Mr. PHAM THANH HA, Deputy Governor of the State Bank :
Regulation of short-term bills does not affect interest rates. The goal set by the Government and the State Bank is to reduce interest rates to support borrowers. In the context that countries around the world continue to increase interest rates, since the beginning of the year, the State Bank has reduced operating interest rates 4 times, and the lending interest rate for priority sectors has decreased by 4% - 5.5% compared to the end of 2022.
The State Bank of Vietnam is currently closely monitoring the foreign exchange market to find solutions to stabilize the exchange rate. Recently, the State Bank of Vietnam has been regulating short-term credit notes to reduce excess liquidity in the system, trying not to have a major impact on the interest rate level. Currently, the interbank market interest rate remains stable.
Maintain monetary easing
Since the beginning of the year, the SBV has maintained a loose monetary policy to support the economy. Although the SBV has implemented many solutions to increase access to capital for businesses, including reducing interest rates, in the context of many economic difficulties and low absorption capacity of the economy, credit growth in the first 9 months of 2023 increased by only 6.92% compared to the end of 2022, reaching only 50% of the target set for this year. Meanwhile, the amount of money stuck in the banking system is very large.
 |
| Production activities at Hanoi Plastics Joint Stock Company. Photo: QUANG PHUC |
From the perspective of a financial expert, Mr. Tran Ngoc Bau - General Director of WiGroup Financial Data and Technology Joint Stock Company, said that this is a sign that only loosening policies, but credit capital cannot reach the economy.
In that context, the exchange rate is again tense. Due to the inability to push credit capital into the economy, the excess liquidity in the banking system has caused interbank interest rates to fall sharply, putting pressure on the USD/VND exchange rate, while the USD is on an upward trend. Recently, the USD/VND exchange rate at banks has continuously peaked, at times exceeding 24,600 VND/USD. Excess bank liquidity has also led to an increasingly widening interest rate gap between VND and USD. After the exchange rate continuously peaked, the State Bank intervened to stabilize the exchange rate through the issuance of credit notes.
After 13 sessions of issuing treasury bills, from September 21 to October 9, the State Bank of Vietnam has withdrawn nearly VND145,700 billion from the system. This move is aimed at regulating liquidity in the short term, thereby reducing pressure on the exchange rate. Although the exchange rate has cooled down, the USD/VND exchange rate of domestic banks is still high, at VND24,230/USD for buying and VND24,570/USD for selling on October 10.
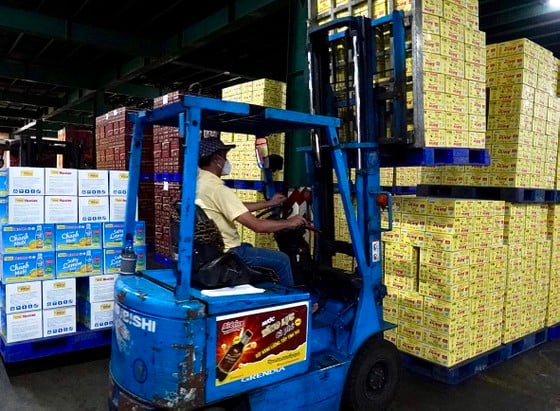 |
| Tan Quang Minh Production and Trading Company Limited - BIDRICO, Vinh Loc Industrial Park, Binh Chanh District, Ho Chi Minh City prepares goods for sale to the market. Photo: HOANG HUNG |
According to Mr. Dinh Quang Hinh, Head of Macroeconomics and Market Strategy Department of VNDirect Securities Company, the interest rate gap between VND and USD continues to narrow because the operating interest rate of the US Federal Reserve (FED) may remain at the peak until the end of 2023 to curb inflation, while the State Bank of Vietnam plans to continue lowering interest rates to support domestic growth and inflation.
“The increase in the USD/VND exchange rate has led to pressure on foreign debt repayment, especially in the private sector; at the same time, it has increased inflationary pressure due to increased prices of imported raw materials and consumer goods. Therefore, the greater the exchange rate pressure, the narrower the “room” to loosen domestic monetary policy,” said Mr. Dinh Quang Hinh.
Maximize fiscal policies
Credit growth remains low, raising concerns about the achievement of the growth target of 6%-6.5% set by the Government in 2023. However, economic experts believe that in the context of the "health" of enterprises not improving, production and business activities not recovering, in addition to promoting credit flow, it is necessary to step up the implementation of fiscal policies, creating capital synergy for the economy, aiming for the highest growth target.
According to Dr. Dinh Trong Thinh, from now until the end of the year, there is almost no room left for monetary policy to support economic growth. Therefore, in order to achieve the set economic growth target, it is necessary to strongly promote the role of fiscal policies such as: reducing 30% of land rent recently issued by the Government, reducing fees, charges, reducing value added tax, etc.
Associate Professor, Dr. Pham The Anh, Chief Economist of the Vietnam Center for Economic and Strategic Studies (VESS), proposed a solution: It is necessary to focus all resources on public investment disbursement. Currently, public investment has only disbursed about 50%, and if it is accelerated at the end of the year, it will contribute significantly to economic growth. According to calculations, if 95% of public investment capital is disbursed this year (about 711,000 billion VND), the GDP growth rate of the economy will increase by about 1.2% - 1.3%.
Meanwhile, Dr. Can Van Luc and the group of authors from BIDV Training and Research Institute forecast that GDP growth for the whole year of 2023 could reach 5%-5.2% (baseline scenario) or 5.3%-5.5% (positive scenario) thanks to solid consumption growth, continued expansion of public investment, improvements in private investment, exports, industrial production, real estate market, etc.
“To achieve a growth rate of 5%-5.2%, GDP in the fourth quarter of 2023 needs to increase by 6.9%-7.7% or higher, requiring greater determination and efforts from the Government, ministries, sectors, localities, and the consensus of businesses and people; at the same time, it is necessary to be more drastic in implementing economic recovery policies,” Dr. Can Van Luc emphasized.
According to the latest report of the State Bank of Vietnam, the amount of people's deposits in the banking system as of the end of July 2023 reached nearly 6.4 million billion VND, the highest level ever. At the regular Government press conference in September, the Standing Deputy Governor of the State Bank of Vietnam said that as of September 30, the total mobilized capital of commercial banks reached about 12.9 million billion VND, an increase of about 5.9% compared to the end of 2022. Meanwhile, in terms of lending, as of the end of September, the total outstanding debt of the economy reached about 12.63 million billion VND, an estimated increase of 6.1% - 6.2% compared to the end of 2022.
* DR. NGUYEN TRI HIEU
Finance and banking expert:
The issue of the State Bank's exchange rate management depends heavily on the actions of the US Federal Reserve (FED). If the FED raises interest rates, the value of VND will be pushed down, and the exchange rate will increase. To reverse this trend, the State Bank will have to raise interest rates to narrow the gap between US and Vietnamese interest rates.
Currently, if we calculate the overnight interest rate, the difference between the US and Vietnam is around 5%, which is relatively large. If the FED continues to increase interest rates, the above difference will be large, and when the impact on the exchange rate is too strong, the State Bank will have to adjust the interest rate to narrow the difference in overnight interest rates between VND and USD.
If the State Bank increases interest rates at this time, it will increase the cost of capital for businesses, especially for those who still borrow credit and continue to do business and production.
However, in my opinion, increasing or decreasing interest rates at this time will not have much impact on current economic growth. Because economic growth is slow as it is now not because of bank interest rates creating barriers, but market output is the main bottleneck.
Therefore, the main issue now is how well the economic foundations cope with the context of falling global demand.
* Mr. NGUYEN MINH TUAN
AFA Capital General Director:
According to my calculations, VND depreciates due to the exchange rate difference with USD of about 3.5%. There is a difference between the Vietnamese market and the US market, so the exchange rate must compensate; otherwise, capital will be withdrawn. The "pumping - sucking" of treasury bills by the State Bank of Vietnam in the recent past is normal.
The economy can be metaphorically considered a field, and the interbank market is just the area of the system that can distribute water to the field. This also implies that monetary policy needs to affect the entire field. That is, enough water for the field - enough capital for the economy to operate. And the "pumping - sucking" activity is just the activity of the "water tank" - the banks.
The FED’s focus is on fighting inflation, while Vietnam’s focus is on GDP growth. If we still cannot achieve this goal, the monetary policy will remain the same.
FLOWING WATER
Source




![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam chairs the third meeting to review the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/10f646e55e8e4f3b8c9ae2e35705481d)
![[Photo] General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping arrives in Hanoi, starting a State visit to Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/9e05688222c3405cb096618cb152bfd1)


























![[Photo] Opening of the 44th session of the National Assembly Standing Committee](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/03a1687d4f584352a4b7aa6aa0f73792)





























































Comment (0)