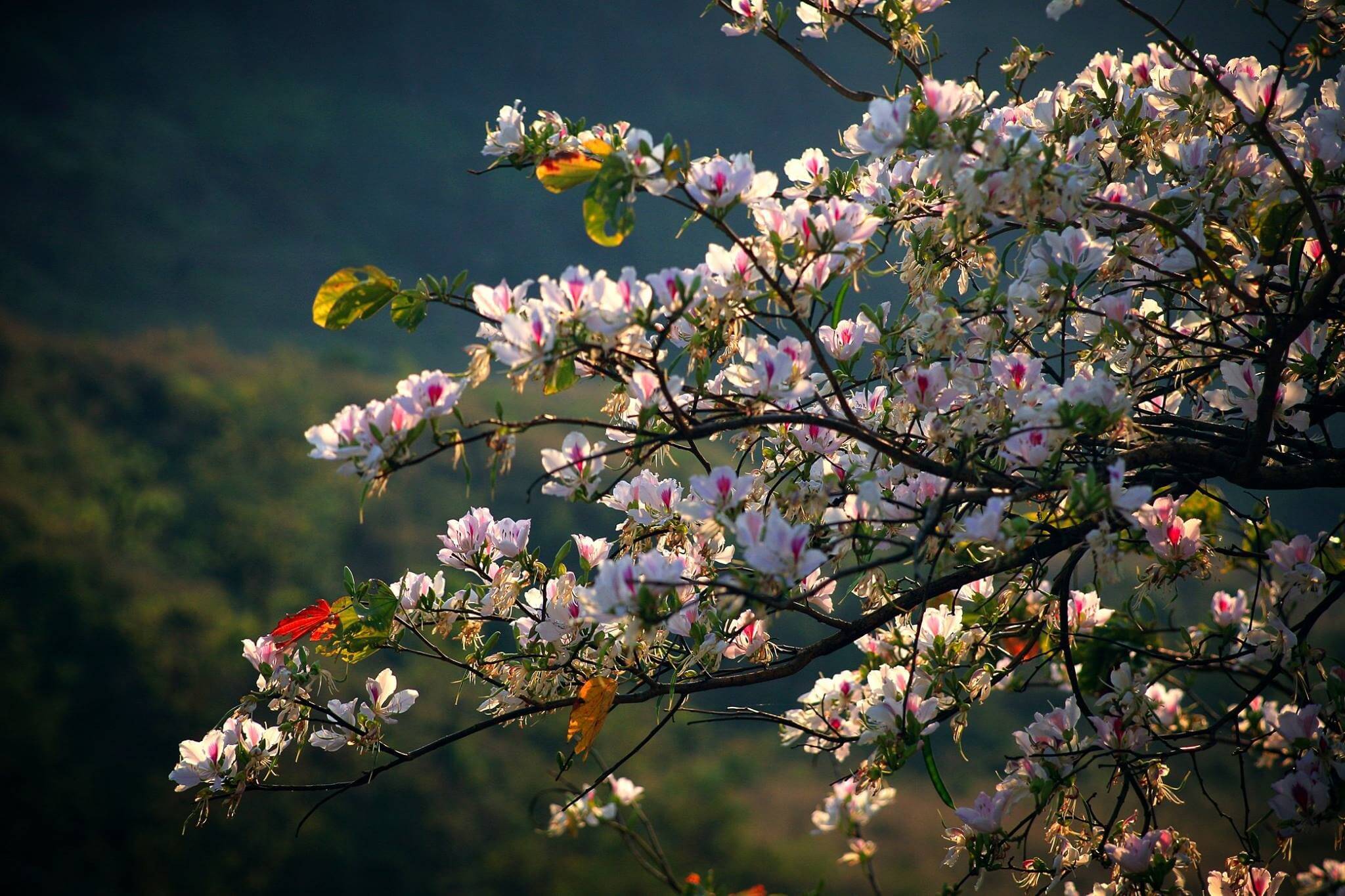
To absorb enough of this vitamin, children should sunbathe for about 30 minutes every day in the early morning or late afternoon, avoiding the hours of strong sunlight around 10-15h. Parents can let their children play and exercise outdoors so that the skin can synthesize vitamin D. Fresh milk and dairy products such as cheese, cream, yogurt are rich in calcium and vitamin D.
While egg whites are rich in protein, fat, vitamin D and minerals are found mainly in the yolk. On average, 100 grams of wild-caught salmon contains up to 988 IU of vitamin D.
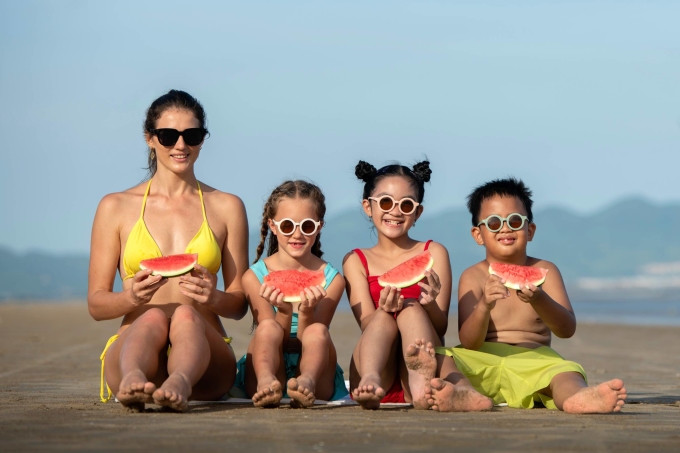

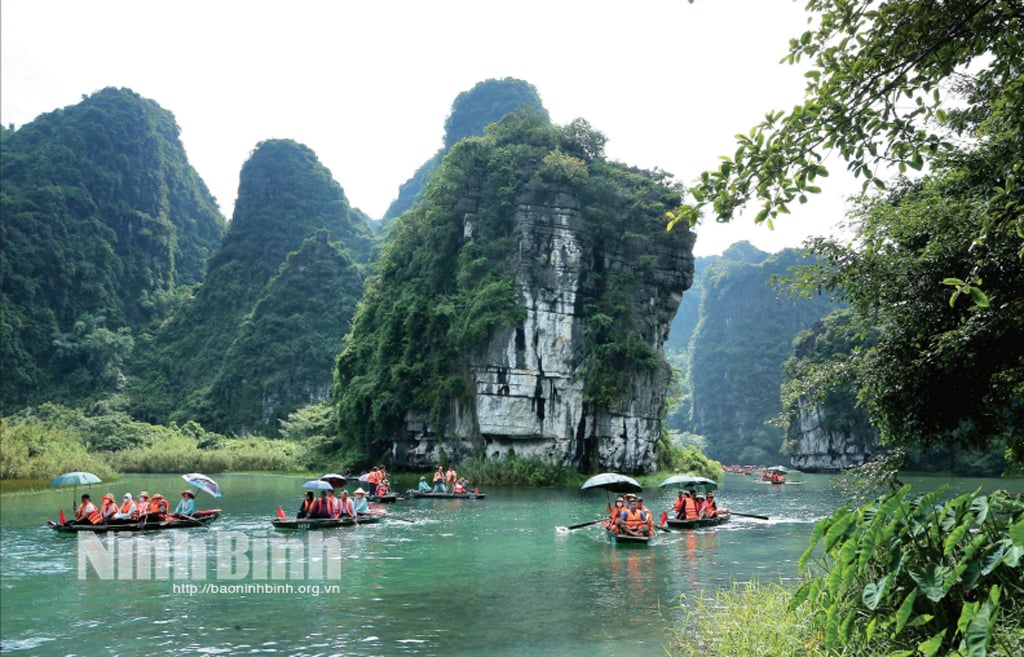
Children exposed to sunlight helps the body synthesize vitamin D. Photo: Freepik
Calcium
Calcium helps build bones. Children who lack this nutrient often have rickets, malnutrition, slow growth, slow and uneven teeth growth, weak teeth, and hair loss in a ring shape at the back of the neck. Milk, dairy products, spinach, broccoli, almonds, beans, seafood... provide abundant calcium. Children 0-12 months old should be exclusively breastfed. Children 1-3 years old should drink at least 100 ml of milk per day.
Vitamin K
This is one of the vitamins that is good for bones and joints. Vitamin K includes three types: vitamin K1, K2, K3. If vitamin K1 is good for blood clotting, vitamin K2 is good for bones. Foods rich in vitamin K2 include egg yolks, fish, chicken, pork skin, fruits, and vegetables.
Magnesium
This nutrient plays a role in building new bone cells, increasing bone mineral density, and reducing the rate of fractures due to osteoporosis. Magnesium is needed to promote calcium absorption.
Eating mackerel, salmon, halibut, and tuna can boost your intake of magnesium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. According to the American Heart Association, eating fatty fish at least twice a week can help reduce your risk of heart disease. Nuts like cashews, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, and almonds are also good sources of magnesium.
100 grams of avocado contains about 20 mg of magnesium. The fruit is also rich in vitamins, heart-healthy nutrients, and disease-preventing chemicals. Nonfat or low-fat yogurt is rich in magnesium, with a 170-gram container containing about 19 mg of magnesium.
Dark chocolate is also rich in magnesium and provides flavanols, antioxidants that help regulate blood pressure.
Le Nguyen (According to Timesofindia )
| Readers send questions about children's diseases here to get answers from doctors |
Source link





























































































Comment (0)