Choosing the wrong SPF, not reapplying sunscreen after sweating, or applying it too soon before going out reduces the effectiveness of the sunscreen.
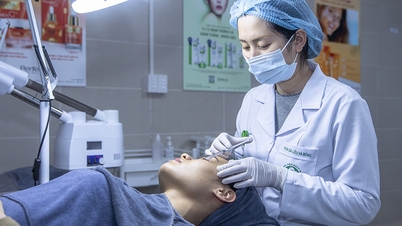
Sunscreen is one of the indispensable cosmetics on hot summer days, when the temperature rises and the ultraviolet (UV) index reaches its maximum level. The product reduces the risk of sunburn, prevents skin cancer, reduces the harmful effects of sunlight, and prevents dark spots.
However, in reality, in many cases, the more sunscreen is used, the darker the skin becomes. Some people experience premature aging such as wrinkled skin, larger pores, acne, and even the risk of skin cancer. Dr. Howard Murad, the father of modern skin care principles, explains why.
The first reason is the inappropriate application time. Normally, sunscreen takes about 30 minutes to fully absorb, forming a protective shield for the skin. If you go out before this time, your skin will not be fully protected, leading to darkening. Wearing clothes immediately after applying sunscreen also causes the cream to smudge onto the fabric, causing a loss of cream on the skin.
Some people don’t use sunscreen with enough SPF. SPF is a measure of how well a product protects against UVB rays. To calculate SPF, manufacturers test skin with and without sunscreen to see how long it takes for the skin to turn red.
The SPF rating and the protection offered by a sunscreen do not increase linearly. For example, SPF 30 does not provide twice the protection offered by SPF 15. The difference is that SPF 15 protects against 93% of UVB rays, while SPF 30 protects against 97% of the radiation.
In theory, the higher the SPF, the longer the protection period. However, this is only the most basic estimate. The protection period of sunscreen depends on skin type, sunlight intensity, and the amount of cream used.
Dr. Murad noted that when outdoors, exposed to a lot of sunlight, people should choose a cream with an SPF of about 50+. He also recommends applying about 30 ml of sunscreen to the entire body, and need to reapply the cream continuously when outdoors for a long time.
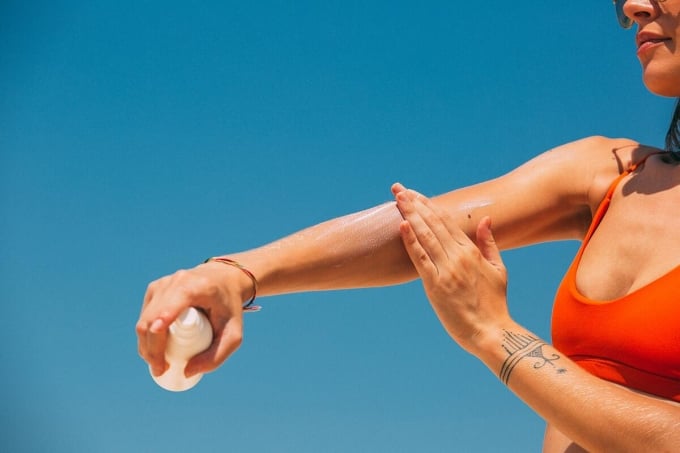

A woman applies sunscreen. Photo: Pexel
Not reapplying sunscreen after sweating can also cause sunburn. "Whether you're jogging in the park or simply sweating on the beach, you need to monitor your sunscreen and reapply as needed," says Dr. Murad. He adds that if you're swimming or doing any other activity that causes you to sweat, use a water-resistant sunscreen and reapply every 40 to 80 minutes.
Many chemical sunscreens can react and cause sunburn when exposed to sunlight. Some sunscreen ingredients, including avobenzone, can cause a photoallergic reaction. The skin changes over several days, causing the skin to become red and hot, similar to a sunburn.
Experts recommend checking the ingredients of the cream before use, preferring mineral sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which are gentler on sensitive skin.
Using sunscreen while taking certain antibiotics also reduces the effectiveness of UV protection. Antibiotics can make the skin more susceptible to inflammation and phototoxicity. This condition develops within a few hours of exposure to sunlight. This is why experts recommend that people taking antibiotics cover their skin carefully and stay in the shade whenever possible.
Some acne products and birth control pills also make your skin more sensitive to sunlight, reducing the effectiveness of sunscreen.
Thuc Linh (According to Women's Health Magazine, Cosmopolitan )
Source link




![[Photo] Ready for the top competitions of Vietnamese table tennis](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/18/9c547c497c5a4ade8f98c8e7d44f5a41)
![[Photo] Many young people patiently lined up under the hot sun to receive a special supplement from Nhan Dan Newspaper.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/18/6f19d322f9364f0ebb6fbfe9377842d3)
![[Photo] Party and State leaders attend the special art program "You are Ho Chi Minh"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/18/6895913f94fd4c51aa4564ab14c3f250)
























































































Comment (0)