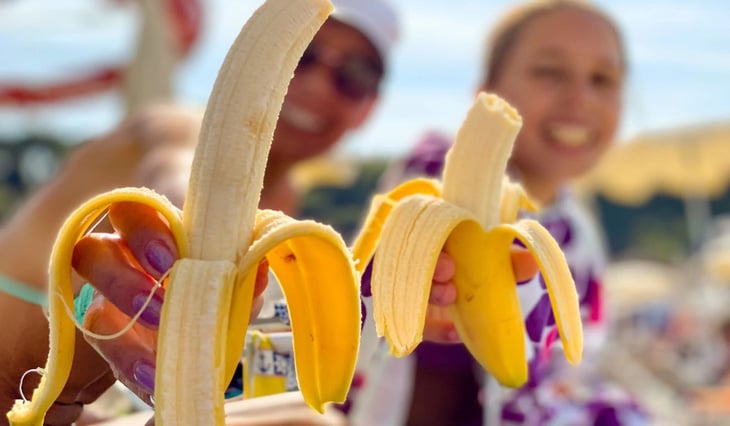

Scientists have found that consuming an extra 1g of potassium per day, equivalent to two medium-sized bananas, can help reduce the risk of high blood pressure - Photo: TELEGRAPH
According to the British newspaper Telegraph , scientists have discovered that consuming an extra 1g of potassium per day - equivalent to two medium-sized bananas, a cup of spinach or a large sweet potato - could be a simple way to tackle high blood pressure.
To reach the above conclusion, experts from the George Institute for Global Health at Imperial College London (UK) analyzed data from the Stroke and Salt Substitution Study. This study spent 5 years following 20,995 people in China who had a stroke or people over 60 with high blood pressure.
In the study, half of the participants continued to use regular table salt when cooking, while the other half were given a "salt substitute" in which a quarter of the sodium chloride was replaced with potassium chloride.
Results showed that people who consumed potassium-rich salt had lower blood pressure levels as well as a reduced risk of stroke and heart disease.
A new analysis published in The Journal of Human Hypertension on February 21 shows that up to 80% of blood pressure reduction is due to increased potassium, not due to reduced salt intake.
This is the first study to directly compare the benefits of sodium chloride and potassium chloride and rely on participants' urinary sodium and potassium levels to determine intake.
Research shows that increasing daily potassium intake reduces systolic blood pressure by an average of 2 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
When analyzed further, they found that increasing potassium consumption reduced the risk of stroke by about 10%, while reducing salt intake only reduced the risk by about 4%.
“High sodium intake and low potassium intake are common. Both are linked to high blood pressure and a higher risk of stroke, heart disease and premature birth. Using a salt substitute in which some of the sodium chloride is replaced with potassium chloride would address both problems at once,” said Dr Polly Huang, lead author of the study from the George Institute.
International experts are now calling for a review of official recommendations on high blood pressure, which recommend increasing potassium intake.
A global collaboration of researchers from the US, Australia, Japan, South Africa and India also called for potassium supplementation to be included in international health guidelines.
Is it okay to eat too much potassium?
Typically, for adults, health experts recommend eating 3.5g of potassium per day and a maximum of 6g of salt per day.
Potassium is found in many foods, including green leafy vegetables, beans and nuts, but amounts are often reduced during processing.
Too much potassium can lead to hyperkalemia, which affects heart function. However, experts say this condition is rare and only occurs in people who consume too much potassium, such as eating hundreds of bananas in one sitting.
Source
































![[Photo] Magical moment of double five-colored clouds on Ba Den mountain on the day of the Buddha's relic procession](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/9/7a710556965c413397f9e38ac9708d2f)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam begins official visit to Russia and attends the 80th Anniversary of Victory over Fascism](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/5d2566d7f67d4a1e9b88bc677831ec9d)
































































Comment (0)