Burn accidents in children can occur in daily life. To prevent burns in young children, families need to watch their children carefully and let them play away from areas where there are burning agents.
Situations that can easily cause burn accidents
Hospitalized pediatric burns are common in children aged 9-24 months. At this age, children are very active when playing and crawling, easily causing burns by knocking over objects such as soup bowls, thermoses containing hot water, etc.

BRITISH RED CROSS DATA
Among the burn patients being treated at the Burn Department - Xanh Pon General Hospital, there is a boy who was burned when his mother was carrying a plastic bag containing hot pho soup, the boy touched it, spilled it and burned his right leg. At home, the child received proper and timely first aid, so when he was admitted to the hospital, the burn was not deep and the treatment was favorable.
In addition, there are situations that cause burns that need to be noted, such as the case of a boy who was burned by putting his hand into a bowl of hot porridge while his mother left the bowl on the table waiting to cool. Burns in this situation can easily cause deep burns because the skin is thin and the porridge is hot for a long time, with a long contact time.
Steam burns from rice cookers are also common in young children because they put their hands into the steam that comes out when the rice boils. Steam burns from rice cookers are often very deep burns, causing contracture scars.
In the family, appliances such as electric kettles can easily cause burns, because children can knock them over when there is hot water inside, causing burns to their feet and hands.
First aid properly
When a child is unfortunately burned, adults and babysitters need to provide first aid properly to prevent the child from getting burned further.
First, separate the causative agent from the affected area, then rinse with cool water for 15 minutes, then cover the burn area with clean, sterile gauze and transfer the patient to the nearest medical facility.
5 first aid steps for children with thermal burns
Step 1: Cool the burn with clean water. Immediately put the baby's burned skin in clean water to cool, leave for about 15 - 20 minutes. Use tap water, turn it on gently and pour it on the skin. Do not use ice or very cold water to apply to the burn.
Step 2: Air out the burn. Quickly remove any jewelry, accessories (bracelets, anklets, etc.) from the child, and any clothing that is not stuck to the burn.
Step 3: Clean the wound. Never apply creams, fish sauce, egg whites, etc. to the burn. Always keep the burn clean.
Step 4: For children with minor burns: After giving first aid with water, you can let the child stay at home to let the skin recover and monitor the child for signs of infection.
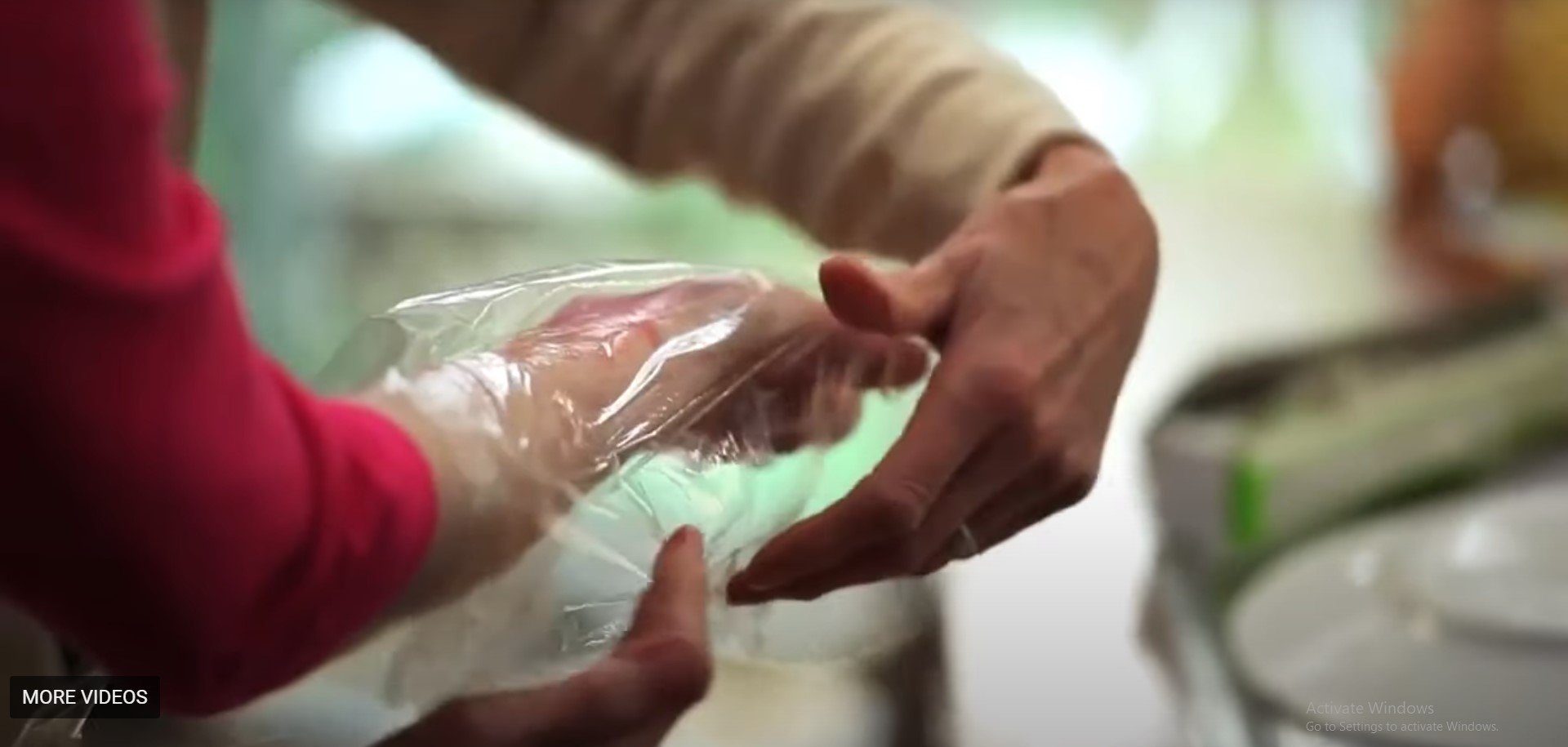
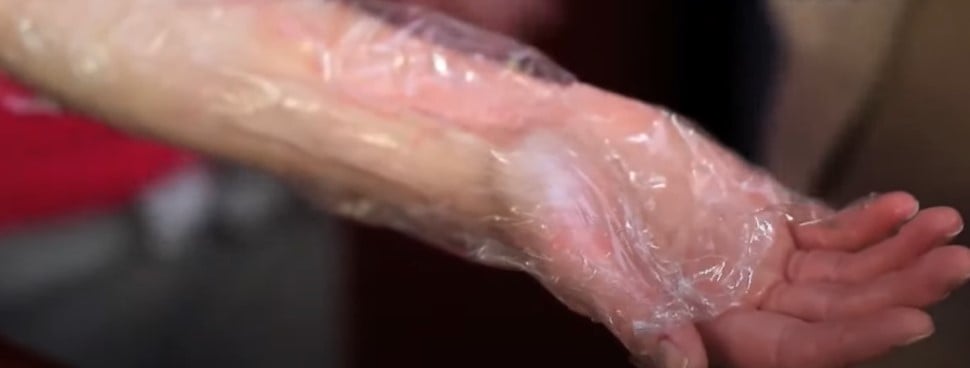
Step 5: For children with severe burns (level 2, 3): If the child's burn has burned the skin, after first aid with water, the child needs to be taken to the hospital. Cover the burn with clean plastic to limit infection (photo). The reason to choose plastic is because this is a non-sticky material. Regular cotton towels and gauze easily absorb the secretions from the burn and stick tightly to the wound.
(Source: Survival Skills Vietnam)
In unfortunate situations of burns, children need to be given first aid quickly and properly by cooling the burn wound with clean water to avoid deep burns. Improper first aid can easily cause the burn to become deeper and more difficult to treat.
Note to families, the water to cool the burn should be clean water, such as tap water, and should be cool water about 20 degrees Celsius, not cold water or ice because it will cause further damage.
Avoid applying traditional medicine, toothpaste or fish sauce on burn wounds because it can easily cause secondary infection and make treatment more difficult.
To prevent burns for children, keep them away from sources of burns such as stoves, appliances such as electric kettles, hot pots of soup, rice cookers, etc.
Source link



![[Photo] Readers line up to visit the photo exhibition and receive a special publication commemorating the 135th birthday of President Ho Chi Minh at Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/85b3197fc6bd43e6a9ee4db15101005b)
![[Photo] More than 17,000 candidates participate in the 2025 SPT Competency Assessment Test of Hanoi National University of Education](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/e538d9a1636c407cbb211b314e6303fd)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on science and technology development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/ae80dd74c384439789b12013c738a045)



























![[Photo] Nearly 3,000 students moved by stories about soldiers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/17/21da57c8241e42438b423eaa37215e0e)



































































Comment (0)