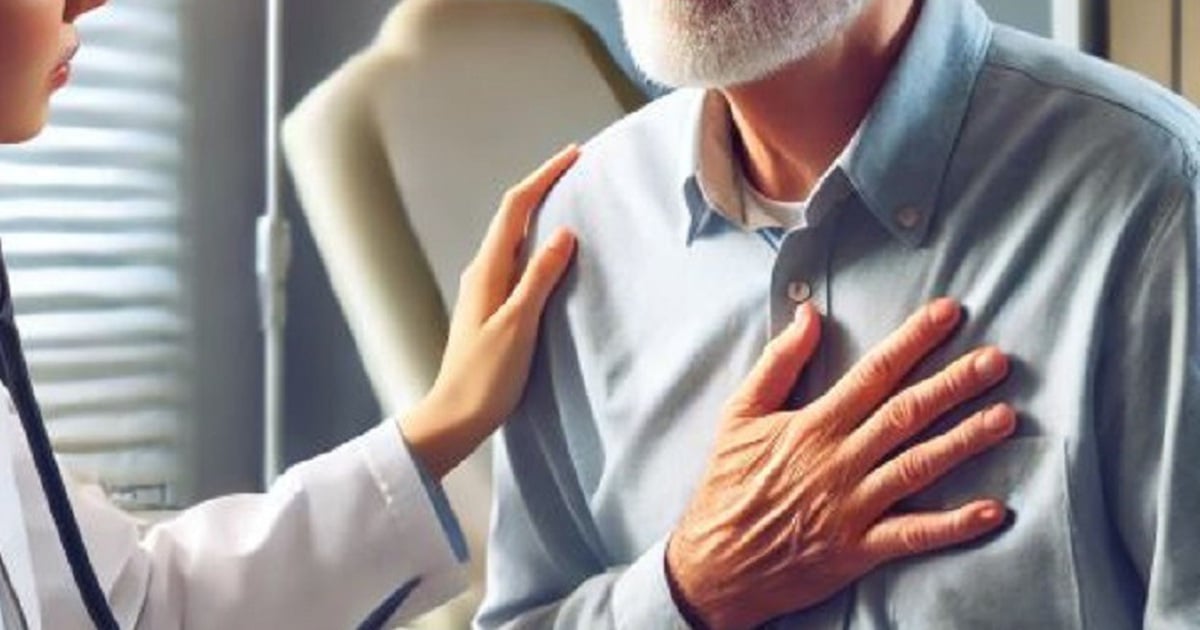
Male patient, 63 years old, had a myocardial infarction that went undetected for many days. When he arrived at the hospital, the disease progressed rapidly, causing heart failure and threatening cardiogenic shock.
Before that, the patient had chest pain, shortness of breath, and sweating. The symptoms occurred both when resting and when exerting, lasting 15 minutes and then stopping, recurring many times. He tried to endure, hesitating to go to the doctor.
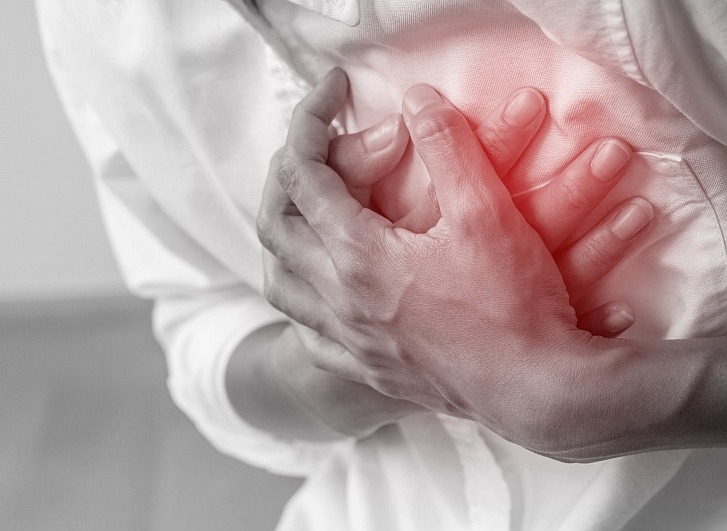 |
| Myocardial infarction is a condition in which blood flow to part of the heart muscle is reduced or completely stopped by a blood clot blocking a coronary artery. |
Half a month later, the patient suddenly had severe chest pain that did not subside, difficulty breathing, and dizziness. He was taken to the emergency room. The patient was admitted with left chest pain, a pressing pain that lasted more than 30 minutes, accompanied by sweating and difficulty breathing. The heart rate was up to 120 beats/minute.
The patient was activated by the team for emergency coronary angiography. The results showed that the blood vessels supplying the heart were severely narrowed: the circumflex artery and right coronary artery were 99% narrowed with scattered thrombosis, and the anterior interventricular artery was 95% narrowed.
Usually, acute myocardial infarction is caused by stenosis of only one coronary artery, in severe cases, all three branches are blocked. This means that the remaining stenosis (5%) of the anterior interventricular artery must "shoulder" the task of supplying blood to the heart, without the support of collateral blood vessels.
The heart does not receive enough blood supply and gradually weakens. The disease will quickly progress to acute pulmonary edema and cardiogenic shock if not intervened promptly.
Doctor Duong Thanh Trung, Cardiovascular Center, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that myocardial infarction is a condition in which blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is reduced or completely stopped by a blood clot blocking the coronary artery. This is a serious event, causing sudden myocardial ischemia and necrosis of the ischemic heart muscle.
Every year, there are 32.4 million cases of myocardial infarction and stroke worldwide. Patients who survive myocardial infarction have a risk of recurrence and a mortality rate 6 times higher than healthy people of the same age. Therefore, timely emergency care and intervention during the “golden hour” will help treat effectively, reduce complications and reduce mortality.
Coronary intervention is the golden key to quickly correcting myocardial ischemia, improving heart failure, and preventing cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest - something that medical treatments cannot do. However, each minute that passes, the heart muscle is further damaged.
Therefore, to achieve optimal effectiveness, the entire process from emergency, coronary angiography to intervention must take place at lightning speed. The "golden hour" for myocardial infarction intervention is within the first 1-2 hours when the patient first experiences chest pain, helping to limit myocardial death, reduce mortality and complications for the patient.
Stent placement only improves coronary artery stenosis, but does not treat atherosclerosis - the precursor to blood vessel blockage. Blockage can continue to occur at other locations in the artery. Therefore, after coronary stent placement, patients need to have a healthy diet and lifestyle, and have regular check-ups to prevent recurrence.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 17.5 million people die each year from cardiovascular diseases. Myocardial infarction is an emergency; if not treated promptly, the risk of death is 50%.
In Vietnam, each year about 200,000 people die from cardiovascular disease, accounting for 33% of all deaths. This rate is double the number of people who die from cancer, which is also the leading cause of death today.
According to medical experts, myocardial infarction is a dangerous acute cardiovascular event, a phenomenon in which a blood clot suddenly blocks the coronary artery (blood vessels surrounding the heart).
Doctors say that myocardial infarction occurs when there is a sudden partial or complete blockage of one or both coronary arteries. If mild, it will cause heart failure, damage to the heart muscle, if severe, it will cause an acute myocardial infarction.
Pathological results also show that up to 50% of myocardial infarction patients die before being admitted to the hospital. Some patients who are admitted to the hospital may also have a very high mortality rate.
Associate Professor, Dr. Pham Manh Hung, Director of the National Heart Institute, Bach Mai Hospital, said that patients with high blood pressure, diabetes, a history of stroke or myocardial infarction, or a family history of epilepsy are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
To protect overall cardiovascular health and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke in young people, each person needs to have a reasonable diet, limit eating fat, animal skin, liver, fast food. Actively exercise, limit alcohol and stimulants.
In particular, young people should not subjectively think that the disease only occurs in the elderly, ignoring the warning signs. Patients need to have regular health check-ups at least every 6 months, proactively preventing the risk of disease.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/dau-nguc-co-phai-dau-hieu-cua-benh-suy-tim-d227164.html


























































































Comment (0)