The habit of sharing eating utensils, dipping sauces, etc. of Vietnamese people has made it easy for HP bacteria to spread within the family.
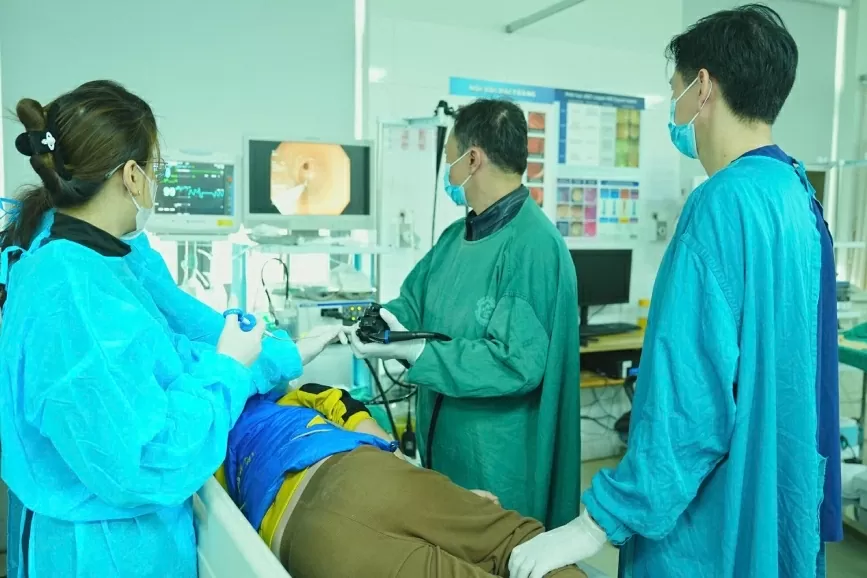 |
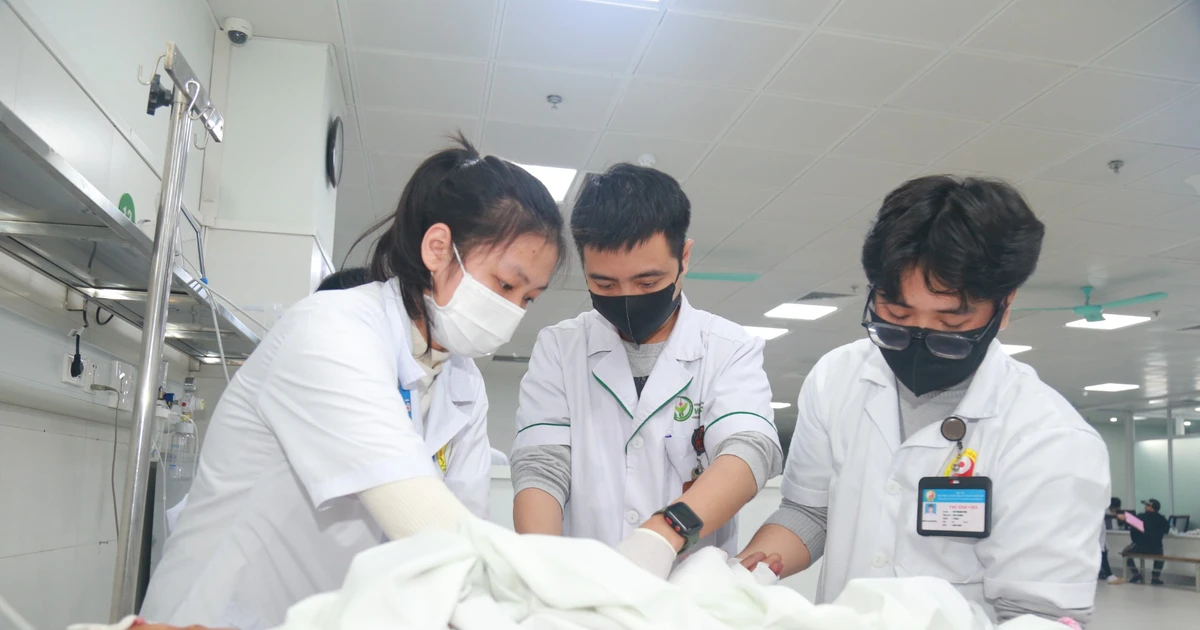
HP bacteria are highly contagious in families, and are also the main cause of stomach and duodenal diseases, including stomach cancer. In the photo, a doctor performs a gastroscopy on a patient. (Photo: The Anh) |
Ms. BH (27 years old, Long Bien, Hanoi) came to Bach Mai Hospital (Hanoi) for examination with symptoms of epigastric pain, loss of appetite, and abdominal distension. Initially, the patient bought probiotics to take but they were not effective, so she went to the hospital for examination. The endoscopy doctor discovered that her stomach lining was edematous, congested with many inflammatory nodules... A quick test gave a positive result for HP bacteria ((Helicobacter Pylori).
Previously, Ms. Hanh’s family was also found to carry this bacteria, and after treatment, it relapsed. The woman is worried that this bacteria can cause stomach cancer.
NTH (12 years old, Hanoi) had a dull abdominal pain in the epigastric region, especially after eating, which usually went away on its own. Recently, the child's abdominal pain increased, accompanied by frequent belching, heartburn, and vomiting after eating. The family took H. for a check-up.
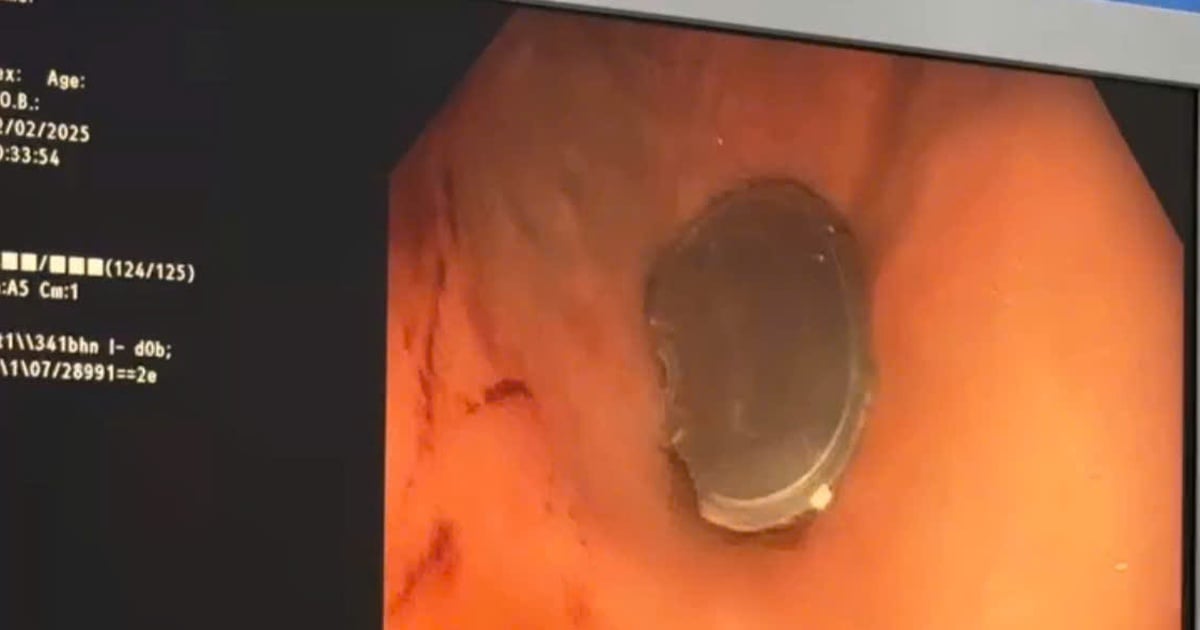
At the hospital, the endoscopy image of baby H. showed rough, edematous mucosa at the antrum and prepyloric position. The duodenum had two large symmetrical ulcers, the base of the large, deep ulcers, the base covered with white pseudomembrane. Accompanied by a positive HP bacteria test result.
The doctor concluded that baby H. had gastritis - duodenal ulcer, HP positive. Immediately, the child was required to be hospitalized and treated according to the regimen. The doctor advised baby H.'s whole family to do an HP bacteria test to have a suitable treatment plan.
According to Dr. Hoang Chuong, Center for Digestion - Hepatobiliary, Bach Mai Hospital (Hanoi), people infected with HP have a 6 times higher rate of stomach cancer, 8 times higher rate of atrophic gastritis, and 2.17 times higher rate of gastric intestinal metaplasia than normal people. 93% of people with gastric and duodenal ulcers are infected with HP and cause other diseases such as anemia, iron deficiency or thrombocytopenia, chronic urticaria.
HP bacteria are transmitted through many different ways such as: unsanitary food and drink, infection from medical equipment such as endoscopes, dental equipment that do not ensure sterilization process. If a family has a father or mother infected with HP bacteria, the children have a 30-50% risk of infection.
The doctor pointed out that family habits such as eating with the same spoon, fork, and sharing dipping sauce... are also factors leading to the spread of this bacteria.
According to specialist doctor Nguyen Thi Thu Hien, Digestive - Hepatobiliary Center, Bach Mai Hospital, there are currently many different ways to test for HP bacteria.
- Blood test for HP antibodies: This test has the advantage of being minimally invasive, easy to do and easy to perform. The disadvantage is that it does not know clearly whether HP bacteria are still active or not, and is prone to high false positives in people who have been infected with this bacteria.
- HP stool test: Easy to perform but prone to false positives in people taking antibiotics or other medications.
- Breath test: Minimally invasive, highly effective in clearly seeing whether HP bacteria is active or not. Disadvantages: higher cost, not suitable for people with respiratory and lung diseases.
- Gastroscopy with HP biopsy: Advantages: observing the mucosa, taking HP bacteria samples to evaluate other stomach lesions. However, this method is invasive, causing discomfort to the patient and is expensive.
Doctor Hien said that depending on each case, the doctor will give specific advice to have the most appropriate method and prescribe treatment or not.
Some people need treatment to kill HP bacteria such as:
- People with gastric ulcers accompanied by HP bacteria infection.
- People who are positive for HP bacteria and have relatives with digestive tract cancer such as father, mother, brothers, and sisters.
- People with atrophic gastritis.
- Smokers, people taking other anti-inflammatory pain relievers such as osteoarthritis drugs.
Source
































Comment (0)