Transferring vocational education to the Ministry of Education and Training is a major policy of the Party and the State, creating a unified and synchronous national education system. This is also an opportunity to adjust the Education Law and the University Education Law.
TRAINING LEVEL OF VOCATIONAL EDUCATION CHANGES MANY TIMES
Along with the development of education and training, the Education Law, the Vocational Education Law (VET) and the University Education Law (UHE) were born, after a period of amendments and supplements to improve and synchronize. Particularly, the training level of VET and UHE has changed over time, shown in the table below:
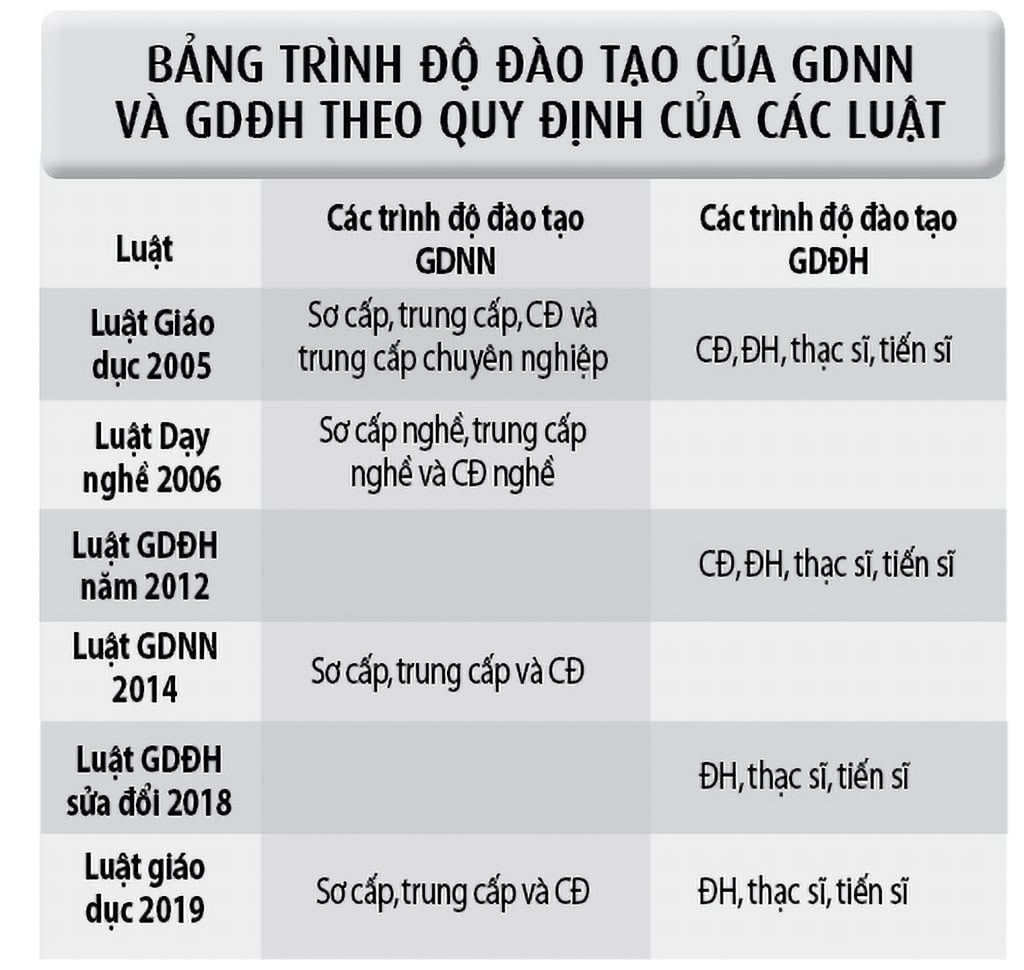
Source: Author's synthesis from the Education Law, Vocational Education Law and Higher Education Law
The above table shows that there are disagreements on the training levels of vocational education and higher education between the Ministry of Education and Training and the Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
First of all, the training levels of vocational education are inconsistent. Specifically, the 2005 Education Law stipulates that vocational education has 4 levels (primary, intermediate, college, intermediate vocational), the 2006 Vocational Training Law stipulates that vocational education has 3 levels (primary vocational, intermediate vocational, vocational college), and the 2014 Vocational Education Law and the 2019 Education Law stipulate that vocational education has 3 levels (primary, intermediate and college). This makes learners not understand how (primary, intermediate, college) and (primary vocational, intermediate vocational, vocational college) are different.
Second, the training levels of higher education are also inconsistent. The 2005 Education Law and the 2012 Higher Education Law stipulate that higher education has 4 levels (college, university, master's, doctorate), but the revised 2018 Higher Education Law and the 2019 Education Law stipulate that higher education has 3 training levels (university, master's, doctorate). This is different from the world, where most countries stipulate that higher education has 4 levels (college, university, master's, doctorate).
Third, the Law on Vocational Education considers vocational education as a separate level of education in the national education system, which is incompatible with international practice. Most countries consider vocational education to train in occupations as a training stream, integrated into other levels of education. For example, in lower secondary schools (there are 2 streams: general education is junior high school, and vocational education is primary vocational education); in higher secondary schools (there are 2 streams: general education is high school, and vocational education is secondary vocational education). Considering vocational education as a level of education to train elementary, intermediate and college levels has erased the boundary between vocational education and professional education, so the division of students after junior high school, high school and the transfer from intermediate and college levels to university has many obstacles.
Therefore, to ensure smooth student streaming and connection between levels, it is necessary to stipulate that college level belongs to higher education.

A class of students at a vocational secondary school. Currently, this school system is under the management of the Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
Vocational education and continuing education centers will be convenient
Currently, vocational education and continuing education centers are under the authority of the district-level People's Committee. The operations of these centers are carried out according to two different documents, namely Circular 05/2020/TT-BLDTBXH dated August 16, 2020 promulgating the regulations on the organization and operation of district-level public vocational education centers; and Circular 01/2023/TT-BGDDT dated January 6, 2023 regulating the regulations on the organization and operation of vocational education and continuing education centers.
Even Circular 01 of the Ministry of Education and Training shows contradictions. In Article 2, which regulates the legal status and state management of the center, it is affirmed that this is a continuing education facility belonging to the national education system, subject to the state management of continuing education of the Ministry of Education and Training; vocational education activities of the Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs; and at the same time subject to the state management of the People's Committees of provinces and centrally-run cities. This makes it very difficult for the centers to operate.
One difficulty that many directors of these centers have raised is that in recent years, the centers have not invested in vocational training equipment, because the national target program under the Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs only invests in equipment for vocational training facilities, and does not have an investment target for vocational training - continuing education centers. The main teaching and learning of these centers is continuing education classes for grades 10, 11 and 12.
Therefore, it is said that after junior high school, there are 3 streams of further study: high school, vocational education center - continuing education and vocational education facility, but in fact there are only 2 streams.
In the world, there is no vocational education center - continuing education like in Vietnam, but a vocational high school (or technical high school), which both teaches vocational skills and studies necessary cultural subjects. Vocational high school graduates are awarded a "vocational high school" diploma equivalent to a "high school" diploma, and have the right to apply to universities for applied and practical universities.
In our country, the technical high school model was piloted in Phu Tho, Quang Binh, Dong Thap and Can Tho in the period after 2001. However, after more than 10 years of implementing this model (students both study vocational training and study high school), it showed many shortcomings, leading to the pilot being stopped. The biggest shortcoming is that vocational training equipment is not invested in like vocational secondary schools and vocational colleges. The situation is completely similar to the current vocational education and continuing education centers.
Therefore, when vocational education is transferred to the Ministry of Education and Training, it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of the vocational education and continuing education centers. If they are not effective, they must stop operating and transfer the cultural teaching part to vocational secondary schools and colleges. Each province only retains a few continuing education centers to carry out the task of universalizing education.

Transferring vocational education to the Ministry of Education and Training will create a unified and synchronous national education system.
TO BE COMPATIBLE WITH THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF EDUCATION
In order to meet the requirements of international classification and comparison in the field of education, UNESCO has developed the International Classification of Education (ISCED). The first classification was adopted in 1975, called ISCED 1976. Since then, UNESCO has published two subsequent versions, ISCED 1997 and ISCED 2011. Over 160 countries and territories have applied ISCED 2011.
According to ISCED 2011, the education system is divided into 9 levels. Level 0: preschool education; level 1: primary education; level 2 (junior high school and vocational school); level 3 (high school and vocational school); level 4: post-secondary but not university; level 5: college, which is a short-term university; level 6: bachelor's degree and equivalent; level 7: master's degree and equivalent; level 8: doctorate.
In our country, in 2016, the Government issued Decision 1982/QD-TTg approving the national qualification framework. Regarding qualifications, there are 8 levels: Level 1 - Primary I, Level 2 - Primary II, Level 3 - Primary III, Level 4 - Intermediate, Level 5 - College, Level 6 - University, Level 7 - Master, Level 8 - Doctor.
According to ISCED 2011, levels 2 and 3 belong to secondary education, levels 5, 6, 7 and 8 belong to higher education, while Vietnam considers level 5 (college) to belong to vocational education. At the same time, level 4 in ISCED 2011 is very diverse, with many different levels but is not university, while according to Vietnam's regulations, level 4 is intermediate.
Therefore, to be compatible with international education classification, to facilitate the recognition of Vietnamese degrees by other countries and the easy transfer of labor between Vietnam and other countries, it is necessary to amend and supplement the Education Law as follows:
Amending the 2019 Education Law to regulate the college training level under higher education.
It is necessary to review and re-evaluate the model of vocational education and training centers, and should convert this model into vocational high schools or technical high schools like many countries.
Compulsory education should be regulated for 9 years as in the spirit of Resolution 29-NQ/TW to improve the quality of education at all secondary levels; when vocational education is transferred to the Ministry of Education and Training, there will be better conditions for student streaming after secondary school.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/chuyen-giao-duc-nghe-nghiep-ve-bo-gd-dt-co-hoi-dieu-chinh-luat-giao-duc-185241227211536304.htm


![[Photo] Closing of the 4th Summit of the Partnership for Green Growth and the Global Goals](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/c0a0df9852c84e58be0a8b939189c85a)
![[Photo] Promoting friendship, solidarity and cooperation between the armies and people of the two countries](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0c4d087864f14092aed77252590b6bae)
![[Photo] The beauty of Ho Chi Minh City - a modern "super city" after 50 years of liberation](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/18/81f27acd8889496990ec53efad1c5399)

![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper announces the project "Love Vietnam so much"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/362f882012d3432783fc92fab1b3e980)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with outstanding workers in the oil and gas industry](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/1d0de4026b75434ab34279624db7ee4a)


























![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives French Ambassador to Vietnam Olivier Brochet](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/49224f0f12e84b66a73b17eb251f7278)





























































Comment (0)