Mass food poisoning: Expensive lessons and solutions
Many recent mass food poisoning incidents show that there are still many loopholes in food quality control and processing.
Why?
Poor quality food is one of the main causes of unpredictable harm. Not only acute poisoning can be fatal, but contamination with toxic substances below the threshold, over time, can cause unforeseen diseases, such as cancer, unexplained dysfunction, infertility, and even birth defects.
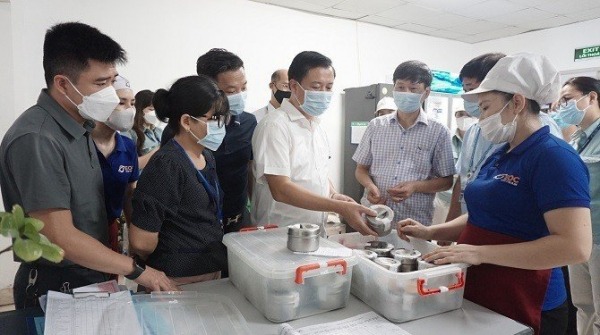 |
| Many recent mass food poisoning incidents show that there are still many loopholes in food quality control and processing. |
2024 is the 12th year since the Food Safety Law was promulgated and put into effect, along with Decree 15 and circulars of ministries and branches participating in food management.
However, food poisoning still occurs and is a concern, especially in crowded industrial areas. The provision of meals for schools is still a problem. Food poisoning is still a concern at banquets in both urban and rural areas.
Food insecurity has many causes such as overlapping in state management; local irresponsibility and lack of close supervision; livestock and crop farmers using growth stimulants without permission;
The greedy traders and processors and finally the careless consumers (although that is very difficult). Recently, the whole country has had consecutive mass poisoning cases with hundreds of people infected, many of which are related to the collective kitchens for students and workers.
The "culprits" of food poisoning cases are mainly found to be bacteria Salmonella, E.coli, histamine, microorganisms Bacillus cereus... found in food.
In the recent incident of hundreds of students in Lao Cai suffering from food poisoning, the results of food sample testing by the National Institute for Food Safety and Hygiene Control discovered that 4 dishes at the dinner on October 8, including cucumber, grilled pork roll, fried chicken, and water spinach soup, tested positive for Salmonella bacteria.
Or the case of 150 workers at Sunrese Apparel Vietnam Co., Ltd. (Phu Tho) having to be hospitalized after lunch due to high levels of histamine in the braised mackerel dish during the meal.
The most recent case of mass food poisoning occurred at Shinsung Vina Company Limited after a party on October 20, causing 91 people to be hospitalized. Through testing of patient samples, the cause of the poisoning was E.coli and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
Deal with the root of the problem
It is known that there are currently 3 sectors including Health, Industry and Trade, Agriculture and Rural Development participating in food sector management, each Ministry and sector manages a number of products.
That is why there is overlap and interweaving between product groups, when there is an incident, the responsibility is not clear, so management is ineffective. Thus, to ensure food safety, it is necessary to build a "chain"; food insecurity leading to food poisoning has actually formed a "chain", so to solve the root of this problem, there must be synchronous measures.
Although food safety management has been decentralized to local wards and communes, many mass poisoning cases with hundreds of people infected have only recently revealed shortcomings in inspection and management. Some establishments operate without business licenses, and only when they cause major poisoning cases are they exposed.
The Ministry of Health itself, through inspection, also pointed out the fact that many businesses have not yet implemented regulations on ensuring food hygiene and safety.
There are establishments that are not registered for business, do not have a certificate of food safety eligibility, do not have a certificate of training in food safety knowledge, and do not conduct periodic health check-ups for those involved in production and processing...
There are even establishments that do not perform 3-step food inspection and store food samples as prescribed; and cannot provide contracts and documents related to the origin of food ingredients.
Some for-profit establishments may use poor quality ingredients or lack safety testing. This leads to a high risk of poisoning when harmful substances from food are not detected.
Failure to follow hygienic procedures in food preparation, storage and transportation is a major risk factor. Practices such as improper hand washing, unclean kitchen utensils, or undercooked food can create conditions for bacteria to grow.
Many consumers and food processors still lack understanding of the risk of food poisoning. This leads to subjectivity in food selection and processing.
To clarify the cause, according to Mr. Nguyen Duy Thinh, a food expert, the hands of the food processor are very important.
The principle before preparing food is to wash hands with soap; utensils must be clean, have cabinets to prevent cockroaches and microorganisms from flying in; cooked and raw food must be kept separate.
In particular, trash bins and toilets must be far away from food preparation areas. If not, flies from trash bins and toilets will fly and land on cooked food, carrying E.coli bacteria.
Or the food processor does not wash his hands after using the toilet, or does not wash his hands properly, bringing E.coli bacteria into the food.
Similarly, Staphylococcus aureus bacteria often enter food when processing and storage are not hygienic. Salmonella bacteria also often spread when not following hand washing before eating or not washing hands properly after using the toilet.
To limit mass poisoning incidents, according to experts, state management agencies need to strengthen food safety inspection and supervision.
Authorities need to step up regular inspections at food production, processing and supply establishments. Strictly handling establishments that violate food safety and hygiene regulations will help raise compliance awareness among businesses.
Facilities need to select raw materials from reputable suppliers with food safety certificates. Food traceability is very important to ensure quality and minimize risks.
Organize food safety training courses for employees in restaurants and communal kitchens. Understanding the process of preserving, processing and cooking food will help reduce the risk of infection.
Applying advanced technologies in food preservation and processing helps prolong shelf life and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. Temperature control systems and the use of safe packaging are effective solutions.
Information on food poisoning cases should be reported promptly to warn consumers. In addition, communication campaigns should focus on educating people on how to select, store and prepare food safely.
Mass food poisoning is an alarming problem and requires drastic intervention from authorities, businesses, as well as awareness from each individual.
Implementing synchronous preventive measures will not only help limit the risk of poisoning but also improve the quality of food services, ensuring health safety for the community.
According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, in the first 9 months of 2024, there were 111 food poisoning cases nationwide, the number of people suffering from food poisoning increased more than 2 times.


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Cambodian Minister of Commerce](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/28/be7f31fb29aa453d906df179a51c14f7)


![[Photo] A long line of young people in front of Nhan Dan Newspaper, recalling memories of the day the country was reunified](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/28/4709cea2becb4f13aaa0b2abb476bcea)
![[Photo] Signing ceremony of cooperation and document exchange between Vietnam and Japan](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/28/e069929395524fa081768b99bac43467)
![[Photo] Special supplement of Nhan Dan Newspaper spreads to readers nationwide](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/28/0d87e85f00bc48c1b2172e568c679017)












![[Infographic] 45 communes and wards of Dong Thap province after rearrangement](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/29/8553108109fa44b3b0493f9a2cf2bde8)














![[Photo] People lined up in the rain, eagerly receiving the special supplement of Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/28/ce2015509f6c468d9d38a86096987f23)


























































Comment (0)