Key Health Benefits of Tuna
Helps prevent heart disease
Because it contains omega 3, a healthy fat that has anti-inflammatory effects, tuna helps control levels of "bad" cholesterol, LDL, in the blood, preventing heart diseases such as heart attacks, arrhythmias and heart failure.
Promotes muscle mass gain
Because it is rich in protein, tuna is a fish that works in the formation of muscle cells, promoting muscle mass gain and preventing muscle loss.
Prevent anemia
With optimal amounts of vitamin B12, a nutrient involved in the formation of blood cells, tuna helps prevent megaloblastic anemia, a type of anemia in which the bone marrow produces larger-than-normal red blood cells and smaller white blood cells and platelets.
Maintain nerve cell health
Tuna helps maintain nerve cell health as it is rich in vitamin B12, a nutrient that works on the functions of central nervous system cells.
Additionally, vitamin B2 found in tuna also helps balance levels of homocysteine in the body, an amino acid that, in high amounts, is linked to a higher risk of Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and cognitive decline.
Maintain thyroid health
Because it is rich in the mineral selenium, tuna helps maintain thyroid health by converting the thyroid hormone T4 to T3, regulating their levels in the body.
Therefore, tuna may help reduce the risk of thyroid problems.
Prevent osteoporosis
Because it is a fish rich in vitamin D and phosphorus, nutrients important for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the gut and maintaining bone health, tuna helps prevent bone fractures and osteoporosis.
Boost the immune system
Tuna helps boost the immune system, as it contains vitamin D, selenium and protein, nutrients that protect and improve the function of defense cells.
Maintain healthy skin
Omega 3 found in tuna is a healthy fat that helps maintain skin health by maintaining the natural protective barrier, preventing water loss and promoting skin hydration, leaving skin supple and soft.
Vitamin D, on the other hand, works by regulating the formation of keratinocytes, the cells responsible for protecting and moisturizing the skin.
Prevent eye problems
Tuna helps prevent eye problems like dry eyes and macular degeneration because it contains omega 3, a healthy fat that prevents inflammation and stimulates tear production to help prevent dry eyes.
Reduce the risk of cancer
Tuna helps reduce the risk of cancer, because omega 3 and selenium have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, preventing damage to healthy cells in the body, which can lead to tumor growth.
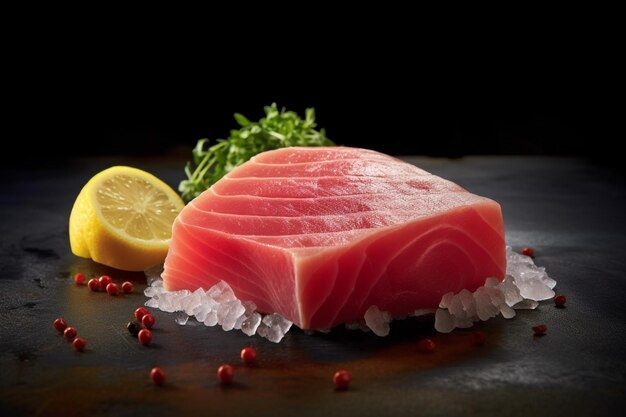 |
Classification of main types of tuna
Bluefin tuna : it is considered the "king of tuna". This type of tuna grows up to 2 meters long and can weigh up to 700 kg;
Yellowfin tuna, or white tuna: this species can grow up to 208 cm in length and weigh up to 176 kg;
Albacore tuna : it is found in all oceans, has a maximum size of 140 cm and weighs up to 40 kg.
These tunas can be sold fresh. Additionally, tuna is also sold in canned or canned form.
Is canned tuna healthy?
Canned tuna is a product made from any type of tuna, fillet or slice, and is often seasoned with water, or oil and salt, which helps preserve the food for longer.
Canned tuna may also include other ingredients, such as sauces, spices, and herbs.
In general, canned tuna is healthy, because it has good amounts of protein, omega 3, selenium and vitamin D.
However, because canned tuna can contain high amounts of sodium, frequent and large amounts of consumption can cause high blood pressure.
Therefore, it is advisable to prioritize consuming fresh tuna or even opt for canned versions that are low in sodium.
The following table contains nutritional information for 100g of fresh and canned tuna:
Ingredient | Amount in 100g fresh tuna | Amount in 100g canned tuna, in water |
Energy | 144 calories | 128 calories |
Protein | 23.3g | 23.6g |
Total fat | 4.9g | 2.97g |
Omega 3 | 1.37g | 1.05g |
Phosphorus | 254mg | 217mg |
Selen | 36.5mcg | 65.7mg |
Vitamin B12 | 9.43mcg | 1.17mcg |
Vitamin D | 5.7mcg | 2mcg |
Vitamin A | 655mcg | 6mcg |
Sodium | 39mg | 377mg |
Can pregnant women eat tuna?
Yes, pregnant women can eat tuna. However, some types of tuna contain high levels of mercury, a mineral that is toxic to the body.
Therefore, pregnant women should avoid bigeye tuna and bluefin tuna, and can only eat 170 g per week of white tuna (yellowfin tuna).
Source: https://kinhtedothi.vn/nhung-ai-khong-nen-an-ca-ngu-dong-hop.html




![[Photo] April Festival in Can Tho City](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/bf5ae82870e648fabfbcc93a25b481ea)
![[Photo] Opening of the 11th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/f9e717b67de343d7b687cb419c0829a2)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh commends forces supporting Myanmar in overcoming earthquake consequences](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/e844656d18bd433f913182fbc2f35ec2)


















![[Photo] Reliving the heroic memories of the nation in the program "Hanoi - Will and belief in victory"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19ce7bfadf0a4a9d8e892f36f288e221)



























































Comment (0)