According to a report from the Pasteur Institute of Ho Chi Minh City, from the beginning of 2023 to the end of last week, the entire southern region recorded 9,028 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease, including 4 deaths with a diagnosis of hand, foot and mouth disease level 4 and positive EV71 virus test.
In Ho Chi Minh City, from the beginning of 2023 until now, there have been 2,844 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease, with no recorded deaths.
Regarding treatment, since the beginning of the year, there have been a total of 936 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease treated as inpatients at hospitals in Ho Chi Minh City, including 46 severe cases and 4 deaths (these were seriously ill children transferred from other provinces).
The total number of hospitalizations yesterday (June 18) was 41, of which 8 cases were located in Ho Chi Minh City (20%).
As of this morning (June 19), the total number of inpatients is 147, all of whom are children under 6 years old. There are 18 children with severe hand, foot and mouth disease being treated in the intensive care units of 3 children's hospitals, including 1 case residing in Tan Thoi Nhat Ward (District 12). The rest are cases transferred from other provinces, 14 of whom are in critical condition and needing ventilators, and 1 case of dialysis.
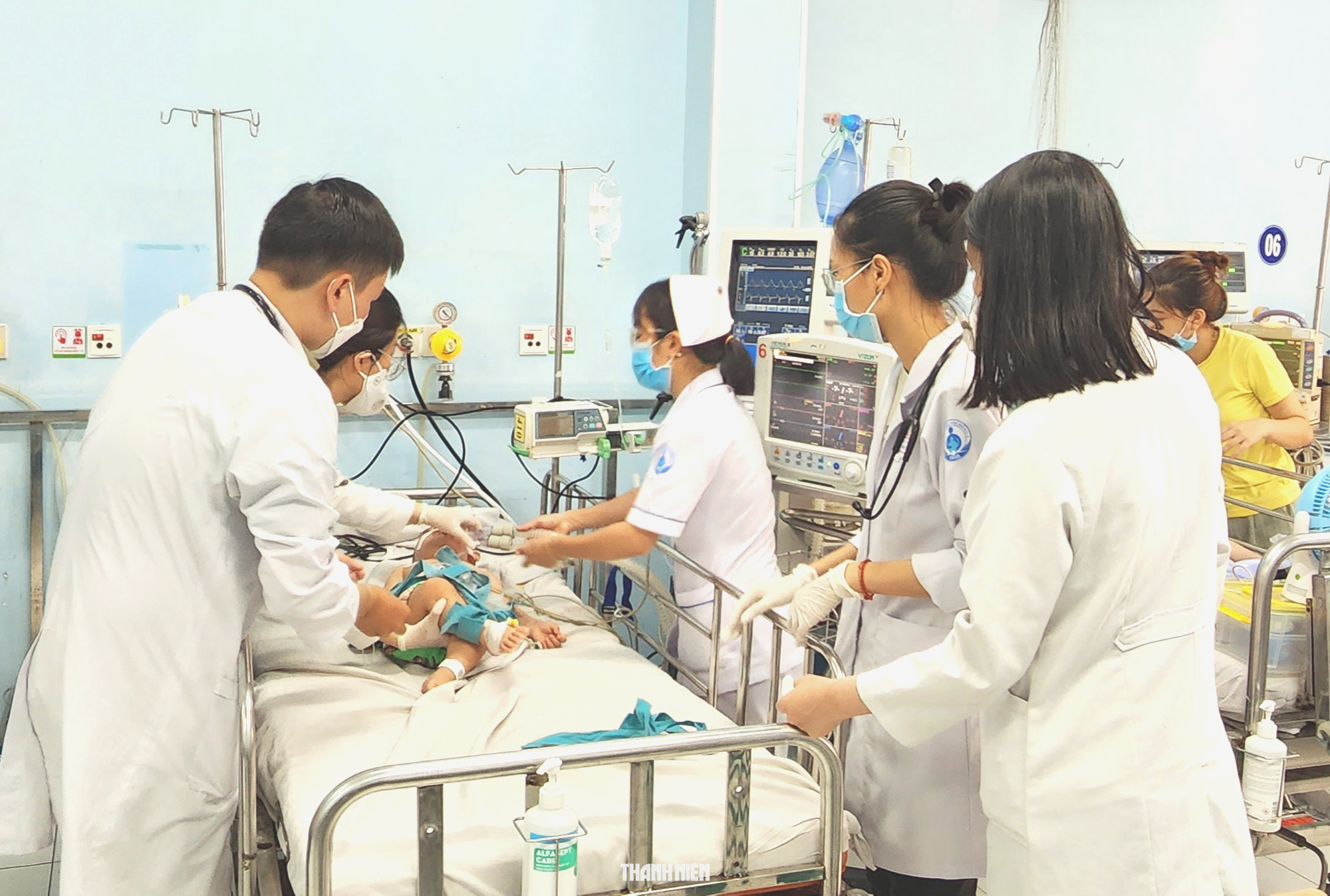
A severe case of hand, foot and mouth disease is being treated at Children's Hospital 1, Ho Chi Minh City.
3 situations when severe hand, foot and mouth disease increases
Faced with the worsening situation of hand, foot and mouth disease, the Ho Chi Minh City Department of Health has developed a plan to ensure the admission and treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease in the city.
Scenarios to respond to 3 situations if there are many severe cases (grade 2a or higher, estimated to account for about 10% of inpatient cases).
Scenario 1: Expected when there are less than 50 new hospitalizations/day, less than 200 inpatients and less than 20 severe cases in hospitals. Accordingly, the total number of beds for hand, foot and mouth disease treatment in this scenario is more than 200, with 30 beds for intensive care. Hand, foot and mouth disease patients are given priority for treatment at 3 specialized pediatric hospitals in the city.
Scenario 2: When the number of new hospitalizations per day increases from 50-100, the health system serves 200-700 inpatients and 20-70 severe cases in hospitals. At this time, the total number of beds for hand, foot and mouth disease treatment will need 700 beds, including 80 intensive care beds. Children with hand, foot and mouth disease are treated at 3 specialized pediatric hospitals and the Hospital for Tropical Diseases.
Scenario 3: Expected to be implemented when the city has 100-200 new cases of hand, foot and mouth disease admitted to the hospital each day and medical facilities have 700-1,400 inpatients with about 70-140 severe cases in hospitals. The total number of treatment beds needed to be prepared in this scenario is 1,400 beds with about 150 intensive care beds. Severely ill children are treated at 3 specialized pediatric hospitals and the Hospital for Tropical Diseases.
At the same time, the treatment system implements the process of classifying outpatient and inpatient pediatric patients and assigning treatment routes to avoid local overload at end-line hospitals and minimize deaths.
Recommendations for support in finding more suppliers of hand, foot and mouth disease medicine
The Ho Chi Minh City Department of Health has directed units to urgently prepare medicines and infusions, medical equipment and supplies for the above response plans. The Department of Health has also sent a dispatch requesting the Drug Administration to support finding additional suppliers of specific drugs, and requesting the National Institute for Control of Vaccines and Medical Biologicals to support speeding up the testing of related medical biologicals necessary for the treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease in order to promptly circulate imported drugs, serving the medical examination and treatment work in the current rapidly progressing epidemic situation.
In addition to actively treating patients, the three pediatric hospitals and the Tropical Diseases Hospital are also assigned to provide professional support in treating hand, foot and mouth disease for lower-level hospitals and provinces in the region, preventing cases of unsafe transfer of patients from the provincial level to the city.
Along with that, re-training on diagnosis and treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease, detection of signs of severe disease, basic and advanced emergency resuscitation for all medical examination and treatment facilities from clinics to district hospitals, general hospitals with pediatric departments in the city.
The team of hand, foot and mouth disease experts is on duty at the "hotline" and is ready to provide professional support to the facilities when necessary. In case of a serious case that is assessed through consultation as unsafe for transfer to a higher level, the final level hospital will proactively send experts to provide direct professional support to the facility.
The Department of Health also requested the city's three children's hospitals and the Hospital for Tropical Diseases to continue to coordinate with the Oxford University Clinical Research Unit (OUCRU) to sequence genes to identify severe disease-causing genes of EV71 from samples of hand, foot and mouth disease patients.
Hand , foot and mouth disease is a disease transmitted through the digestive tract, which can progress rapidly and threaten life . The health sector encourages all people, especially families with children under 5 years old, to strictly implement the following disease prevention measures:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and running water for children and caregivers.
- Regularly clean surfaces and tools that children come into contact with every day.
- When detecting signs of suspected illness in children, take the child to the nearest medical facility for examination.
- Closely monitor children with hand, foot and mouth disease to detect early signs of worsening illness such as sudden startle, continuous high fever, constant crying, rapid pulse, purple rash, and weak limbs.
Source link


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam meets and expresses gratitude to Vietnam's Belarusian friends](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/11/c515ee2054c54a87aa8a7cb520f2fa6e)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam concludes visit to Russia, departs for Belarus](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/11/0acf1081a95e4b1d9886c67fdafd95ed)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam arrives in Minsk, begins state visit to Belarus](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/11/76602f587468437f8b5b7104495f444d)


























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the Party Congress of the Committee for Culture and Social Affairs](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/11/f5ed02beb9404bca998a08b34ef255a6)






























































Comment (0)