The issue of Vietnam's press and media economy has never been as hot, complicated and difficult as in recent years. Both the press and policy makers have discussed many orientations, models and methods to solve the problem.
However, the difficult problem still seems to have no satisfactory answer. The results achieved have only touched on some aspects of the policy mechanism, the proposed opinions seem to have only summarized some external reference models. We have not really frankly mentioned the nature, and are even avoiding the basic bottlenecks that hinder the development of the press and media economy. That bottleneck is a principle, like a "golden ring" that needs to be "chanted" to loosen.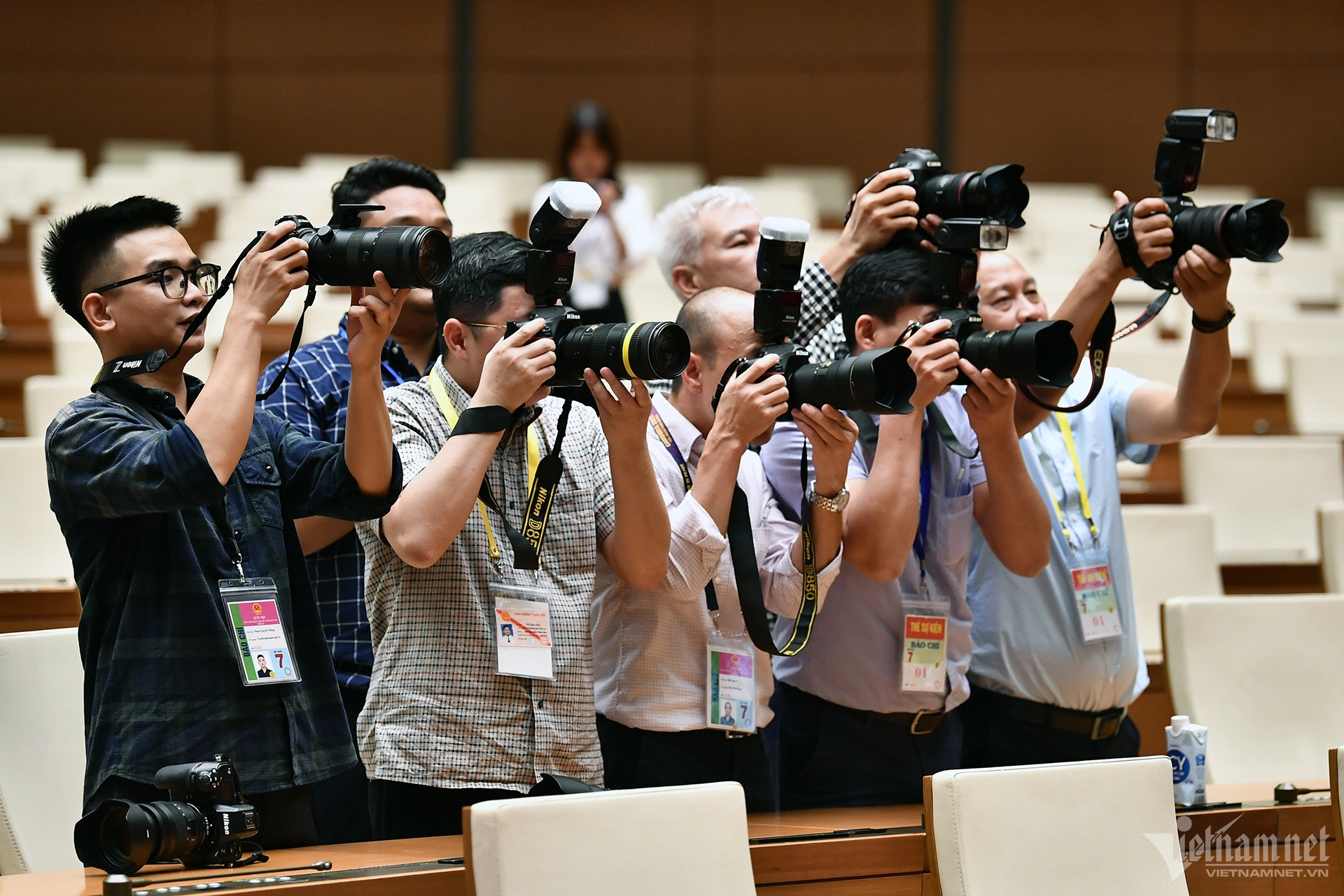 
 The impact of scientific and technological achievements, especially digital technology and artificial intelligence, has been a factor promoting the division of labor and specialization of journalism and media to an unprecedented level. In fact, a division of labor has been formed between departments such as: Units specializing in research and development (for example: idea creators, program format providers or technological innovations in production processes); Units specializing in the production of each content component (Media companies specializing in the production and supply of documentaries, special programs, reports, etc.), equipment suppliers (companies specializing in selling or renting cameras, post-production tables, signal transmission lines, storage devices, digital content distribution infrastructure, etc.), production logistics (companies with sound, lighting, stage equipment, etc.) or service businesses (advertising agencies, sponsorship campaigns, media services, etc.). The economic links between the elements in this chain are increasingly close, increasing interdependence, the production process of one element is completely integrated into a unified production process. As specialization develops, the cooperative relationship between companies, centers, and press and media agencies becomes increasingly close, and cooperation in exchanging products on the market becomes increasingly sustainable.
The impact of scientific and technological achievements, especially digital technology and artificial intelligence, has been a factor promoting the division of labor and specialization of journalism and media to an unprecedented level. In fact, a division of labor has been formed between departments such as: Units specializing in research and development (for example: idea creators, program format providers or technological innovations in production processes); Units specializing in the production of each content component (Media companies specializing in the production and supply of documentaries, special programs, reports, etc.), equipment suppliers (companies specializing in selling or renting cameras, post-production tables, signal transmission lines, storage devices, digital content distribution infrastructure, etc.), production logistics (companies with sound, lighting, stage equipment, etc.) or service businesses (advertising agencies, sponsorship campaigns, media services, etc.). The economic links between the elements in this chain are increasingly close, increasing interdependence, the production process of one element is completely integrated into a unified production process. As specialization develops, the cooperative relationship between companies, centers, and press and media agencies becomes increasingly close, and cooperation in exchanging products on the market becomes increasingly sustainable. 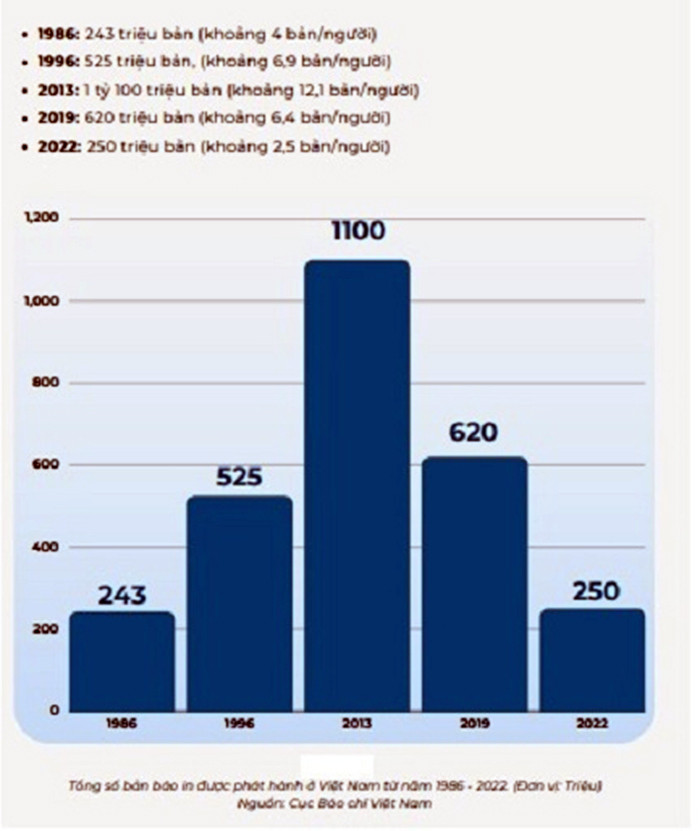 Forms of ownership of means of production in the media sector are diverse. Up to now, the process of producing a media product has not been simple in terms of both material and technical aspects. One of the main reasons lies in the technical issues, production equipment, and means of production of this sector always requiring specialized systems, high technology and large investment costs. For example, a media enterprise owns a single specialized device but with high configuration (for example: 4k-8k advertising camera) with an investment value no less than an electronic newspaper agency equipped with a small studio system to produce live audiovisual content (live stream), etc. With the rapid growth of the economy, living conditions and accumulation as well as the ability to pay for press and media products and services of the people have also increased significantly. In addition, the rapid development of new communication technologies has made many operations and jobs that required specialized equipment become common with civilian equipment, even something that each individual can do by themselves. Personal phones can record videos and take photos, computers and laptops can process images and edit movies. Along with the popularity of communication devices, the amount of specialized equipment for the communication industry, from computers, software, recording equipment, film editing, sound recording, sound systems, lighting to many specialized materials, is increasingly popular in all systems, production centers, and businesses of different scales. From there, ownership of means of content production inevitably arises due to the development requirements of the productive forces as well as the socialization process in general. The forms of ownership of means of production in this field are mainly concentrated in the following forms: state ownership (central and local press agencies), collective ownership (of unions, groups, originating from individuals voluntarily contributing), mixed ownership (joint ventures, socialized coordination between state agencies and non-state organizations) and private ownership (small production models or capitalist ownership). Up to now, Vietnam has not been able to fully count the value of ownership of means of production of non-state economic forces, but through the relationship between the ability to organize and implement high-quality media products with the quantity - quality - type of equipment and means of production, this level can be identified relatively accurately. Up to now, media enterprises in Vietnam have reached the level of producing audiovisual works according to regional and international standards, from video clips, copyrighted game shows and Western television formats, feature films, large-scale event programs such as international beauty pageants, sports competitions, cultural events...
Forms of ownership of means of production in the media sector are diverse. Up to now, the process of producing a media product has not been simple in terms of both material and technical aspects. One of the main reasons lies in the technical issues, production equipment, and means of production of this sector always requiring specialized systems, high technology and large investment costs. For example, a media enterprise owns a single specialized device but with high configuration (for example: 4k-8k advertising camera) with an investment value no less than an electronic newspaper agency equipped with a small studio system to produce live audiovisual content (live stream), etc. With the rapid growth of the economy, living conditions and accumulation as well as the ability to pay for press and media products and services of the people have also increased significantly. In addition, the rapid development of new communication technologies has made many operations and jobs that required specialized equipment become common with civilian equipment, even something that each individual can do by themselves. Personal phones can record videos and take photos, computers and laptops can process images and edit movies. Along with the popularity of communication devices, the amount of specialized equipment for the communication industry, from computers, software, recording equipment, film editing, sound recording, sound systems, lighting to many specialized materials, is increasingly popular in all systems, production centers, and businesses of different scales. From there, ownership of means of content production inevitably arises due to the development requirements of the productive forces as well as the socialization process in general. The forms of ownership of means of production in this field are mainly concentrated in the following forms: state ownership (central and local press agencies), collective ownership (of unions, groups, originating from individuals voluntarily contributing), mixed ownership (joint ventures, socialized coordination between state agencies and non-state organizations) and private ownership (small production models or capitalist ownership). Up to now, Vietnam has not been able to fully count the value of ownership of means of production of non-state economic forces, but through the relationship between the ability to organize and implement high-quality media products with the quantity - quality - type of equipment and means of production, this level can be identified relatively accurately. Up to now, media enterprises in Vietnam have reached the level of producing audiovisual works according to regional and international standards, from video clips, copyrighted game shows and Western television formats, feature films, large-scale event programs such as international beauty pageants, sports competitions, cultural events... 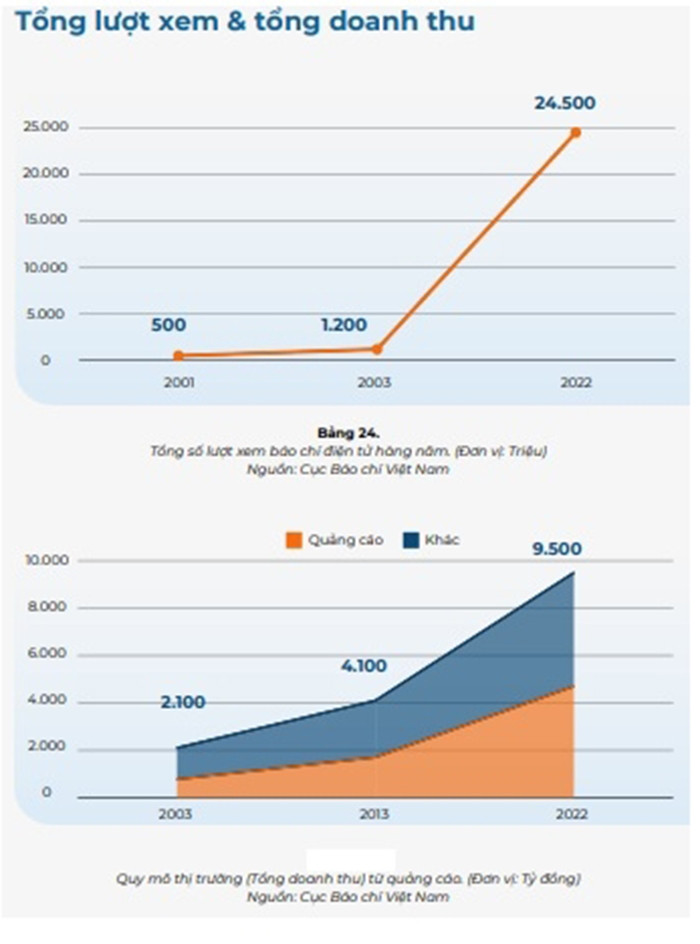 The development of new techniques and technologies and the need for enjoyment create great pressure on press and media agencies. The development of digital media technology with features and technologies far beyond the "normal imagination", technical devices with information technology platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), digital connections (internet of things)... are increasingly modern, not only meeting the needs of improving people's quality of life, but also an important driving force stimulating the development of the press and media market in terms of scale, product value, circulation of goods and increasing liquidity.
The development of new techniques and technologies and the need for enjoyment create great pressure on press and media agencies. The development of digital media technology with features and technologies far beyond the "normal imagination", technical devices with information technology platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), digital connections (internet of things)... are increasingly modern, not only meeting the needs of improving people's quality of life, but also an important driving force stimulating the development of the press and media market in terms of scale, product value, circulation of goods and increasing liquidity.  The division of labor has reached a level of specialization and exchange in the field of journalism and media has gradually moved towards the level of connection and profound influence on the regional and international scale. The trend of globalization has developed strongly, attracting and influencing all countries and markets on all continents in the world, in other words, into a "flat world". One of the factors of the globalization process is the cultural exchange between countries and ethnic groups, including the penetration of audiovisual products in many different forms. It is undeniable that the remarkable development of world journalism and media products in all genres, excluding toxic, anti-cultural - non -political elements, many international audiovisual products have become indispensable spiritual food for the Vietnamese people. The increasingly wide international exchange and cooperation process has opened the door for the media public to access a variety of products, and is also a driving force for development to break the isolation and boredom of the previously isolated information content system. Many press and media products are not only implemented by applying foreign technology and foreign formats, but also approach the separation of each pre-production and post-production process into many domestic and foreign systems to achieve the highest quality and business efficiency. International division of labor and exchange have become factors promoting the development of the Vietnamese television market, especially since the early years of the 21st century. The process of exchange and contact is a positive sign for the press and media industry in Vietnam today, but in reality, the domestic press and media economic picture still has specific factors. First of all, it shows that in some aspects, the Vietnamese press and media market has not clearly demonstrated and optimally promoted the factors of the market mechanism: because an economy wants to operate, it must first rely on the market, which means relying on the automatic machine of both supply, demand, and commodity prices, with a competitive environment, the driving force is profit. The components of this market mechanism are closely related to each other, like links in the machine. Price is the core of the market, supply and demand are the center and competition is the soul and strength of the market. To better understand the components of the market mechanism, it is necessary to learn related concepts such as: Demand for goods : The quantity of goods or press and media services that buyers are able and willing to buy at different prices at the same time has appeared and is increasing day by day. Public needs are always changing and developing over time, they cannot limit the enjoyment of information to the limited capacity framework and many years of unchanged press - media department following the target plan. Supply of goods : Is the quantity of goods or services that sellers (press agencies, press - media enterprises, domestic and international organizations and individuals) are able and willing to sell at different prices in a certain period of time. In fact, press agencies produce according to the State's orders, many contents follow a fixed mechanism, not entirely originating from the needs and preferences of the public. Media products and media agencies were previously limited by geographical space (province - city) and are no longer suitable for development with the nature and characteristics of digital media. Price: Is a factor reflecting the supply and demand relationship of specific press - media products or services. The cost of media products does not fully reflect the production cost, because there is a subsidy from the budget for propaganda and policy communication tasks. Meanwhile, private enterprises producing media products must "swim" on their own and need to calculate the selling price in comparison with production costs and the issue of profit. Competition : Is the race between enterprises, agencies, and economic organizations in the consumption of press and media goods and services, aiming to gain the highest profit. This is an inevitable part of the market economy and is also a basic factor in forming the television market. This competitiveness is reduced and eliminated with the existence of a fixed press budget. Currency, value: Is the measurement and expression of the value of press and media products. Press and media labor, press and media products with the characteristics of "creative" labor need to be measured and paid in currency and with market fluctuations. Profit : With the press and media market, profit is the income of agencies after deducting production costs, taxes, etc. and becomes one of the driving forces governing the activities of business people. Profit brings press and media businesses to production fields that attract consumers (the media public). Profit is also the factor that makes press and media businesses interested in using the most effective production techniques. When 4 problems appear: what to produce? how to produce? produce for whom? how to profit? then that is when the press and media market completes its economic goals. However, with press agencies, political goals are the most important requirement, it is difficult to harmonize both of these goals at the same time. If the profit target is not set, the customer (the governing agency) is forced to have a policy of maximum support for public service activities, but in reality that is not suitable. It is time to consider journalism as an economic sector, journalism products as specific goods, and press agencies with an operating mechanism like a business. Press agency leaders must think in the direction that their newspaper is a company in the news industry, and must find an effective business model for the editorial office to be able to thoroughly solve and create a new source of vitality for the current and future Vietnamese press economy. * Part 2: Bottlenecks hindering the development of the Vietnamese press and media economy
The division of labor has reached a level of specialization and exchange in the field of journalism and media has gradually moved towards the level of connection and profound influence on the regional and international scale. The trend of globalization has developed strongly, attracting and influencing all countries and markets on all continents in the world, in other words, into a "flat world". One of the factors of the globalization process is the cultural exchange between countries and ethnic groups, including the penetration of audiovisual products in many different forms. It is undeniable that the remarkable development of world journalism and media products in all genres, excluding toxic, anti-cultural - non -political elements, many international audiovisual products have become indispensable spiritual food for the Vietnamese people. The increasingly wide international exchange and cooperation process has opened the door for the media public to access a variety of products, and is also a driving force for development to break the isolation and boredom of the previously isolated information content system. Many press and media products are not only implemented by applying foreign technology and foreign formats, but also approach the separation of each pre-production and post-production process into many domestic and foreign systems to achieve the highest quality and business efficiency. International division of labor and exchange have become factors promoting the development of the Vietnamese television market, especially since the early years of the 21st century. The process of exchange and contact is a positive sign for the press and media industry in Vietnam today, but in reality, the domestic press and media economic picture still has specific factors. First of all, it shows that in some aspects, the Vietnamese press and media market has not clearly demonstrated and optimally promoted the factors of the market mechanism: because an economy wants to operate, it must first rely on the market, which means relying on the automatic machine of both supply, demand, and commodity prices, with a competitive environment, the driving force is profit. The components of this market mechanism are closely related to each other, like links in the machine. Price is the core of the market, supply and demand are the center and competition is the soul and strength of the market. To better understand the components of the market mechanism, it is necessary to learn related concepts such as: Demand for goods : The quantity of goods or press and media services that buyers are able and willing to buy at different prices at the same time has appeared and is increasing day by day. Public needs are always changing and developing over time, they cannot limit the enjoyment of information to the limited capacity framework and many years of unchanged press - media department following the target plan. Supply of goods : Is the quantity of goods or services that sellers (press agencies, press - media enterprises, domestic and international organizations and individuals) are able and willing to sell at different prices in a certain period of time. In fact, press agencies produce according to the State's orders, many contents follow a fixed mechanism, not entirely originating from the needs and preferences of the public. Media products and media agencies were previously limited by geographical space (province - city) and are no longer suitable for development with the nature and characteristics of digital media. Price: Is a factor reflecting the supply and demand relationship of specific press - media products or services. The cost of media products does not fully reflect the production cost, because there is a subsidy from the budget for propaganda and policy communication tasks. Meanwhile, private enterprises producing media products must "swim" on their own and need to calculate the selling price in comparison with production costs and the issue of profit. Competition : Is the race between enterprises, agencies, and economic organizations in the consumption of press and media goods and services, aiming to gain the highest profit. This is an inevitable part of the market economy and is also a basic factor in forming the television market. This competitiveness is reduced and eliminated with the existence of a fixed press budget. Currency, value: Is the measurement and expression of the value of press and media products. Press and media labor, press and media products with the characteristics of "creative" labor need to be measured and paid in currency and with market fluctuations. Profit : With the press and media market, profit is the income of agencies after deducting production costs, taxes, etc. and becomes one of the driving forces governing the activities of business people. Profit brings press and media businesses to production fields that attract consumers (the media public). Profit is also the factor that makes press and media businesses interested in using the most effective production techniques. When 4 problems appear: what to produce? how to produce? produce for whom? how to profit? then that is when the press and media market completes its economic goals. However, with press agencies, political goals are the most important requirement, it is difficult to harmonize both of these goals at the same time. If the profit target is not set, the customer (the governing agency) is forced to have a policy of maximum support for public service activities, but in reality that is not suitable. It is time to consider journalism as an economic sector, journalism products as specific goods, and press agencies with an operating mechanism like a business. Press agency leaders must think in the direction that their newspaper is a company in the news industry, and must find an effective business model for the editorial office to be able to thoroughly solve and create a new source of vitality for the current and future Vietnamese press economy. * Part 2: Bottlenecks hindering the development of the Vietnamese press and media economy

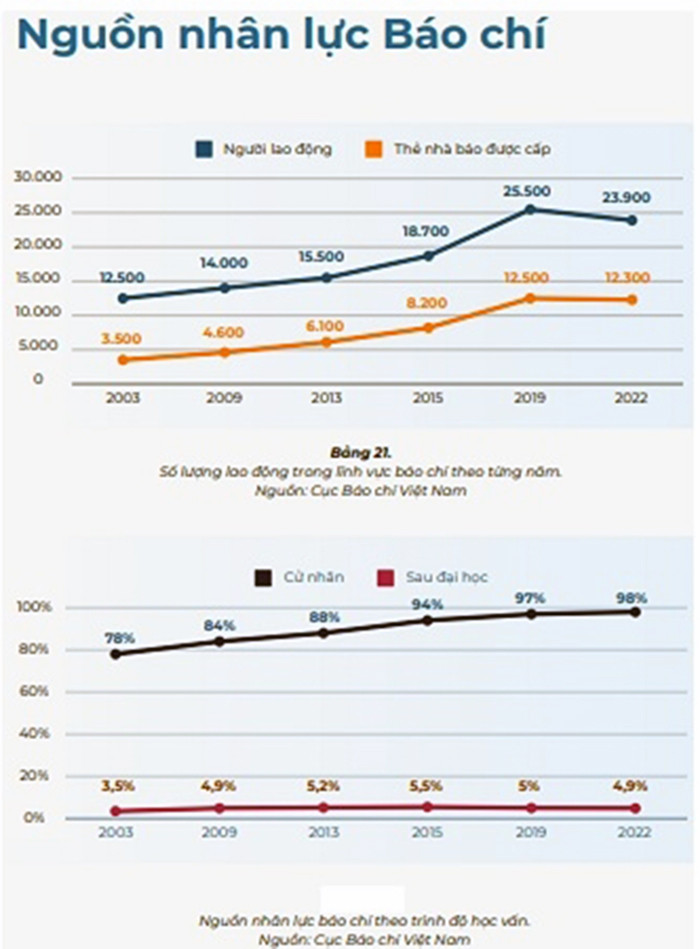
The total number of employees in the industry in 2023 is estimated at 1,767,766, an increase of 2.72% compared to 2022. Illustration photo: Hoang Ha
Development level of Vietnam's press and media economy According to the latest statistics of the Ministry of Information and Communications in 2023, the total revenue of the industry is estimated at 3,744,214 billion VND, an increase of 1.49% compared to 2022; State budget contribution is estimated at 99,323 billion VND, an increase of 1.31% compared to 2022; Contribution to GDP of the information and communications industry is estimated at 887,398 billion VND, an increase of 1.34% compared to 2022; The total number of employees in the industry in 2023 is estimated at 1,767,766 workers, an increase of 2.72% compared to 2022. Media revenue alone reaching the threshold of 4 billion USD shows the growth and potential of the media industry in creating economic value. According to statistics from the Ministry, the revenue of press agencies ranges widely from 200-300 million to 4-5,000 billion VND. However, in reality, the number of press agencies with revenue at the trillion level is only about one or two press agencies. In the strategy "Digital transformation of press to 2025, orientation to 2030" (approved by Deputy Prime Minister Tran Hong Ha under Decision No. 348/QD-TTg on April 6, 2023), a specific goal is set that by 2030, press agencies need to optimize revenue, in which 50% of press agencies increase revenue by at least 20%. Thus, it can be seen that the Government has raised the issue of press economy as an important driving force for press and media development in the digital economy era. To find the right solution for the development of the press and media economy, we must first define correctly its basic concepts, characteristics, roles, and properties. It is necessary to correctly assess the current state of capacity and development level of this economic sector, approaching both general economic laws and placing it in the specific factors of Vietnam. In particular, the aspects that need to be clarified are: How is the gathering of production forces, organization and division of labor in this sector? What are the emerging issues of ownership of means of production? The level of technology and the needs of the public in the role of consumers of goods? The level of specialization and the ability to connect and influence in the region and internationally? Looking at the reality of the press and media sector in Vietnam today, we can see four manifestations that are also the basic characteristics of this sector in the digital age. Correctly recognizing these manifestations contributes to understanding the trends of journalism and communication, thereby providing a satisfactory solution to the economic problem in the field of journalism. The organization and division of labor in journalism and communication have reached a level of specialization. The division of labor in the field of journalism and communication is increasingly profound and in the direction of specialization and diversification. Thereby eliminating the self-sufficiency, self-sufficiency, conservatism, and stagnation of the closed model of journalism and communication activities, accelerating the process of socialization of production and labor. The impact of scientific and technological achievements, especially digital technology and artificial intelligence, has been a factor promoting the division of labor and specialization of journalism and media to an unprecedented level. In fact, a division of labor has been formed between departments such as: Units specializing in research and development (for example: idea creators, program format providers or technological innovations in production processes); Units specializing in the production of each content component (Media companies specializing in the production and supply of documentaries, special programs, reports, etc.), equipment suppliers (companies specializing in selling or renting cameras, post-production tables, signal transmission lines, storage devices, digital content distribution infrastructure, etc.), production logistics (companies with sound, lighting, stage equipment, etc.) or service businesses (advertising agencies, sponsorship campaigns, media services, etc.). The economic links between the elements in this chain are increasingly close, increasing interdependence, the production process of one element is completely integrated into a unified production process. As specialization develops, the cooperative relationship between companies, centers, and press and media agencies becomes increasingly close, and cooperation in exchanging products on the market becomes increasingly sustainable.
The impact of scientific and technological achievements, especially digital technology and artificial intelligence, has been a factor promoting the division of labor and specialization of journalism and media to an unprecedented level. In fact, a division of labor has been formed between departments such as: Units specializing in research and development (for example: idea creators, program format providers or technological innovations in production processes); Units specializing in the production of each content component (Media companies specializing in the production and supply of documentaries, special programs, reports, etc.), equipment suppliers (companies specializing in selling or renting cameras, post-production tables, signal transmission lines, storage devices, digital content distribution infrastructure, etc.), production logistics (companies with sound, lighting, stage equipment, etc.) or service businesses (advertising agencies, sponsorship campaigns, media services, etc.). The economic links between the elements in this chain are increasingly close, increasing interdependence, the production process of one element is completely integrated into a unified production process. As specialization develops, the cooperative relationship between companies, centers, and press and media agencies becomes increasingly close, and cooperation in exchanging products on the market becomes increasingly sustainable.  Forms of ownership of means of production in the media sector are diverse. Up to now, the process of producing a media product has not been simple in terms of both material and technical aspects. One of the main reasons lies in the technical issues, production equipment, and means of production of this sector always requiring specialized systems, high technology and large investment costs. For example, a media enterprise owns a single specialized device but with high configuration (for example: 4k-8k advertising camera) with an investment value no less than an electronic newspaper agency equipped with a small studio system to produce live audiovisual content (live stream), etc. With the rapid growth of the economy, living conditions and accumulation as well as the ability to pay for press and media products and services of the people have also increased significantly. In addition, the rapid development of new communication technologies has made many operations and jobs that required specialized equipment become common with civilian equipment, even something that each individual can do by themselves. Personal phones can record videos and take photos, computers and laptops can process images and edit movies. Along with the popularity of communication devices, the amount of specialized equipment for the communication industry, from computers, software, recording equipment, film editing, sound recording, sound systems, lighting to many specialized materials, is increasingly popular in all systems, production centers, and businesses of different scales. From there, ownership of means of content production inevitably arises due to the development requirements of the productive forces as well as the socialization process in general. The forms of ownership of means of production in this field are mainly concentrated in the following forms: state ownership (central and local press agencies), collective ownership (of unions, groups, originating from individuals voluntarily contributing), mixed ownership (joint ventures, socialized coordination between state agencies and non-state organizations) and private ownership (small production models or capitalist ownership). Up to now, Vietnam has not been able to fully count the value of ownership of means of production of non-state economic forces, but through the relationship between the ability to organize and implement high-quality media products with the quantity - quality - type of equipment and means of production, this level can be identified relatively accurately. Up to now, media enterprises in Vietnam have reached the level of producing audiovisual works according to regional and international standards, from video clips, copyrighted game shows and Western television formats, feature films, large-scale event programs such as international beauty pageants, sports competitions, cultural events...
Forms of ownership of means of production in the media sector are diverse. Up to now, the process of producing a media product has not been simple in terms of both material and technical aspects. One of the main reasons lies in the technical issues, production equipment, and means of production of this sector always requiring specialized systems, high technology and large investment costs. For example, a media enterprise owns a single specialized device but with high configuration (for example: 4k-8k advertising camera) with an investment value no less than an electronic newspaper agency equipped with a small studio system to produce live audiovisual content (live stream), etc. With the rapid growth of the economy, living conditions and accumulation as well as the ability to pay for press and media products and services of the people have also increased significantly. In addition, the rapid development of new communication technologies has made many operations and jobs that required specialized equipment become common with civilian equipment, even something that each individual can do by themselves. Personal phones can record videos and take photos, computers and laptops can process images and edit movies. Along with the popularity of communication devices, the amount of specialized equipment for the communication industry, from computers, software, recording equipment, film editing, sound recording, sound systems, lighting to many specialized materials, is increasingly popular in all systems, production centers, and businesses of different scales. From there, ownership of means of content production inevitably arises due to the development requirements of the productive forces as well as the socialization process in general. The forms of ownership of means of production in this field are mainly concentrated in the following forms: state ownership (central and local press agencies), collective ownership (of unions, groups, originating from individuals voluntarily contributing), mixed ownership (joint ventures, socialized coordination between state agencies and non-state organizations) and private ownership (small production models or capitalist ownership). Up to now, Vietnam has not been able to fully count the value of ownership of means of production of non-state economic forces, but through the relationship between the ability to organize and implement high-quality media products with the quantity - quality - type of equipment and means of production, this level can be identified relatively accurately. Up to now, media enterprises in Vietnam have reached the level of producing audiovisual works according to regional and international standards, from video clips, copyrighted game shows and Western television formats, feature films, large-scale event programs such as international beauty pageants, sports competitions, cultural events...  The development of new techniques and technologies and the need for enjoyment create great pressure on press and media agencies. The development of digital media technology with features and technologies far beyond the "normal imagination", technical devices with information technology platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), digital connections (internet of things)... are increasingly modern, not only meeting the needs of improving people's quality of life, but also an important driving force stimulating the development of the press and media market in terms of scale, product value, circulation of goods and increasing liquidity.
The development of new techniques and technologies and the need for enjoyment create great pressure on press and media agencies. The development of digital media technology with features and technologies far beyond the "normal imagination", technical devices with information technology platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), digital connections (internet of things)... are increasingly modern, not only meeting the needs of improving people's quality of life, but also an important driving force stimulating the development of the press and media market in terms of scale, product value, circulation of goods and increasing liquidity.  The division of labor has reached a level of specialization and exchange in the field of journalism and media has gradually moved towards the level of connection and profound influence on the regional and international scale. The trend of globalization has developed strongly, attracting and influencing all countries and markets on all continents in the world, in other words, into a "flat world". One of the factors of the globalization process is the cultural exchange between countries and ethnic groups, including the penetration of audiovisual products in many different forms. It is undeniable that the remarkable development of world journalism and media products in all genres, excluding toxic, anti-cultural - non -political elements, many international audiovisual products have become indispensable spiritual food for the Vietnamese people. The increasingly wide international exchange and cooperation process has opened the door for the media public to access a variety of products, and is also a driving force for development to break the isolation and boredom of the previously isolated information content system. Many press and media products are not only implemented by applying foreign technology and foreign formats, but also approach the separation of each pre-production and post-production process into many domestic and foreign systems to achieve the highest quality and business efficiency. International division of labor and exchange have become factors promoting the development of the Vietnamese television market, especially since the early years of the 21st century. The process of exchange and contact is a positive sign for the press and media industry in Vietnam today, but in reality, the domestic press and media economic picture still has specific factors. First of all, it shows that in some aspects, the Vietnamese press and media market has not clearly demonstrated and optimally promoted the factors of the market mechanism: because an economy wants to operate, it must first rely on the market, which means relying on the automatic machine of both supply, demand, and commodity prices, with a competitive environment, the driving force is profit. The components of this market mechanism are closely related to each other, like links in the machine. Price is the core of the market, supply and demand are the center and competition is the soul and strength of the market. To better understand the components of the market mechanism, it is necessary to learn related concepts such as: Demand for goods : The quantity of goods or press and media services that buyers are able and willing to buy at different prices at the same time has appeared and is increasing day by day. Public needs are always changing and developing over time, they cannot limit the enjoyment of information to the limited capacity framework and many years of unchanged press - media department following the target plan. Supply of goods : Is the quantity of goods or services that sellers (press agencies, press - media enterprises, domestic and international organizations and individuals) are able and willing to sell at different prices in a certain period of time. In fact, press agencies produce according to the State's orders, many contents follow a fixed mechanism, not entirely originating from the needs and preferences of the public. Media products and media agencies were previously limited by geographical space (province - city) and are no longer suitable for development with the nature and characteristics of digital media. Price: Is a factor reflecting the supply and demand relationship of specific press - media products or services. The cost of media products does not fully reflect the production cost, because there is a subsidy from the budget for propaganda and policy communication tasks. Meanwhile, private enterprises producing media products must "swim" on their own and need to calculate the selling price in comparison with production costs and the issue of profit. Competition : Is the race between enterprises, agencies, and economic organizations in the consumption of press and media goods and services, aiming to gain the highest profit. This is an inevitable part of the market economy and is also a basic factor in forming the television market. This competitiveness is reduced and eliminated with the existence of a fixed press budget. Currency, value: Is the measurement and expression of the value of press and media products. Press and media labor, press and media products with the characteristics of "creative" labor need to be measured and paid in currency and with market fluctuations. Profit : With the press and media market, profit is the income of agencies after deducting production costs, taxes, etc. and becomes one of the driving forces governing the activities of business people. Profit brings press and media businesses to production fields that attract consumers (the media public). Profit is also the factor that makes press and media businesses interested in using the most effective production techniques. When 4 problems appear: what to produce? how to produce? produce for whom? how to profit? then that is when the press and media market completes its economic goals. However, with press agencies, political goals are the most important requirement, it is difficult to harmonize both of these goals at the same time. If the profit target is not set, the customer (the governing agency) is forced to have a policy of maximum support for public service activities, but in reality that is not suitable. It is time to consider journalism as an economic sector, journalism products as specific goods, and press agencies with an operating mechanism like a business. Press agency leaders must think in the direction that their newspaper is a company in the news industry, and must find an effective business model for the editorial office to be able to thoroughly solve and create a new source of vitality for the current and future Vietnamese press economy. * Part 2: Bottlenecks hindering the development of the Vietnamese press and media economy
The division of labor has reached a level of specialization and exchange in the field of journalism and media has gradually moved towards the level of connection and profound influence on the regional and international scale. The trend of globalization has developed strongly, attracting and influencing all countries and markets on all continents in the world, in other words, into a "flat world". One of the factors of the globalization process is the cultural exchange between countries and ethnic groups, including the penetration of audiovisual products in many different forms. It is undeniable that the remarkable development of world journalism and media products in all genres, excluding toxic, anti-cultural - non -political elements, many international audiovisual products have become indispensable spiritual food for the Vietnamese people. The increasingly wide international exchange and cooperation process has opened the door for the media public to access a variety of products, and is also a driving force for development to break the isolation and boredom of the previously isolated information content system. Many press and media products are not only implemented by applying foreign technology and foreign formats, but also approach the separation of each pre-production and post-production process into many domestic and foreign systems to achieve the highest quality and business efficiency. International division of labor and exchange have become factors promoting the development of the Vietnamese television market, especially since the early years of the 21st century. The process of exchange and contact is a positive sign for the press and media industry in Vietnam today, but in reality, the domestic press and media economic picture still has specific factors. First of all, it shows that in some aspects, the Vietnamese press and media market has not clearly demonstrated and optimally promoted the factors of the market mechanism: because an economy wants to operate, it must first rely on the market, which means relying on the automatic machine of both supply, demand, and commodity prices, with a competitive environment, the driving force is profit. The components of this market mechanism are closely related to each other, like links in the machine. Price is the core of the market, supply and demand are the center and competition is the soul and strength of the market. To better understand the components of the market mechanism, it is necessary to learn related concepts such as: Demand for goods : The quantity of goods or press and media services that buyers are able and willing to buy at different prices at the same time has appeared and is increasing day by day. Public needs are always changing and developing over time, they cannot limit the enjoyment of information to the limited capacity framework and many years of unchanged press - media department following the target plan. Supply of goods : Is the quantity of goods or services that sellers (press agencies, press - media enterprises, domestic and international organizations and individuals) are able and willing to sell at different prices in a certain period of time. In fact, press agencies produce according to the State's orders, many contents follow a fixed mechanism, not entirely originating from the needs and preferences of the public. Media products and media agencies were previously limited by geographical space (province - city) and are no longer suitable for development with the nature and characteristics of digital media. Price: Is a factor reflecting the supply and demand relationship of specific press - media products or services. The cost of media products does not fully reflect the production cost, because there is a subsidy from the budget for propaganda and policy communication tasks. Meanwhile, private enterprises producing media products must "swim" on their own and need to calculate the selling price in comparison with production costs and the issue of profit. Competition : Is the race between enterprises, agencies, and economic organizations in the consumption of press and media goods and services, aiming to gain the highest profit. This is an inevitable part of the market economy and is also a basic factor in forming the television market. This competitiveness is reduced and eliminated with the existence of a fixed press budget. Currency, value: Is the measurement and expression of the value of press and media products. Press and media labor, press and media products with the characteristics of "creative" labor need to be measured and paid in currency and with market fluctuations. Profit : With the press and media market, profit is the income of agencies after deducting production costs, taxes, etc. and becomes one of the driving forces governing the activities of business people. Profit brings press and media businesses to production fields that attract consumers (the media public). Profit is also the factor that makes press and media businesses interested in using the most effective production techniques. When 4 problems appear: what to produce? how to produce? produce for whom? how to profit? then that is when the press and media market completes its economic goals. However, with press agencies, political goals are the most important requirement, it is difficult to harmonize both of these goals at the same time. If the profit target is not set, the customer (the governing agency) is forced to have a policy of maximum support for public service activities, but in reality that is not suitable. It is time to consider journalism as an economic sector, journalism products as specific goods, and press agencies with an operating mechanism like a business. Press agency leaders must think in the direction that their newspaper is a company in the news industry, and must find an effective business model for the editorial office to be able to thoroughly solve and create a new source of vitality for the current and future Vietnamese press economy. * Part 2: Bottlenecks hindering the development of the Vietnamese press and media economy On June 14, the Information and Communication Magazine, VietNamNet Electronic Newspaper (Ministry of Information and Communications) in collaboration with the Institute of Journalism and Communication Training (University of Social Sciences and Humanities, Vietnam National University, Hanoi) will organize an international conference: "Vietnam's journalism and communication economy in the context of digital economic development". The conference is part of the annual event of the Vietnamese journalism community called "June Journalism Forum" - the third time (2024), co-chaired by the Information and Communication Magazine, VietNamNet Electronic Newspaper and the Institute of Journalism and Communication Training. The conference is held in 1 working day, with 3 sessions and discussions.
Vietnamnet.vn
Source: https://vietnamnet.vn/nen-kinh-te-bao-chi-truyen-thong-viet-nam-toan-canh-va-nhung-nut-that-2290362.html

![[Photo] Close-up of Tang Long Bridge, Thu Duc City after repairing rutting](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/19/086736d9d11f43198f5bd8d78df9bd41)

![[Photo] President Luong Cuong presents the 40-year Party membership badge to Chief of the Office of the President Le Khanh Hai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/19/a22bc55dd7bf4a2ab7e3958d32282c15)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the conference to review 10 years of implementing Directive No. 05 of the Politburo and evaluate the results of implementing Regulation No. 09 of the Central Public Security Party Committee.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/19/2f44458c655a4403acd7929dbbfa5039)
![[Photo] Panorama of the Opening Ceremony of the 43rd Nhan Dan Newspaper National Table Tennis Championship](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/19/5e22950340b941309280448198bcf1d9)






























![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh inspects the progress of the National Exhibition and Fair Center project](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/19/35189ac8807140d897ad2b7d2583fbae)






















































![[VIDEO] - Enhancing the value of Quang Nam OCOP products through trade connections](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/5be5b5fff1f14914986fad159097a677)



Comment (0)