In addition to some medical conditions, headaches are sometimes caused by allergies, stress, drinking too much alcohol or eating sweets regularly.
Headaches are a very common condition, usually occurring in the head and face. The pain occurs on one or both sides of the head, in a specific location or spreads. Below are common causes.
Allergy
Food allergies, environmental substances (dust, pet dander, pollen, etc.) often cause runny nose, sneezing, itchy or watery eyes, and headaches. According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, allergies cause swelling in the sinus cavities due to blocked sinus openings and increased pressure, leading to sinus headaches.
Dehydration
Dehydration from exposure to high temperatures or cold, dry air can lead to headaches. Dehydration causes the brain to shrink, putting pressure on the nerves. Dehydration headaches often develop along with dizziness, excessive thirst, and dry mouth. The pain is in one spot or all over the head, and is often dull but sometimes throbbing.
Headaches usually go away with adequate hydration, rest, and pain medication. If signs of severe dehydration such as confusion, fatigue, or muscle weakness appear, seek medical attention.
Drug abuse
People who overuse pain medications may develop rebound headaches. These headaches may develop after taking pain medications more than 10 to 15 days a month, depending on the medication.
Stress
Stress causes the body to release chemicals in the brain that affect the blood vessels inside the head, a condition called a tension headache. According to the American Migraine Foundation, a tension headache can last 30 minutes and occur for up to a week. Deep breathing or meditation may help.
Covid-19, cold, flu
Headaches are common symptoms of Covid-19, colds and flu due to the body's inflammatory response to the virus. Pain that causes pressure in the head and gets worse when coughing or sneezing can be caused by Covid-19. Vaccination reduces the risk of Covid-19 and flu. To prevent colds, wash your hands often, keep warm and avoid contact with sick people.

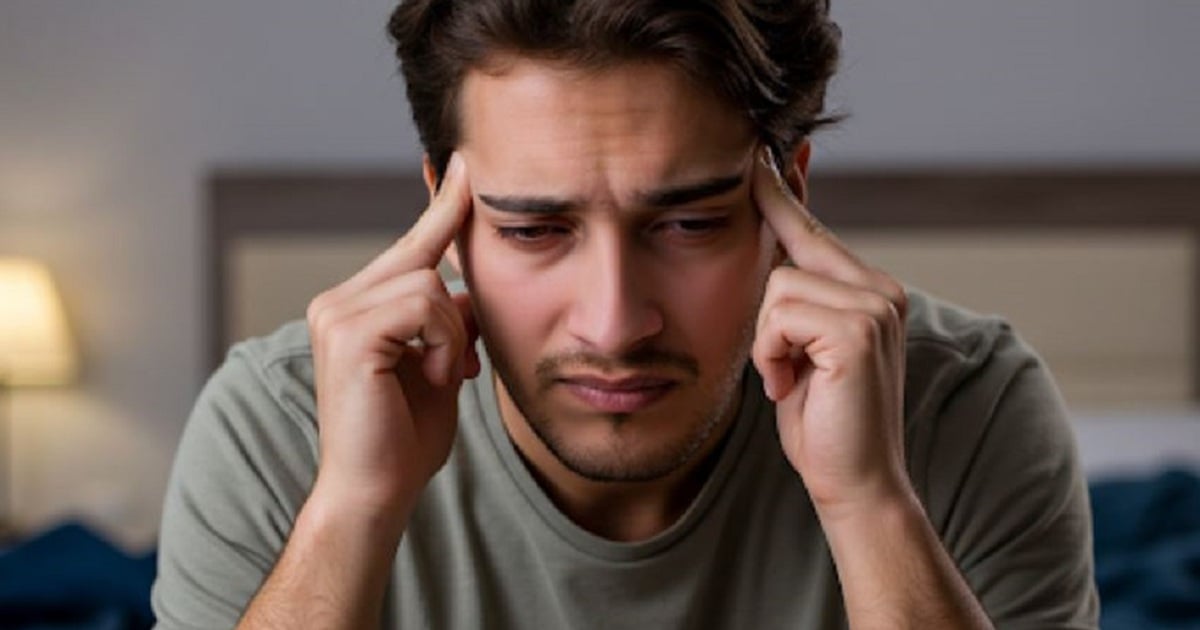
Headaches can be dull or severe like a "hammer". Photo: Freepik
Sleeping too much or too little
According to the American Migraine Foundation, not getting enough sleep or getting too much sleep can both trigger headaches. This is because poor sleep habits cause changes in the brain.
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder. Reduced oxygen flow to the brain leads to headaches upon waking. People with sleep apnea are at risk of heart disease and stroke.
Chatter
If you wake up with a dull headache and jaw pain, your headache may be caused by grinding your teeth while you sleep. Poor sleep and stress can also cause teeth grinding. Using a mouth guard can help protect your teeth and prevent headaches.
Caffeine
Consuming certain drinks such as tea, coffee, and soft drinks that contain caffeine is also a cause. Gradually reduce your caffeine intake to reduce headaches. Do not cut it out suddenly if you are used to drinking it every day because the symptoms may get worse.
Smoke
Smoking and inhaling cigarette smoke cause headaches and migraines in many people. This is because the nicotine in tobacco products is an addictive substance that causes these headaches.
According to the National Headache Institute, the nicotine in cigarettes constricts blood vessels in the brain, causing less blood flow to the brain and surrounding tissues. Nicotine stimulates nerves that transmit pain signals.
Drink alcohol
Drinking too much alcohol can lead to hangovers and headaches due to dehydration. Because alcohol has a diuretic effect, it causes the drinker to urinate more, leading to dehydration. Drinking plenty of water or non-alcoholic beverages helps to stay hydrated and regulate the amount of alcohol consumed.
Eat lots of sweets
An allergy to artificial sweeteners in sweets can also cause headaches. Consuming too much sugar or refined carbohydrates can cause reactive hypoglycemia, which causes headaches, shaking, sweating, and nausea. This is because the body produces too much insulin in response to the high sugar intake, causing blood sugar to drop. Reactive hypoglycemia usually occurs about 2-4 hours after eating.
Cutting down on sugar and refined carbohydrates and replacing them with foods containing slower-digesting carbohydrates can help prevent this condition.
Mai Cat (According to Everyday Health )
| Readers ask neurological questions here for doctors to answer |
Source link




![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/4e8fab54da744230b54598eff0070485)
![[Photo] Reception to welcome General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/9afa04a20e6441ca971f6f6b0c904ec2)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/893f1141468a49e29fb42607a670b174)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam holds talks with General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/b3d07714dc6b4831833b48e0385d75c1)




















































































Comment (0)