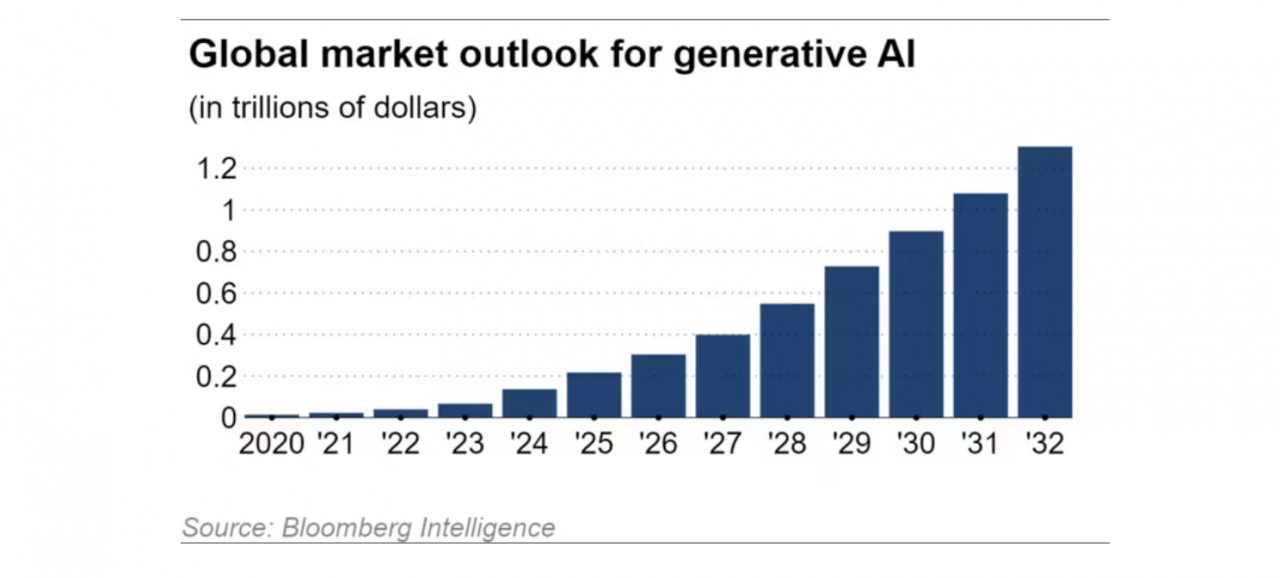
The global market for synthetic AI is expanding 42% annually, according to estimates from Bloomberg Intelligence, and is expected to reach $1.3 trillion by 2032, about 32 times its $40 billion size in 2022.
Leading the way are US tech companies like OpenAI, Google and Amazon – tech giants with deep pockets and talent.
Despite intense competition, VinGroup chose to develop its own version, using Vietnamese data to create AI with higher accuracy than foreign competitors, said Vu Ha Van, a professor of mathematics at Yale University who serves as VBD's chief science officer.
To date, generative AI programs have been trained primarily on English data. That means there is relatively little data from Vietnam, reducing the accuracy of those programs when it comes to local culture, history, and laws.
ViGPT's large language model (LLM) is said to consist of 1.6 billion parameters, a few percent of the size of OpenAI's GPT-4.
More parameters usually equate to higher intelligence. But according to the general AI assessment customized for the Vietnamese market, ViGPT outperformed many foreign competitors and achieved a score second only to ChatGPT.
VinFast Group will apply AI technology to the production of electric vehicles. Drivers will be able to control the vehicle through Vietnamese voice commands. The group also plans to incorporate AI into the fields of finance, insurance and logistics.
The AI Development Race in Asia
It is estimated that only about 5% of the global population speaks English as a first language, meaning there is a huge potential need for AI developed for non-native English speakers.
In Japan, companies are developing AI that generates Japanese. In August, electronics giant NEC launched a service using a cotomi LLM. Telecom company NTT will launch a service in March based on another LLM, tsuzumi. Japanese mobile carrier SoftBank is also developing its own LLM.
“Understanding Japanese business practices gives us advantages in terms of usability, such as responding to emails and performing call center work more naturally,” said SoftBank President Junichi Miyakawa.
Fueling the race to develop indigenous AI are the risks of over-reliance on the US, especially when it comes to international competitiveness and national security. There are also concerns that using AI programs developed in other countries could lead to data breaches that could compromise sensitive information.
Professor Van said that emerging technology should not be left to foreign companies because more and more students are using AI to study, which means innovation has a huge impact on the younger generation.
In China, which is competing with the US in technology, Baidu, Tencent Holdings and Alibaba Group Holding are developing innovative AI. Baidu’s Ernie Bot boasted more than 100 million users as of the end of last year.
“The generative large language model we are developing now will be more suitable for the Chinese language and the Chinese market,” said Baidu Chairman and CEO Robin Li.
Last August, South Korean internet service company Naver unveiled HyperClova X, a synthetic AI tailored for the Korean language. The program will be integrated with the company's search engine and online shopping platform to help users find the results they want more efficiently.
Naver says its Korean database is 6,500 times larger than ChatGPT's Korean database, resulting in more natural-reading text and smoother language recognition.
Last month, Singapore announced plans to develop LLMs tailored to Indonesian, Malaysian and Thai languages. However, such initiatives will face challenges, such as a lack of data that can be trained in less-used languages and the profitability of developing such models.

Source





































![[Photo] Prime Ministers of Vietnam and Thailand visit the Exhibition of traditional handicraft products](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/15/6cfcd1c23b3e4a238b7fcf93c91a65dd)




































































Comment (0)