Skin cancer is a malignant disease that occurs when skin cells grow uncontrollably, mainly due to the effects of ultraviolet rays from sunlight.
Skin cancer is a malignant disease that occurs when skin cells grow uncontrollably, mainly due to the effects of ultraviolet rays from sunlight.
If not detected and treated promptly, skin cancer can metastasize to other organs such as bones, liver, lungs, brain... and endanger life. So is skin cancer hereditary?
 |
| Skin cancer is a malignant disease that occurs when skin cells grow uncontrollably, mainly due to the effects of ultraviolet rays from sunlight. |
Is skin cancer hereditary? According to Dr. Ngo Tuan Phuc, Oncology Department, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, most cases of skin cancer diagnosed are not related to genetic syndromes or family history of the disease. The leading cause of skin cancer is ultraviolet rays from sunlight.
Ultraviolet rays can cause DNA damage in skin cells. Normally, the body is able to repair this damage on its own.
However, if UV exposure is prolonged and frequent, DNA damage may not be repaired, leading to abnormal changes in genes that control cell growth and division (tumor growth genes and tumor suppressor genes), which in turn lead to cancer. These changes are called acquired mutations or genetic alterations.
Although rare, a small number of skin cancers are linked to family genetics, such as: Gorlin syndrome (basal cell nevus syndrome).
This is a rare syndrome, associated with changes in the PTCH1 gene. People with this syndrome often have multiple basal cell carcinoma lesions and abnormalities of the nervous system, eyes, and bones. About 70% of people with this syndrome have a family history of the disease, while 30% are due to an acquired gene mutation.
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP). This rare condition is caused by a genetic mutation in the XP gene (ERCC), which causes abnormalities in the DNA repair process.
People with xeroderma pigmentosum have poor DNA repair and are susceptible to damage from UV rays, increasing their risk of skin cancer, especially in sun-exposed areas.
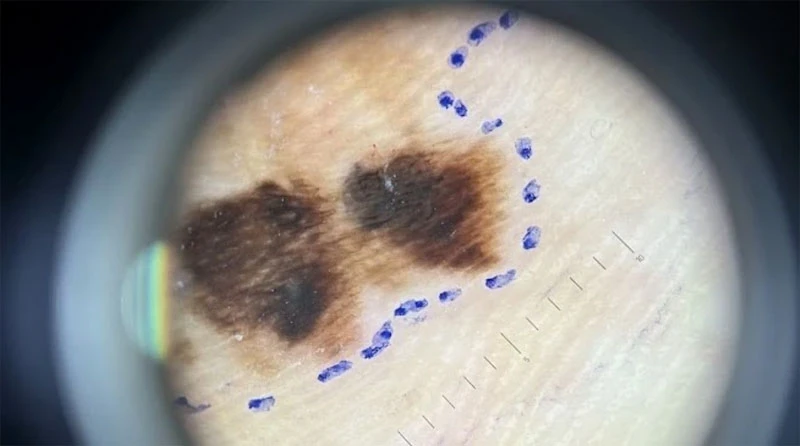
Melanoma: Some cases of melanoma are linked to genetics, such as abnormal changes in the CDKN2A (p16), CDK4, and BAP1 genes.
Merkel cell skin cancer: This is a rare, dangerous cancer that spreads quickly. The main causes include exposure to ultraviolet rays, infection with the Merkel cell polyoma virus, and a weakened immune system.
Kaposi sarcoma and cutaneous lymphoma: These diseases can present with skin lesions, such as brown or red lumps or patches that appear on the face, legs, arms, or genitals.
Who is at risk for skin cancer? The risk of developing skin cancer depends on many factors, including being fair-skinned or having light-colored skin, red or blond hair, or light-colored eyes.
People with many moles that are unusual, asymmetrical, have irregular borders, different colors (brown, black, red), or are larger than 0.6 cm in diameter.
People who are regularly exposed to coal or arsenic compounds, work outdoors, or have had sunburn. People with weakened immune systems or who are taking immunosuppressive drugs (such as after an organ transplant).
People who smoke, which increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma, especially on the skin of the lips. People with a family history of rare genetic diseases, such as Gorlin syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum.
To reduce the risk of skin cancer, everyone should avoid direct exposure to sunlight, especially between 10am and 2pm, when UV rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Apply liberally to all areas at least 10 minutes before going outside and reapply every 2-3 hours.
Cover your body with sunscreen, wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and masks. Get regular health checkups every 6 months, especially if you are at high risk of skin cancer.
Build a healthy lifestyle: eat a balanced diet, add lots of green vegetables and fruits, limit fat, avoid smoking, drinking alcohol and staying up late.
Control your weight and maintain regular physical activity. Be proactive in understanding your family history: if you have a relative with skin cancer, you should consult your doctor for advice and genetic testing if necessary.
Most cases of skin cancer are not linked to genetics or family history. However, a small number of cases do have a genetic component, especially melanoma.
For people with a strong family history of skin cancer or unusual skin lesions, they should consult a doctor and undergo genetic testing to determine their risk of developing the disease.
Preventing and protecting your skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays is the most effective way to reduce the risk of skin cancer, while maintaining a regular health check-up routine helps detect and promptly treat dangerous diseases.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/nhung-ai-co-nguy-co-mac-ung-thu-da-d229837.html




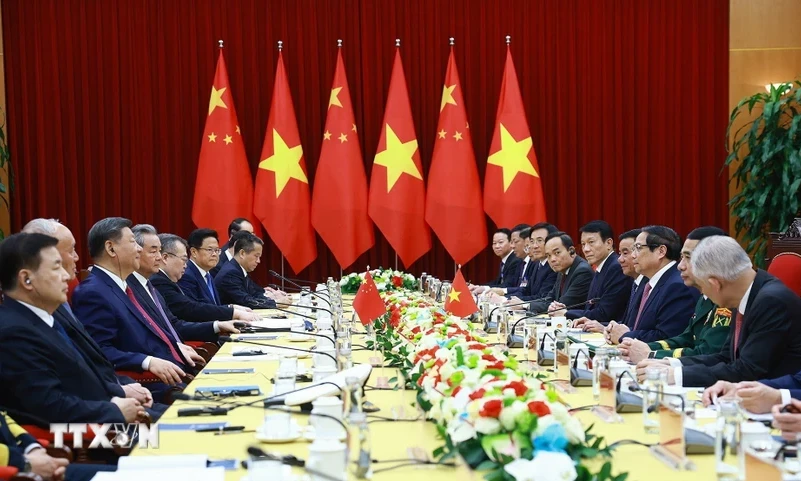
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/893f1141468a49e29fb42607a670b174)
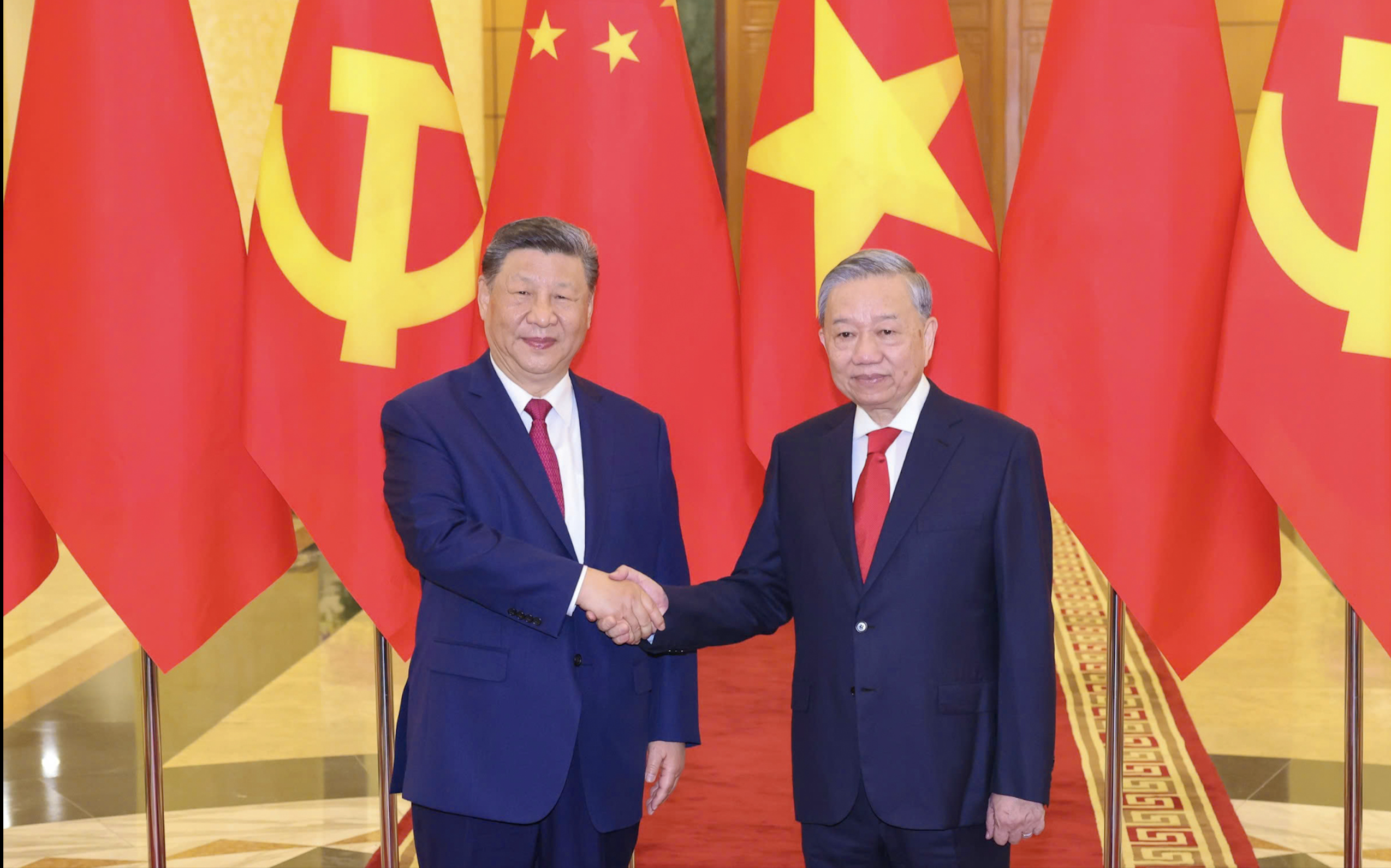
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam holds talks with General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/b3d07714dc6b4831833b48e0385d75c1)
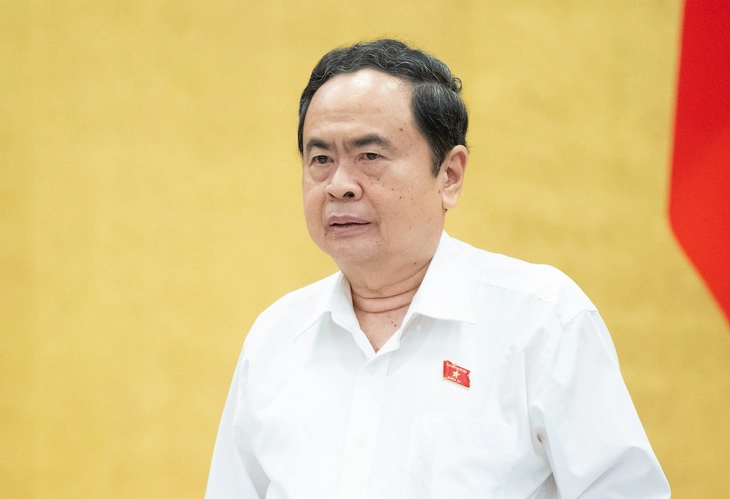
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man meets with General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/4e8fab54da744230b54598eff0070485)
![[Photo] Reception to welcome General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/9afa04a20e6441ca971f6f6b0c904ec2)








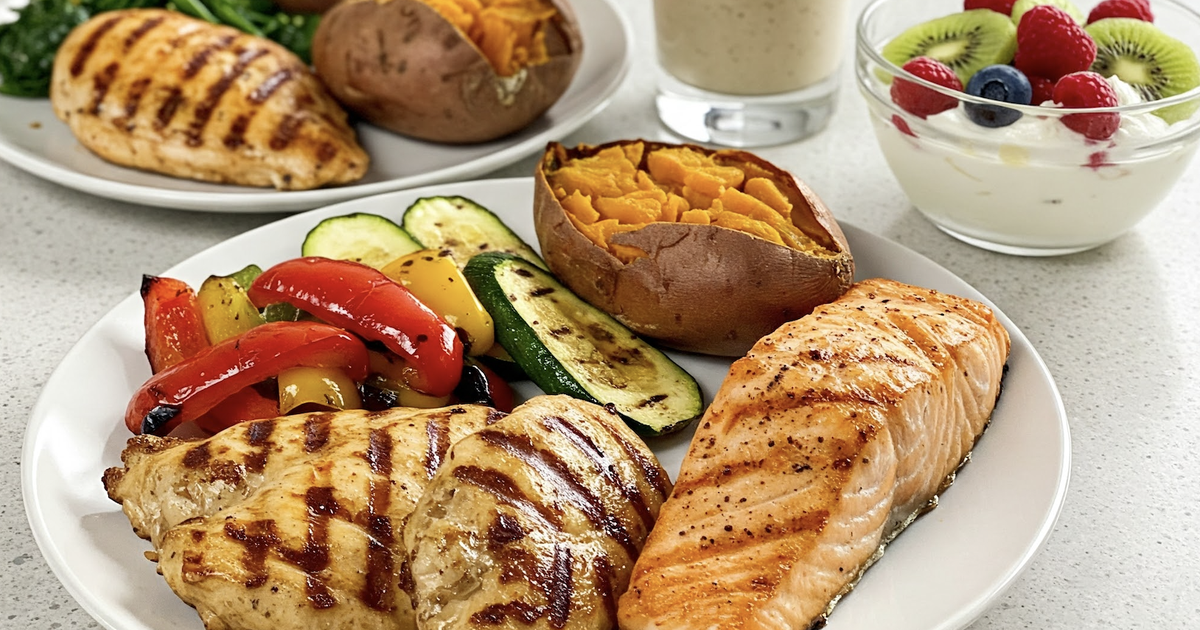






































































Comment (0)