 |
| Economic news review |
Overview
The time for the US to activate reciprocal tariffs is approaching, but Vietnam has already had specific foreign policies.
During President Donald Trump’s second term, US trade policy continued to move towards strong protectionism with a focus on the use of tariffs. From February 2025, Washington officially imposed an additional 10% tax on all imports from China, while raising the tax rate on steel and aluminum to 25%. Not stopping there, a plan to apply a 10% base tax to all imported goods is also being considered.
Mr. Trump is expected to announce the new tax rate on April 2nd according to the “reciprocal” approach. The list of countries that could be subject to tariffs under Mr. Trump’s new plan includes major economies in the G-20 group, as well as India, Japan, China and Vietnam. This shows that the US is specifically targeting countries that have large trade surpluses with them, of which Vietnam is a typical case with a trade surplus of more than 105 billion USD in 2024 (according to data from the General Department of Customs).
To minimize the possible impacts of the US protectionist policy, the Vietnamese Government has taken many proactive measures to attract and retain foreign investors, to gradually balance trade with the US, and to promote domestic consumption...
Regarding foreign investment flows, Vietnam retains current investors with competitive advantages compared to other countries in the region such as increasingly complete infrastructure with a system of seaports, highways, and synchronously connected airports; advantages in labor and domestic supply chains; with salaries only about 45% of China's, Vietnamese workers are considered skillful, quick learners and highly productive; strong preferential policies to attract FDI such as corporate income tax of only 10% for 15 years or 5% for 37 years for special projects...
In addition, Vietnam is also actively attracting new capital flows. In the first 3 months of 2025, Vietnam welcomed two large business delegations from the United States, including leading corporations such as Apple, Boeing, Intel, Amazon, Coca-Cola, etc.
Mr. Ted Osius, President of the US-ASEAN Business Council (USABC), said that this is the largest US business delegation ever to visit Vietnam. Besides the US, the Prime Minister also continuously had meetings with leaders of large corporations from Japan, Europe and China...
An important measure to balance trade balances with Vietnam's strategic partners is to reduce import taxes. Recently, the Ministry of Finance has submitted to the Government a draft Decree amending Decree 26/2023/ND-CP dated May 31, 2023 to adjust the MFN import tax rates for a number of goods to ensure fair treatment among Vietnam's comprehensive strategic partners.
Specifically, some car codes are reduced from 64% and 45% to the same tax rate of 32%; ethanol from 10% to 5%; Ethane is added with a tax rate of 0%; frozen chicken thighs from 20% to 15%; some food items are also proposed to be reduced including pistachios from 15% to 5%, almonds from 10% to 5%, fresh apples from 8% to 5%, sweet cherries from 10% to 5%; raisins from 12% to 5%; wood and wood products from tax rates of 20% and 25% to the same tax rate of 5%.
Notably, liquefied natural gas (LNG), the raw material for LNG power plants, will be reduced from 5% to 2%. Thus, with the expected adjustment of the MFN import tax rate, many products from markets such as the US will benefit. Currently, Vietnam has established a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership - the highest level in the diplomatic relations system with 12 countries, including the US, France, Russia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Singapore. Except for the US, 11 of these countries are already in bilateral and multilateral trade agreements and Vietnam is a member, so they enjoy preferential tariffs.
According to the Ministry of Finance's calculations, the tax reduction according to this draft Decree will reduce about 1,400 billion VND/year. However, the reduction of MFN preferential import tax on some goods is necessary, ensuring fair treatment among Vietnam's Comprehensive Strategic Partners, contributing to improving the trade balance with major trading partners, encouraging businesses to diversify imported goods, stimulating domestic consumption...
Domestic market summary from March 24 - 28
In the foreign exchange market during the week of March 24-28, the central exchange rate was adjusted by the State Bank of Vietnam to increase in the first 3 sessions of the week and decrease in the last 2 sessions of the week. At the end of March 28, the central exchange rate was listed at 24,843 VND/USD, an increase of 30 VND compared to the previous weekend session.
The USD buying price is listed at 23,651 VND/USD, 50 VND higher than the floor rate; while the USD selling price is listed at 26,035 VND/USD, 50 VND lower than the ceiling rate.
The interbank dong exchange rate during the week of March 24-28 fluctuated upward in most sessions. At the end of the session on March 28, the interbank exchange rate closed at 25,584, down 36 dong compared to the previous weekend session.
The dollar-VND exchange rate in the free market last week also followed an upward trend. At the close of the session on March 28, the free exchange rate decreased by 10 VND in both buying and selling directions compared to the previous weekend session, trading at 25,860 VND/USD and 25,960 VND/USD.
Interbank money market from March 24 to 28, interbank VND interest rates for terms of 1 month or less increased in the first 3 sessions of the week and then decreased in the last 2 sessions of the week. Closing on March 28, interbank VND interest rates were traded at: overnight 3.58% (-0.64 percentage points); 1 week 4.46% (+0.08 percentage points); 2 weeks 4.56% (+0.06 percentage points); 1 month 4.62% (+0.08 percentage points).
Interbank USD interest rates decreased slightly in most terms last week. On March 28, interbank USD interest rates were traded at: overnight 4.30% (unchanged); 1 week 4.36% (-0.02 percentage points); 2 weeks 4.41% (-0.04 percentage points) and 1 month 4.46% (-0.03 percentage points).
In the open market from March 24 to 28, in the mortgage channel, the State Bank offered VND275,000 billion for four terms of 7 days, 14 days, 35 days and 91 days, with interest rates all maintained at 4.0%. There were VND53,094.95 billion in winning bids, of which, the 7-day term won VND34,539.42 billion, the 14-day term won VND18,555.53 billion and there was no winning bid volume in the two long terms of 28 days and 91 days. There were VND52,296.39 billion maturing last week in the mortgage channel.
The State Bank of Vietnam did not offer SBV bills for auction. There was no volume of bills maturing last week.
Thus, the State Bank of Vietnam has injected a net VND798.56 billion into the market last week through the open market channel. There are VND81,647.82 billion circulating on the mortgage channel, there are no more State Bank bills circulating on the market.
On the bond market on March 26, the State Treasury successfully bid VND11,971 billion/VND13,000 billion of government bonds for bid (winning rate reached 92%). Of which, the 5-year term mobilized VND100 billion/VND500 billion for bid, the 10-year term mobilized the entire VND11,500 billion for bid, the 15-year term mobilized VND250 billion/VND500 billion for bid and the 30-year term mobilized VND121 billion/VND500 billion for bid. The winning interest rate for the 5-year term was 2.15% (unchanged compared to the previous auction), the 10-year term was 2.96% (unchanged), the 15-year term was 3.05% (+0.05 ppt) and the 30-year term was 3.28% (unchanged).
On April 2, the State Treasury plans to bid VND14,000 billion in government bonds, of which VND500 billion will be offered for 5-year terms, VND12,500 billion for 10-year terms, and VND500 billion for 15-year and 30-year terms.
The average value of Outright and Repos transactions in the secondary market last week reached VND19,204 billion/session, down from VND20,026 billion/session the previous week. Government bond yields last week fluctuated slightly in terms from 5 years to 15 years. At the close of the session on March 28, government bond yields were trading around 1 year 2.08% (unchanged compared to the session at the end of last week); 2 years 2.09% (unchanged); 3 years 2.16% (unchanged); 5 years 2.30% (+0.001 percentage point); 7 years 2.67% (+0.03 percentage point); 10 years 2.96% (+0.004 percentage point); 15 years 3.16% (+0.01 percentage point); 30 years 3.41% (unchanged).
The stock market in the week of March 24-28 tended to decrease on all three exchanges. At the end of the session on March 28, VN-Index stood at 1,317.46 points, down 4.42 points (-0.33%) compared to the previous weekend; HNX-Index decreased 7.62 points (-3.1%) to 238.2 points; UPCoM-Index decreased 0.7 points (-0.7%) to 98.62 points.
Average market liquidity was quite high, reaching over VND19,656 billion/session. Foreign investors continued to net sell more than VND2,100 billion on all three exchanges.
International News
Last week, the US recorded a number of important economic indicators. First, the US Bureau of Economic Analysis announced that the country's GDP officially increased by 2.4% compared to the previous quarter in the last quarter of 2024, a slight upward adjustment compared to the 2.3% increase according to the second preliminary report, slowing down compared to the 3.1% increase in the third quarter of 2024. Thus, the US GDP increased by 2.4% for the whole year of 2024, without any adjustment.
In terms of inflation, the total PCE and core PCE consumer price indexes in the US increased 0.3% and 0.4% month-on-month in February, respectively, after increasing 0.3% in the previous month. Compared to the same period in 2024, the total PCE and core PCE increased 2.5% and 2.8% year-on-year, respectively.
Regarding the labor market, the number of initial unemployment claims in the US in the week ending March 22 was 224 thousand, down slightly from the previous week and also in line with the experts' forecast of 225 thousand. The average number of applications in the most recent 4 weeks was 224 thousand, down 4.75 thousand compared to the average of the previous 4 weeks.
In the housing market, new home sales in the US reached 676 thousand units in February, up slightly from 664 thousand in January (revised from 657 thousand in preliminary), but not meeting expectations of 682 thousand. In addition, the US pending home sales index increased 2.0% month-on-month in February, after falling 4.6% in January, higher than the forecast increase of 0.9%. Compared to the same period in 2024, the number of pending homes for sale decreased slightly by about 3.6% compared to the same period in 2024.
Next, the S&P Global survey said the US manufacturing PMI was at 49.8 points in March, down from 52.7 points in the previous month and below the forecast of 51.9 points. In contrast, the services PMI rose to 54.3 points in March from 51.0 points in February, surpassing the forecast of 51.2 points.
Finally, the Conference Board survey said that the US consumer confidence index was at 92.9 points in March, down from 100.1 points in the previous month (up from 98.3 points according to the preliminary number), and lower than the forecast of 94.2 points. This is the lowest consumer confidence level recorded in the country since 2020.
The UK also received notable economic news. According to the Office for National Statistics, the UK's GDP officially increased by 0.1% compared to the previous quarter in the fourth quarter of 2024, without any adjustment compared to the preliminary statistical results. The current account deficit in the fourth quarter of 2024 was £21 billion, larger than the £12.5 billion deficit in the third quarter and at the same time exceeding the forecast deficit of £16.7 billion.
Regarding inflation, the country's total CPI increased by 2.8% year-on-year in February 2025, contrary to the forecast of continuing to move sideways at 3.0% as in January statistics. In addition, the core CPI also increased by only 3.5% year-on-year last month, cooling down compared to the 3.7% increase in January and at the same time lower than the forecast of 3.6%.
Next, UK retail sales rose 1.0% month-on-month in February, following a 1.4% increase in the previous month and against forecasts for a slight decline of 0.3%.
Finally, S&P Global said the UK manufacturing PMI came in at 44.6 in March, down from 46.9 in February and below expectations for a rise to 47.3. In contrast, the UK services PMI rose to 53.2 this month from 51.0 in the previous month, beating expectations of 51.2.
Source: https://thoibaonganhang.vn/diem-lai-thong-tin-kinh-te-tuan-tu-24-283-162043.html


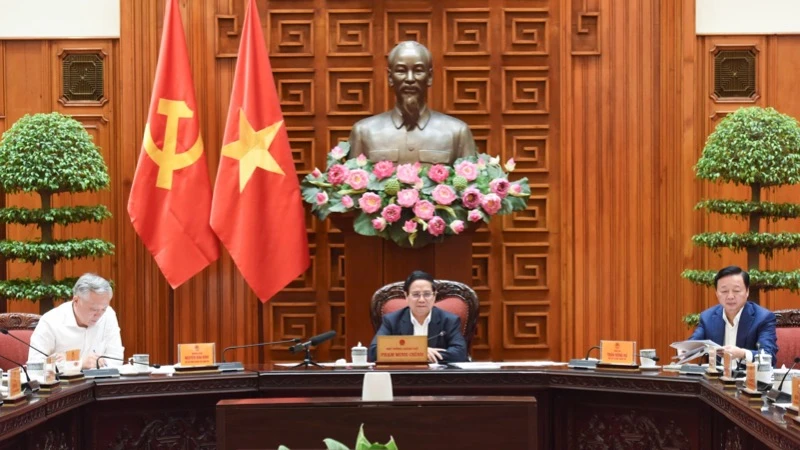
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to discuss tax solutions for Vietnam's import and export goods](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19b9ed81ca2940b79fb8a0b9ccef539a)
![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)



![[Photo] Phuc Tho mulberry season – Sweet fruit from green agriculture](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/1710a51d63c84a5a92de1b9b4caaf3e5)
















































































Comment (0)