Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease, a condition in which inflammation spreads deep into the layers of intestinal tissue, leading to pain and weakness, and sometimes life-threatening complications.
The article was professionally consulted by Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Anh Tuan, Head of the Department of Digestive Surgery, 108 Central Military Hospital.
Reason
- Currently, the exact cause of Crohn's disease is unknown.
- Previously, experts suspected that diet and stress led to the disease. Currently, studies say that these factors aggravate the condition but are not the cause of Crohn's disease.
- Certain factors such as genetics and immune system problems play a role in the development of Crohn's disease:
* Genetics: Crohn's disease is more common in people who have family members with the disease, so genes may play a role in making future generations more susceptible to the disease than other families.
* Immune system: It is hypothesized that Crohn's disease is triggered by certain viruses or bacteria. When the patient's immune system tries to fight off invading microorganisms, an abnormal immune response occurs, causing the immune system to mistakenly attack not only the invading microorganisms but also the cells in the digestive tract.
Symptom
- Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the distal small intestine, but can occur in all other locations of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Symptoms can range from mild to severe and develop gradually, but sometimes they appear suddenly, without warning. People with the disease may have periods of no signs or symptoms, leading them to think their Crohn's disease is in remission.
- When the disease is active, there are typical symptoms as follows:
* Diarrhea.
* Fever.
* Tired.
* Abdominal pain and cramps.
* Blood in stool.
* Reduce appetite and lose weight.
* Pain near or around the anus.
- People with severe Crohn's disease will have some other symptoms such as:
* Inflammation of the skin, eyes and joints.
* Hepatitis or cholangitis.
* Children are slow to grow or slow to develop sexual characteristics during puberty.
- See a doctor if you have persistent changes in bowel habits or any symptoms of Crohn's disease such as:
* Stomach-ache.
* Blood in stool.
* Persistent diarrhea that does not respond to over-the-counter medications.
* Fever of unknown origin lasting one or two days.
* Unexplained weight loss.
Complications
- Bowel obstruction: Crohn's disease affects the thickness of the intestinal wall. Over time, parts of the intestine can become scarred and narrowed, blocking the flow of digested and absorbed food through the digestive tract. As a result, surgery may be required to remove the part of the intestine that is blocking the digestive tract.
- Ulcers: Chronic inflammation can lead to ulcers anywhere in the digestive tract, including the mouth and anus.
- Fistula: Fistulas near or around the anal area are the most common type.
- Anal fissure.
- Malnutrition: Diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramps can cause the patient to lose appetite or the intestines to not absorb enough nutrients, leading to symptoms of iron deficiency anemia or vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Colon cancer: Crohn's disease affects the colon, increasing the risk of cancer.
- Anemia, skin disorders, osteoporosis, arthritis and gallbladder or liver disease.
- Certain drugs that treat Crohn's disease by blocking immune system functions have been linked to a small risk of developing cancers such as lymphoma and skin cancer.
Diagnose
- Blood tests to check for anemia.
- Fecal occult blood test.
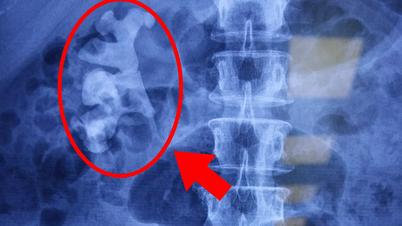
- Colonoscopy: This test allows your doctor to view the entire colon and the last part of the ileum (terminal ileum) using a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera on the end. During the colonoscopy, your doctor may also take small tissue samples for biopsy. If clusters of inflammatory cells called granulomas are present, they help confirm a diagnosis of Crohn's.
- Computed tomography (CT).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI scanner uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues. MRI is especially useful for evaluating fistulas around the anus (pelvic MRI) or small intestine (MR CT scan).
- Capsule endoscopy: For this test, the patient swallows a capsule with a camera attached, which takes pictures of the small intestine and transmits the data to a storage device worn on a belt. The images are then downloaded to a computer, displayed on a computer screen, and checked for signs of Crohn's disease. The camera exits the body after the patient has a bowel movement.
Treatment
- There is currently no cure for Crohn's disease and no treatment is right for everyone.
- The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation that causes the patient's symptoms, limit complications, and relieve long-term symptoms:
* Anti-inflammatory drugs.
* Immunosuppressants.
* Antibiotics.
* Anti-diarrhea: Some fiber supplements help relieve symptoms of mild to moderate diarrhea by increasing stool bulk.
* Pain reliever.
* Iron supplementation: If the patient has chronic intestinal bleeding, it can lead to iron deficiency anemia and iron supplementation is required.
* Vitamin B12 injections: Crohn's disease causes vitamin B12 deficiency, so patients may be prescribed injections to help prevent anemia, promote normal growth and development, and are essential for nerve function.
* Calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Prevent
Sometimes people can feel helpless when dealing with Crohn's disease. But changes in diet and lifestyle can help control symptoms and lengthen the time between flare-ups.
- Diet
There is no definitive proof that what you eat causes Crohn’s disease. But some foods and drinks can make your signs and symptoms worse. Here are some suggestions that may help:
* Limit dairy products.
* Try low-fat foods.
* Limiting fiber such as fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains can make symptoms worse. If raw fruits and vegetables make you uncomfortable, try steaming, baking, or stewing them.
* Avoid foods such as spicy foods, alcohol and caffeine as they can make signs and symptoms worse.
* Eat small meals frequently.
* Drink plenty of fluids: Try to drink plenty of fluids every day. Water is best. Alcohol and caffeinated drinks stimulate the bowels and can make diarrhea worse. While carbonated drinks often produce gas, which can cause bloating.
- Consider taking a multivitamin: Because Crohn's disease interferes with the absorption of nutrients, a person's diet may be limited. Therefore, taking a multivitamin and mineral supplement is often helpful and effective. However, people should consult their doctor before taking any vitamins or supplements.
- Stop smoking:
* Smoking increases the risk of developing Crohn's disease. Once you have the disease, smoking can make it worse. People with Crohn's disease who smoke are more likely to have relapses, need more medications, and have repeat surgeries.
* Quitting smoking can improve overall digestive health as well as provide many other health benefits.
- Stress management:
Although stress does not cause Crohn's disease, it can make signs and symptoms worse. While it's not always possible to avoid stress, people with the condition can learn ways to help manage stress, such as:
* Do exercise.
* Biofeedback.
* Relax and practice breathing regularly.
American Italy
Source link


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Thailand Paetongtarn Shinawatra attend the Vietnam-Thailand Business Forum 2025](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/16/1cdfce54d25c48a68ae6fb9204f2171a)



























![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Thailand Paetongtarn Shinawatra](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/16/52c73b27198a4e12bd6a903d1c218846)






























































Comment (0)