The Luna 25 spacecraft accident was most likely caused by an engine failure, Yury Borisov, director of the Russian space agency Roscosmos, said on August 21.
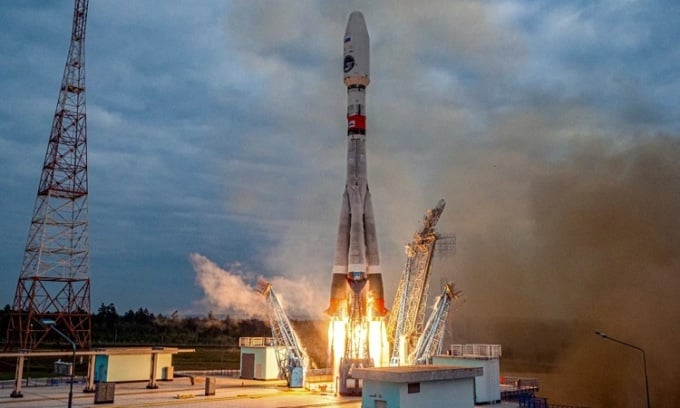

Luna 25 spacecraft launched on August 10. Photo: Roscosmos
In an interview with Russia-24, Borisov said the spacecraft changed direction and fired its engines to prepare for landing. However, the engines did not shut down as scheduled. The engines ran for 127 seconds instead of the expected 84 seconds. That was the main reason why the spacecraft crashed into the lunar surface. According to Borisov, the engine firing had been previously tested in ground simulations.
Roscosmos lost contact with the Luna 25 spacecraft on August 19. They declared the mission a failure the following day. The entire experiment was conducted in a stable radio communication zone, indicating that the communication was most likely interrupted by the spacecraft's failure. Roscosmos revealed via its Telegram channel that Luna 25 had attempted to use its thrusters to correct its trajectory before contact was lost.
The spacecraft was headed for the Moon’s south pole and was scheduled to land there as early as August 21. But attempts to restore contact with Luna 25 over the weekend failed, and Roscosmos concluded that the spacecraft crashed into the lunar surface. Roscosmos has set up a special commission to investigate the cause of the Luna 25 mission’s failure.
The lunar program's nearly 50-year hiatus also contributed to the problem, Borisov said. "Basically, we need to master all the technology again, of course at a new technical level," Borisov said.
Russia is planning more Luna missions, including Luna 26 and Luna 27, TASS reported. Luna 25 is expected to mark a major milestone in Russia's space program. The country has not landed a spacecraft on the Moon since the Soviet era. The last Luna mission, Luna 24, touched down on August 18, 1976.
The Moon’s south pole is a region of great interest to the global space community because it remains largely unexplored. It also holds water ice, a valuable resource for future deep space missions. Water ice could provide rocket fuel and even drinking water for astronauts. The Luna 25 mission is expected to land closer to the Moon’s south pole than any other mission in history. India’s Chandrayaan-3 lander is also set to land at the Moon’s south pole on August 23.
An Khang (According to CNN )
Source link



![[Photo] Phuc Tho mulberry season – Sweet fruit from green agriculture](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/1710a51d63c84a5a92de1b9b4caaf3e5)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to discuss tax solutions for Vietnam's import and export goods](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/19b9ed81ca2940b79fb8a0b9ccef539a)
![[Photo] Unique folk games at Chuong Village Festival](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/10/cff805a06fdd443b9474c017f98075a4)






















































































Comment (0)