
Mr. Cao Hoang Nam, Z & ALPHA initiative, presented at the workshop - Photo: NGUYEN BAO
On October 4, the Institute of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Hanoi Medical University, organized a workshop on social networks and mental health of Vietnamese adolescents to update some information and discuss solutions to improve mental health of adolescents.
Vietnamese people rank 20th in the world in terms of time spent using social networks.
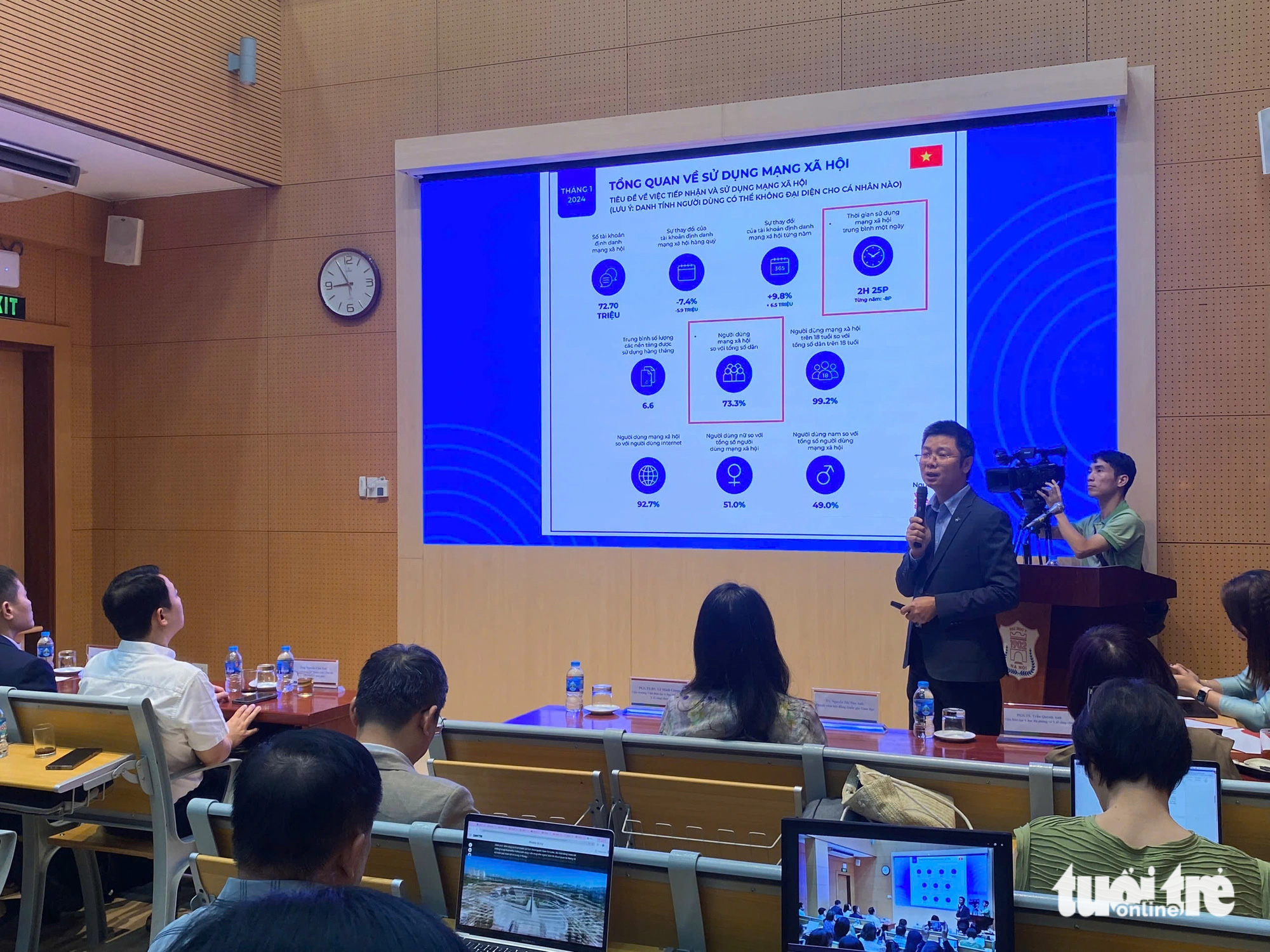
Sharing at the workshop, Mr. Cao Hoang Nam, Z & ALPHA initiative, said that in 2014, Vietnam had 37.2 million internet users and by January 2024, there were about 78.4 million people (accounting for more than 80% of Vietnam's population). Thus, in just 10 years, there has been an increase of more than 41 million internet users.
Statistics for January 2024 with users aged 16 - 64, daily internet usage time on all devices in Vietnam averages 6 hours 18 minutes/day/person, especially internet usage time on mobile phones is 3 hours 30 minutes/day/person, a remarkable number.
Regarding social media access, 73.3% of the population uses social media, with an average time spent on social media of 2 hours and 25 minutes per day per person (Vietnam's social media usage time ranks 20th in the world, with Kenya at the top with 3 hours and 43 minutes).
Facebook is the most used social networking platform in Vietnam with 89.7%, Zalo 88.5%, TikTok 77.8%.
Statistics in January 2024, 96.8% of people aged 16 - 64 years old access websites, chat and messaging applications, and 96.6% access social networks.
The top 5 main purposes for using the internet include keeping in touch with friends and family, searching for information, keeping up with news and events, watching videos, TV shows or movies, accessing and listening to music online.
Previously, UNICEF's 2022 survey on daily internet use among adolescents and children showed that 82% of 12-13 year olds used the internet, while 93% of 14-15 year olds used it.

Psychology students at Hanoi Medical University attend the conference - Photo: NGUYEN BAO
Social networks make it difficult for young people to get out once they're in.
Mr. Nam said that the benefits of social networks cannot be denied because there are "too many great benefits", however, for nearly 20 years, the negative aspects of social networks have rarely been discussed, especially the negative aspects of social networks on the mental health of teenagers and children.
According to Mr. Nam, the designs of social networks have affected users' psychology.
Firstly, social networks design like and comment functions, which impact the endogenous dopamine production mechanism.
Second, social media is designed around the brain's reward mechanism: "variable reinforcement" or "variable reward schedule."
This causes social media users to constantly check their screens in search of “Dopamine rewards”. At the same time, the network manipulates the release of Dopamine in users, especially young users, causing them to interact repetitively like a computer gambler or gamer.
In particular, social networks do not disclose the algorithms used for design, which can create an addictive cycle of engagement.
Third, social networks use their own user data to refine content, track and record behavior, and use that same data to refine and enhance features.
Fourth, design the “like - like” feature and social comparison so that users constantly check the number of likes, increasing the frequency of subsequent postings. If a post is rejected, or feels rejected after being posted with few likes on social networks, it can lead to depressive symptoms, increasing over time.
Fifth, the “notification” feature to continuously promote user engagement by sending notifications to young users. Social networks cause young users’ smartphones to generate audio-visual and tactile alerts that distract and interfere with young users’ educational activities and sleep time.
Sixth, “infinite scroll” and autoplay videos make it difficult for young users to exit because there is no natural end point for the display of new information.
Seventh, visual filters, body dissatisfaction may be associated with increased symptoms of mental health conditions and may lead to a higher risk of developing eating disorders.
According to Dr. Nguyen Thi Mai Huong, Institute of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Hanoi Medical University, when teenagers use social networks, it will affect the frontal lobe, associated with remembering details, planning and arranging work according to priority, thus causing teenagers to lose the ability to set priorities in life.
As a result, spending time online is the priority, and daily life tasks take a back seat.
According to Ms. Huong, in Vietnam, there have been a number of models, interventions, and treatments for social network addiction in adolescents such as substance addiction treatment clinics, life skills training centers to treat internet addiction - online games (however, this model has gone bankrupt and is not feasible).
Things social networks "don't say"
According to Mr. Cao Hoang Nam, there are four things that social networks are not publicizing, affecting the mental health of teenagers, including:
- Social networks are aware that young users' developing brains are vulnerable to these designs, but they choose to do so.
- Social networks hide harmful reports from users.
- Social networks allow minors to use social networks.
- Social networks collect children's data (under 13 years old) without parental consent.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/dang-anh-len-mang-xa-hoi-nhan-it-like-cung-co-the-tram-cam-20241004114316299.htm


![[Photo] Relatives of victims of the earthquake in Myanmar were moved and grateful to the rescue team of the Vietnamese Ministry of National Defense.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/aa6a37e9b59543dfb0ddc7f44162a7a7)



![[Photo] Third meeting of the Organizing Subcommittee serving the 14th National Party Congress](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/2/3f342a185e714df58aad8c0fc08e4af2)





















































































Comment (0)