Ripe bananas provide many nutrients that are beneficial to health. However, not everyone should eat a lot. Some people can eat ripe bananas, but others should limit their intake.
1. Health benefits of eating bananas
Digestive health: Bananas are considered a prebiotic food rich in fiber that helps stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut to help prevent constipation and promote a healthy digestive system.
Fuel your brain: The natural sugars in bananas are important for fueling your body, especially your brain. This makes them a great pre-workout snack.
Heart health: Potassium and magnesium in bananas can help stabilize blood pressure, protecting heart health. Potassium has been shown to help improve high blood pressure. Research shows that magnesium supplementation can reduce high blood pressure and cholesterol, which are major risk factors for heart disease.
Mental Health: Eating bananas can help people with anxiety and depression. This may be due to the B vitamins, folate, antioxidants, natural fiber, or a combination of all of these vitamins. Vitamin B6 found in bananas helps the body produce serotonin, a chemical that affects mood. Bananas also contain tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin that helps with relaxation and sleep.
A cross-sectional study of 24,673 adults in Tianjin, China, examined the association between banana consumption and depressive symptoms in adults. Results showed a negative association between moderate banana consumption and depressive symptoms in men. In women, high banana consumption was positively associated with depressive symptoms.
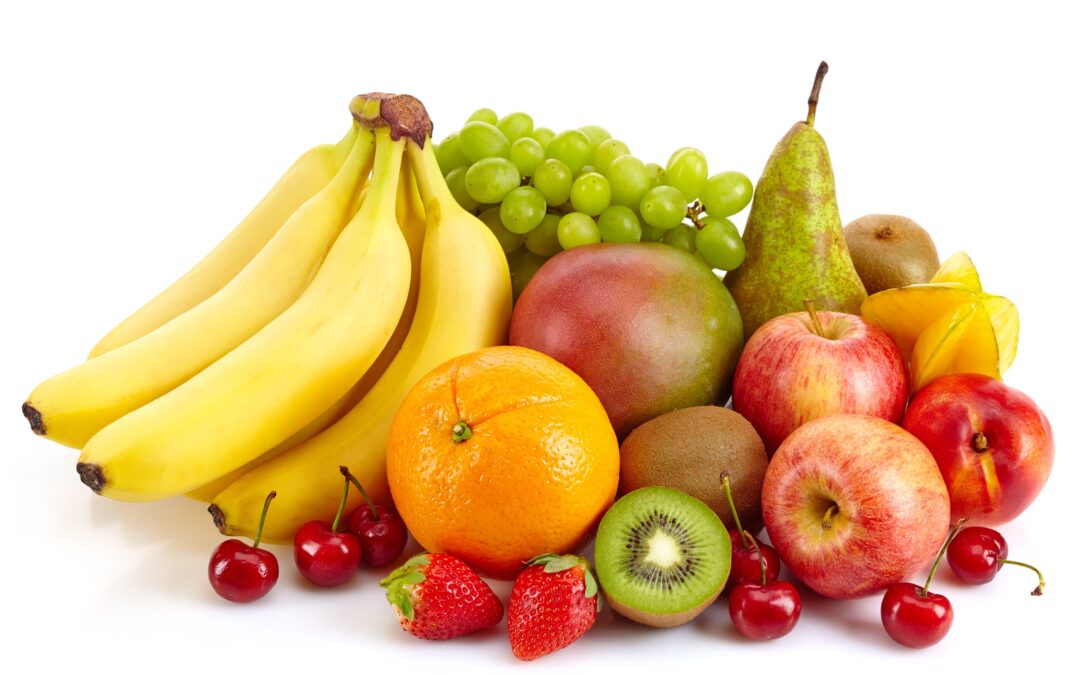

Eating bananas in combination with other fruits and vegetables is healthier.
2. How many bananas should you eat per day?
According to nutritional analysis, a medium-sized banana contains the following:
- Calories: 105
- Carbohydrates: 27 g
- Fiber: 3 g
- Sugar: 14.5 g
- Protein: 1 g
- Total fat: 0.5 g
- Sodium: 1 mg
- Potassium: 422 mg (9% Daily Value)
- Magnesium: 37 mg (9% Daily Value)
- Vitamin B6: 0.5 mg (33% Daily Value)
According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), adults should consume about two cups of fruit per day. A large banana is estimated to be one cup of fruit, so two bananas will meet the recommended daily value.
However, diversifying your fruit intake will bring more benefits. Therefore, nutritionists encourage people to eat a banana every day along with a variety of plant-based foods to increase the amount of nutritious fruits and vegetables in their diet to provide more fiber and essential vitamins and minerals.
3. People who should limit eating ripe bananas
People with diabetes
Bananas contain carbohydrates, which are essential for the body. However, for those who need to monitor their blood sugar or have diabetes, eating ripe bananas can contribute to a spike in blood sugar due to their high carbohydrate content (an average of 27 grams per banana).
The glycemic index (GI) of bananas ranges from 42 to 62, which is low or medium depending on the ripeness of the banana. Yellow or ripe bananas contain less resistant starch and more sugar than green bananas, which means they have a higher GI, causing blood sugar levels to rise more quickly when eaten.
In particular, overripe bananas (skins that have turned dark brown) are sweeter due to their higher sugar content. Studies have shown that during the ripening process, the fiber in bananas begins to break down and the complex starches are converted into simple sugars. This increases the sugar content of overripe bananas, making them a concern for people with diabetes. Therefore, people who are monitoring their blood sugar levels should consult their doctor about banana consumption.
According to MSc. Dr. Nguyen Thu Yen, an Endocrinology - Diabetes specialist, diabetics should choose to eat green bananas, unripe bananas or nearly ripe bananas, and should not eat overripe bananas. Each time, they should only eat 1 small - medium fruit or ½ of a large fruit.
Blood sugar levels should be monitored regularly. If blood sugar levels are higher than the allowed level, bananas should not be eaten.
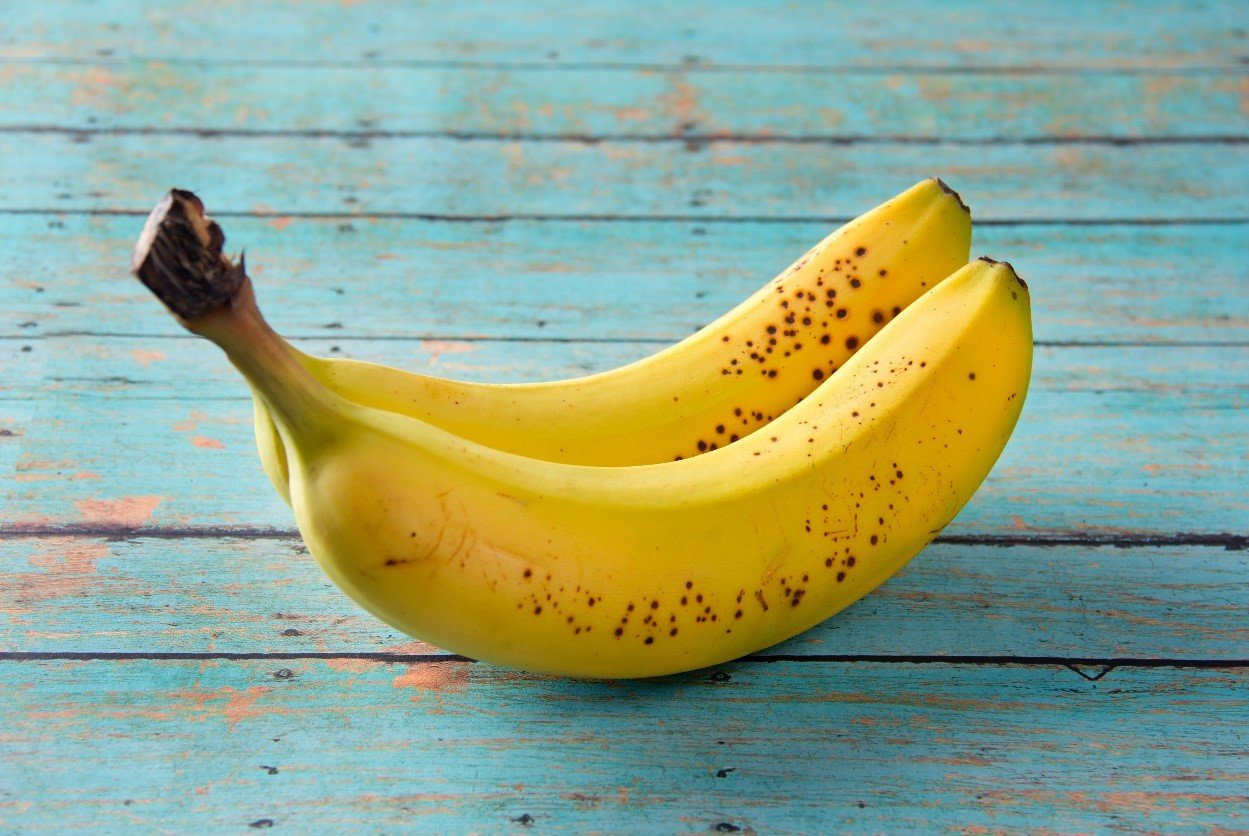

Diabetics should limit eating ripe bananas.
People with irritable bowel syndrome
Ripe bananas contain significant amounts of FODMAPs - a group of short-chain carbohydrates that are difficult to digest. Once in the intestine, FODMAPs ferment and cause unpleasant symptoms in people with irritable bowel syndrome.
As bananas break down in the intestines, they often cause excess gas. For people with normal digestive systems, this usually doesn’t cause any problems, but people with irritable bowel syndrome are more likely to experience abdominal pain due to bloating after eating bananas.
Kidney disease
Bananas are rich in potassium, a mineral that is essential for the body. However, for people with kidney disease, the kidney's ability to excrete potassium is limited, consuming too much potassium can lead to hyperkalemia. Therefore, you should limit your consumption of this fruit.
Diabetics who have chronic kidney disease or are taking potassium-sparing diuretics should not eat bananas because bananas contain a lot of potassium which can make the disease worse.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/3-nhom-nguoi-nen-han-che-an-chuoi-chin-172250105082447917.htm



![[Photo] April Festival in Can Tho City](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/bf5ae82870e648fabfbcc93a25b481ea)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh commends forces supporting Myanmar in overcoming earthquake consequences](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/e844656d18bd433f913182fbc2f35ec2)

![[Photo] Opening of the 11th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/f9e717b67de343d7b687cb419c0829a2)






















![[Photo] Reliving the heroic memories of the nation in the program "Hanoi - Will and belief in victory"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19ce7bfadf0a4a9d8e892f36f288e221)



























































Comment (0)