The Clean Economy and Fair Economy Agreements, two of the four main pillars of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF), entered into force on October 11 and October 12, respectively.
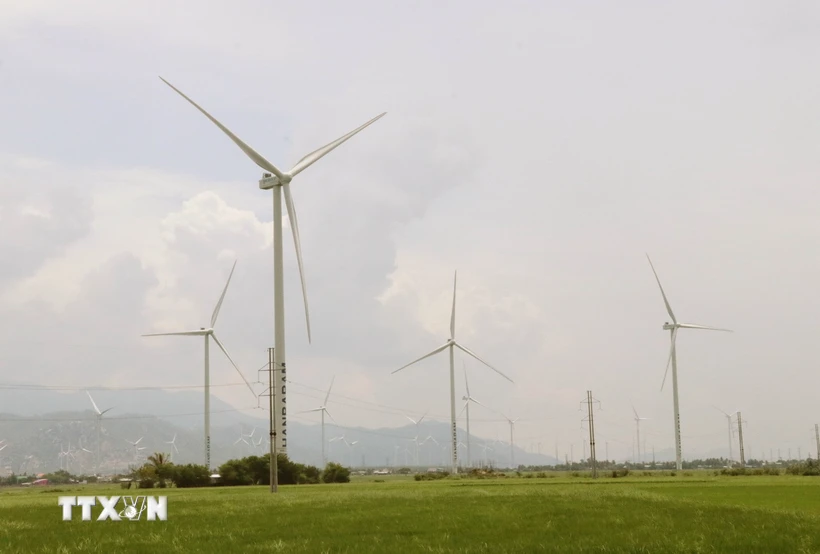

Kyodo News Agency reported on October 12 that the Clean Economy Agreement and the Fair Economy Agreement, two of the four main pillars of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF), entered into force on October 11 and October 12, respectively.
This opens up opportunities for stronger cooperation among member countries towards sustainable economic and trade development based on equity and clean energy.
The Clean Economy Agreement includes provisions for the 14 IPEF member countries to work towards accelerating the energy transition through efforts such as developing hydrogen energy, increasing the deployment of sustainable aviation fuels and trading clean electricity.
The Fair Economic Agreement also includes provisions to prevent corruption and improve transparency and efficiency in tax administration, such as strengthening whistleblower protections and introducing provisions to punish illegal activities in government procurement processes.
IPEF members completed discussions on the two agreements in November 2023 at the 2023 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Summit Week in San Francisco, USA.
Previously, the agreement on strengthening supply chains also took effect in February 2024, while the final agreement on trade is still under discussion and member countries still have many differences on the issue of digital trade.
The administration of US President Joe Biden announced the IPEF in Tokyo in May 2022, aiming to strengthen economic ties with countries in the Indo-Pacific region.
Fourteen countries participated in the negotiations, including the United States, South Korea, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, India, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines, Singapore, Brunei and Fiji.
The IPEF economic framework is divided into four pillars: trade, supply chains, clean economy and fair economy. Accounting for 40% of global Gross Domestic Product (GDP), IPEF is a new generation trade agreement that does not include tariff reduction commitments./.






































Comment (0)