New research published in the biomedical journal The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests a diet that can help regulate blood sugar levels and slow brain aging in older adults.
The international study, conducted by scientists from the University of Leipzig, the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research (Germany), in collaboration with Ben-Gurion University and Soroka University Medical Center, (Israel), and the Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health (USA), is called the DIRECT PLUS Trial.
The study aimed to investigate the impact of diet on brain aging, including 294 participants with an average age of 51, abdominal obesity or abnormal blood lipid levels, who were followed for 18 months.

Both Mediterranean diets can help regulate blood sugar and slow brain aging, with the green Mediterranean diet producing better results.
Participants were divided into 3 groups:
- Regular healthy diet
- Traditional Mediterranean diet, low in simple carbohydrates
- The Mediterranean diet is green, rich in polyphenols and low in red meat.
Both the Mediterranean and Green Mediterranean diets consumed 28 grams of walnuts, providing about 440 mg of polyphenols per day.
The Mediterranean Green group also supplemented with 3–4 cups of green tea and a Mankai smoothie daily, providing an additional 800 mg of polyphenols.
Researchers collected blood samples and brain MRI scans at the start of the study and after 18 months to track changes in brain volume.
A total of 224 participants completed the trial.
Normally, the brain will gradually shrink and age. However, the results show that both the Mediterranean and green Mediterranean diets can help regulate blood sugar and slow down the aging process of the brain, in which the green Mediterranean diet brings better results, according to the medical website Medical News Today.
The authors found that better blood sugar control and daily consumption of foods rich in polyphenols found in Mankai and green tea may slow brain aging, especially in brain regions responsible for cognition, motor function, and sensory information processing.
Specifically, both the Mediterranean and green Mediterranean diets significantly slowed age-related brain shrinkage by about 50 percent within 18 months, according to Medical News Today.
People who followed both the Mediterranean and green Mediterranean diets had a younger brain age than their actual age, as shown by:
- 20.4% weight loss
- 20.7% reduction in waist circumference
- Diastolic blood pressure decreased by 18.6%
- Systolic blood pressure decreased by 18.9%
- Insulin levels decreased by 9.9%
- Average blood sugar index HbA1c decreased by 16.4%.
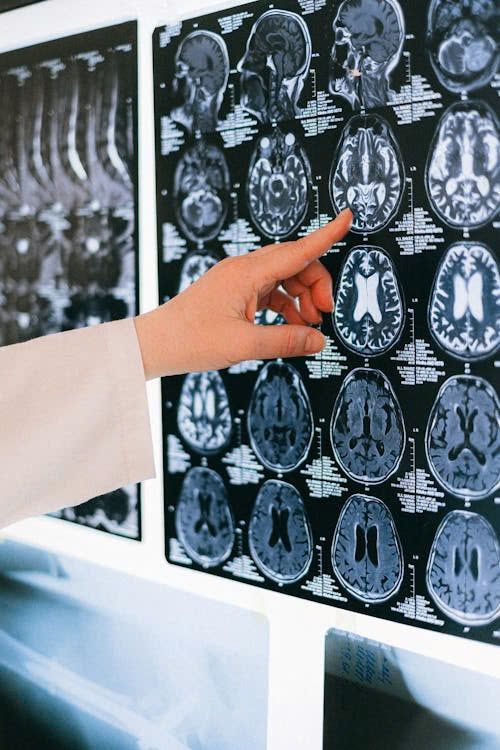
Both the Mediterranean and green Mediterranean diets significantly slowed age-related brain shrinkage by about 50% within 18 months
What is special about the green Mediterranean diet?
Experts recommend adopting a green Mediterranean diet if possible and suggest adding more polyphenol-rich foods to protect brain health.
The Mediterranean diet includes: Lots of vegetables, fruits, legumes and nuts; Lots of whole grains, such as whole wheat bread and brown rice; Lots of olive oil and fatty fish; Some yogurt; Eat poultry and fish, limit red meat; Very few sweets and processed foods.
What else does the green Mediterranean diet encourage?
In addition to reducing meat intake and increasing plant intake, the green Mediterranean diet recommends consuming the following polyphenol-rich foods to slow brain aging:
- Green tea daily, about 3 - 4 cups (240 ml/cup).
- Walnuts are rich in polyphenols and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and polyphenols.
- Green leafy vegetables (like spinach, lettuce, and arugula) contain flavanols, folate, lutein, and antioxidants that help protect cognitive function.
- Berries are rich in flavonoids, especially anthocyanins.
- Fatty fish (such as salmon, sardines) provide the omega-3 fatty acid DHA.
- Turmeric contains the biologically active curcumin.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/phat-hien-moi-ve-che-do-an-cuc-tot-cho-nguoi-tren-50-tuoi-185241113160210221.htm





































































































Comment (0)