In a new report, scientists warn that taking a bath with water that is too hot not only dries out your skin and hair and disrupts your sleep, but can also be dangerous, according to the Express .
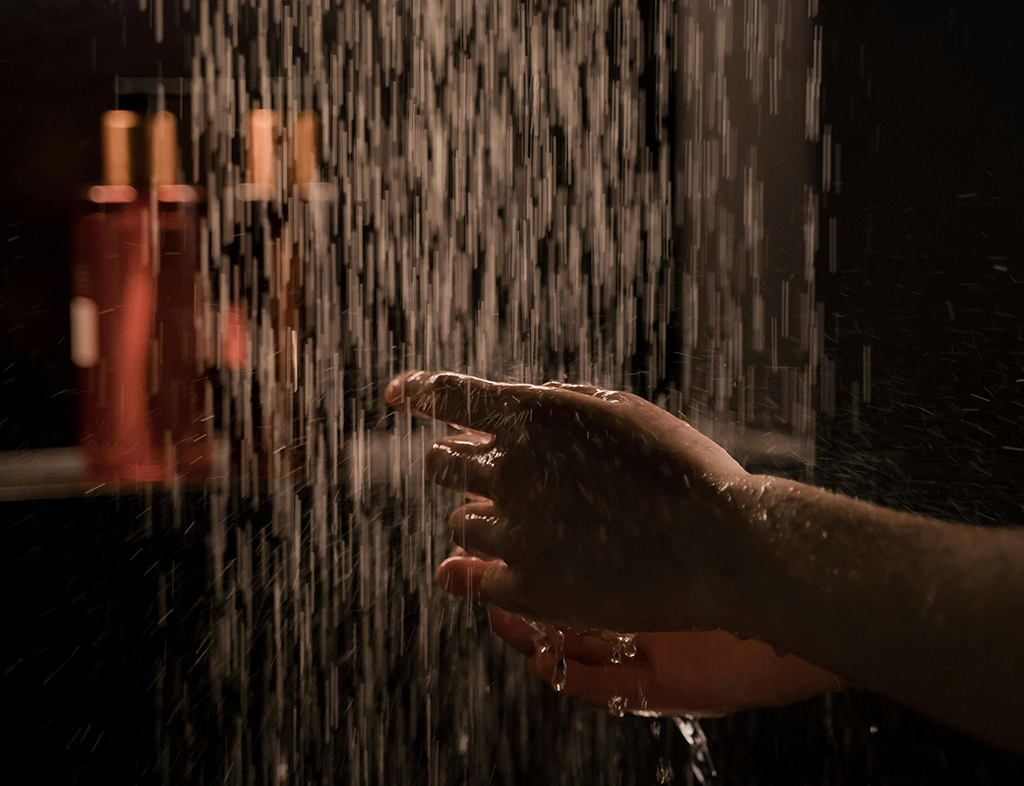

Long hot baths can dry out your skin and hair.
Scientists analyzed data from 18 studies on the harmful effects of bathing in water that is too hot.
As a result, scientists have warned: Conditions such as eczema or psoriasis can be aggravated after bathing in water that is too hot.
Notably, the study results also showed that bathing in water that is too hot will cause additional stress on the heart.
Why is it dangerous for people with heart disease?
The heat from a hot bath causes blood vessels to dilate, forcing the heart to pump harder to maintain blood flow. This increased stress can cause problems for people who already have heart disease, the researchers explain.
For people with certain heart conditions, hot baths can cause low blood pressure, which can manifest as lightheadedness and dizziness, increasing the risk of falling while bathing. The combination of heart strain and a sudden drop in blood pressure significantly increases the risk of fainting. This is especially dangerous while bathing, causing falls that can lead to serious injuries, according to Express.

Bathing in water that is too hot is especially dangerous for people with heart disease.
Taking a very hot bath can also interfere with the natural cooling process needed for sleep. This can delay this process, making it harder to fall asleep.
Bathing in water that is too hot can also make asthma worse.
Research also shows that many people may experience skin damage from hot baths. Hot baths may feel relaxing, but they are a double-edged sword that can affect both your skin and your heart health in the long run.
Experts note that to ensure safety, you should take short baths (5 to 10 minutes) with water that is not too hot, according to Express.
Dr. Teo Soleymani, a physician at the David Geffen School of Medicine in the United States, recommends bathing in warm water at a temperature of 27 - 40°C. Body temperature or a few degrees warmer is ideal, according to the health website Healthline.
Source link



![[Photo] Hanoi people warmly welcome Chinese General Secretary and President Xi Jinping on his State visit to Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/d6ac6588b9324603b1c48a9df14d620c)


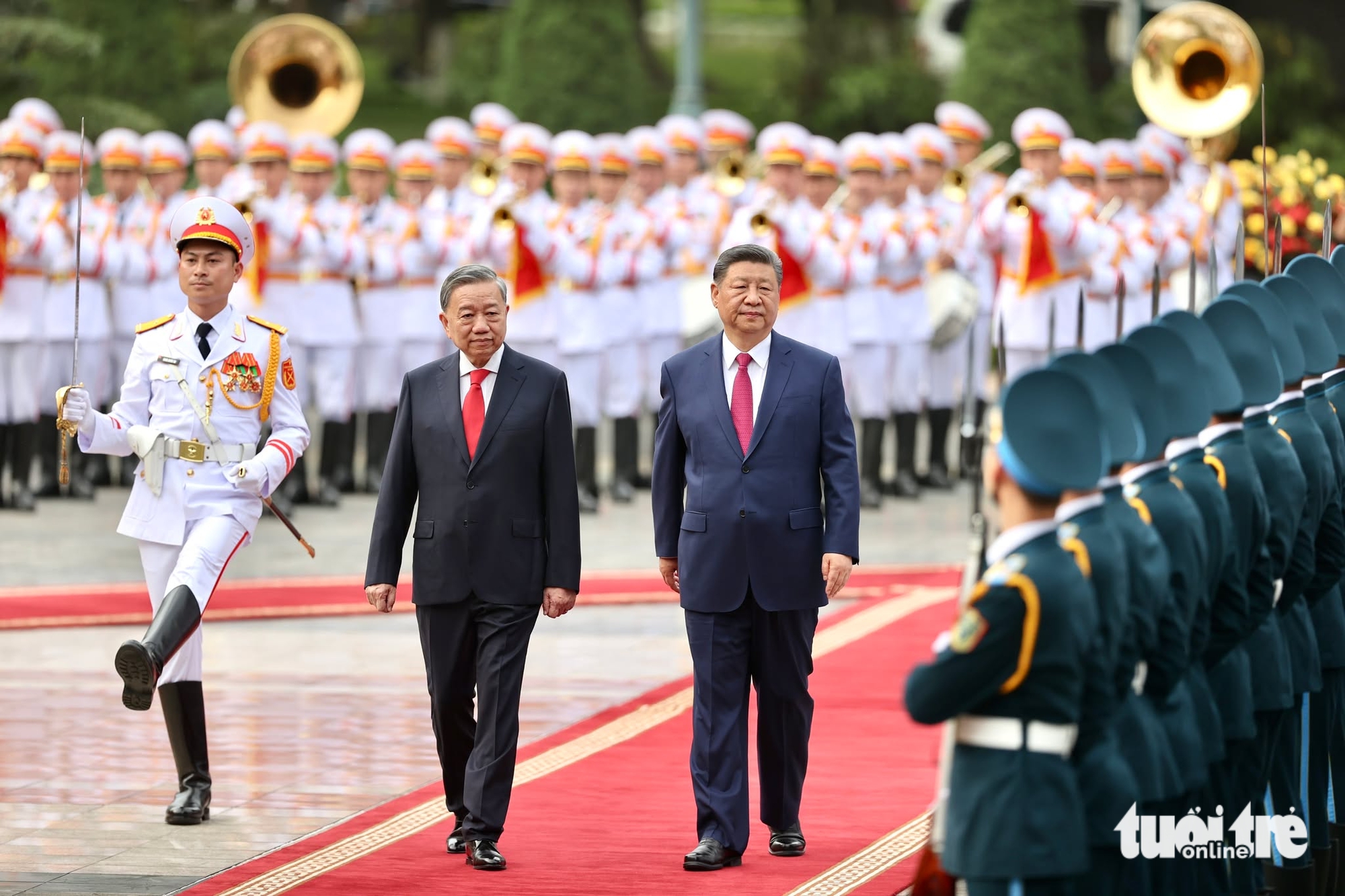
![[Photo] Ceremony to welcome General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping on State visit to Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/5318f8c5aa8540d28a5a65b0a1f70959)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs conference to review the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/dcdb99e706e9448fb3fe81fec9cde410)













![[Video] Bringing Vietnamese clinical allergy and immunology closer to international standards](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/7cb0a51750ed491a9dbccb76f9a3c208)





































































Comment (0)