Kaspersky reports on a malware on the App Store hidden in suspicious apps that contains code that can read the contents of iPhone screenshots.
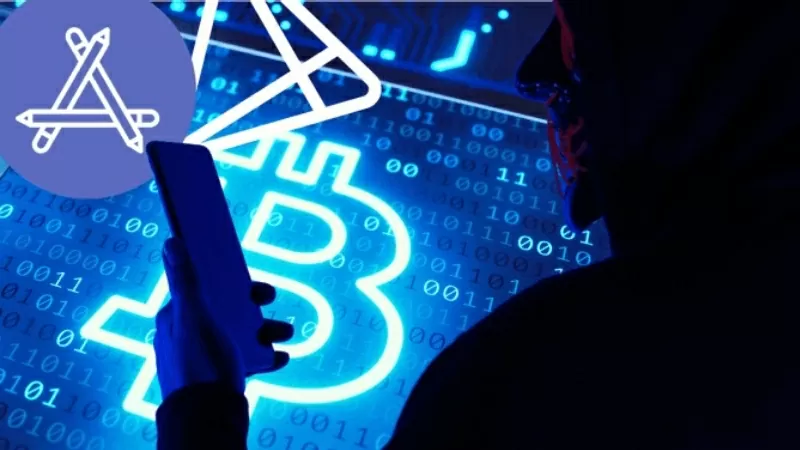 |
The first malware capable of reading screen content on iOS has appeared |
The iPhone malware, dubbed “SparkCat,” uses optical character recognition (OCR) technology to scan and extract sensitive information from iPhone screenshots. This means that any important data that users save by taking screenshots, such as passwords, banking information, or cryptocurrency wallet recovery phrases, can be collected without their knowledge.
According to Kaspersky, the malware targets cryptocurrency-related apps, with the primary goal being to identify recovery phrases for digital wallets. If successful, the attacker could take control and steal digital assets, including bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. The discovery of SparkCat raises serious concerns about data security on iOS, especially since it is one of the first malware that can directly exploit content on the screen of an Apple device.
These apps contain a malicious module that integrates an OCR plugin that uses Google's ML Kit library to recognize text in photos on iPhones. When it detects a photo related to a cryptocurrency wallet, it automatically sends the data to an attacker-controlled server.
According to Kaspersky's Cyber Threat Research Center, SparkCat has been active since March 2024 and is an extension of a malware that targeted Android and PCs in 2023 that has now appeared on iOS. Kaspersky also found several apps on the App Store, including ComeCome, WeTink, and AnyGPT, that contained the OCR spyware. However, it is unclear whether this was an intentional act by the developer or the result of a supply chain attack.
The infected apps would request access to the user’s photo library after installation. If granted, they would use OCR technology to scan and sort images to find relevant text. Some of the malware-infected apps are still on the App Store and appear to be targeting iOS users in Europe and Asia.
While the primary goal of these apps is to steal information related to cryptocurrency wallets, Kaspersky warns that the malware is versatile and can be used to access other sensitive data in screenshots, including passwords. In addition to affecting iOS, the malware has also appeared on Android apps. Therefore, Kaspersky recommends that users avoid storing screenshots containing important information to reduce the risk of being attacked.
Source























































Comment (0)