Oats are rich in fiber and contain anti-inflammatory properties that help control blood sugar, reducing the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Oats are rich in fiber and essential minerals such as magnesium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, zinc and iron. Here are the reasons why diabetics should add oats to their diet.
Blood sugar control
According to Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health, USA, whole grain oats have a low glycemic index (GI), are digested and metabolized more slowly.
The high fiber content of oats helps control blood sugar. One cup of oatmeal has about 30 grams of carbohydrates and 4 grams of fiber.
A 2022 analysis from the University of Toronto, Canada, based on eight studies, about 400 participants, found that beta-glucan (a type of soluble fiber found in oats) increases digestion time and slows the release of glucose (sugar) in the small intestine. As a result, beta-glucan can improve post-meal and fasting blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Losing weight
Oats are low in calories and high in fiber, which increases feelings of fullness, reduces cravings, and aids in weight loss. Diabetics can get at least 10 grams of fiber per meal from foods such as oatmeal, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Low fiber intake can lead to constipation.
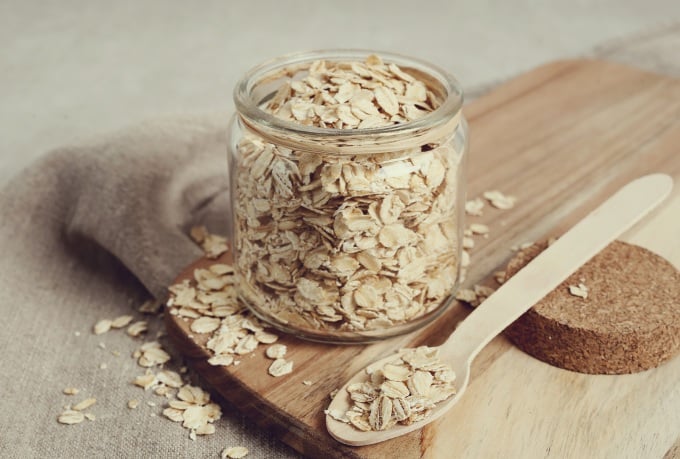

Whole grain oats are good for your health. Photo: Freeik
Reduce inflammation
Chronic inflammation puts undue stress on organs, contributing to complications such as heart disease, brain disease, and diabetes.
Oats contain avenanthramide compounds that help diabetics reduce inflammation, helping to prevent the disease from progressing. According to a 2014 study by the University of Aberdeen, UK, on 22 diabetics, a diet rich in oats reduced microparticles in blood platelets. These microparticles contribute to increased blood sugar and inflammation.
Reduce the risk of heart disease
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, heart disease is a common complication of type 2 diabetes. Eating high-fiber, anti-inflammatory foods like oats can help reduce your risk of heart problems.
Oats also help reduce high cholesterol levels, which can lead to heart disease. A 2015 review of 16 studies from Sichuan University in China found that people with type 2 diabetes who ate oatmeal for breakfast for 12 weeks had lower levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) and total cholesterol. They also had lower blood glucose (sugar) levels.
People with diabetes should choose whole, steel-cut, groats or oat flour. Avoid processed, instant varieties, as they contain high GI sugars that raise blood sugar levels more quickly. For example, a 28-gram serving of oatmeal has a low GI of 55, while instant oatmeal has a high GI of about 79.
For side dishes with oatmeal, choose fresh fruit and nuts such as almonds and walnuts instead of dried fruit or other sugary foods to avoid increasing blood sugar.
Mai Cat (According to Everyday Health )
| Readers ask questions about diabetes here for doctors to answer |
Source link


![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper announces the project "Love Vietnam so much"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/362f882012d3432783fc92fab1b3e980)
![[Photo] Closing of the 4th Summit of the Partnership for Green Growth and the Global Goals](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/c0a0df9852c84e58be0a8b939189c85a)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives French Ambassador to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/49224f0f12e84b66a73b17eb251f7278)
![[Photo] Promoting friendship, solidarity and cooperation between the armies and people of the two countries](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0c4d087864f14092aed77252590b6bae)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with outstanding workers in the oil and gas industry](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/1d0de4026b75434ab34279624db7ee4a)























![[Photo] Welcoming ceremony for Chinese Defense Minister and delegation for friendship exchange](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/fadd533046594e5cacbb28de4c4d5655)




























![[Video] Viettel officially puts into operation the largest submarine optical cable line in Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/f19008c6010c4a538cc422cb791ca0a1)






































Comment (0)