Seafood salad, rare meat, pickled fish and meat, animal organs, raw vegetables, vegetable juices, etc. have the risk of being infected with parasitic worms, which are harmful to health.
Parasitic worm larvae can be transmitted to humans through food when consuming raw or unsanitary food containing eggs or cysts carrying larvae. Some other types can enter the human body through skin contact.
Doctor, PhD Vu Truong Khanh (Head of Gastroenterology Department, Tam Anh General Hospital, Hanoi) said that when infected with worms, patients often have symptoms of abdominal pain, digestive disorders, weight loss, fatigue, itchy skin. The disease progresses silently, many cases are accidentally discovered when going for a health check-up with tests and imaging. If not promptly detected and treated, worms can cause many dangerous complications such as intestinal or bile duct obstruction, gastrointestinal bleeding, anemia, cholangitis, hemoptysis, liver abscess, encephalitis, meningitis... After recovery, patients can still be re-infected if they do not eat hygienically and deworm regularly.
Below are some foods that pose a risk of parasitic infection that people should be careful when using, according to Dr. Khanh's suggestions.
Seafood salad
Seafood salads such as fish salad, sushi, sashimi, shrimp salad... are loved by many people. Seafood living in the sea is less susceptible to bacteria and parasites. However, seafood raised in brackish water, estuaries such as shrimp and fish are susceptible to parasites. Among them, snails can contain thousands of tubeworm parasites due to their habit of living hidden deep in the mud.
If these dishes are not prepared hygienically or cooked thoroughly, the risk of parasitic infection is very high. Manual processing and storage that do not meet food safety and hygiene standards also put seafood at high risk of being infected with parasitic larvae. After entering the body, parasites damage the liver and gallbladder, causing headaches, nausea, and diarrhea.
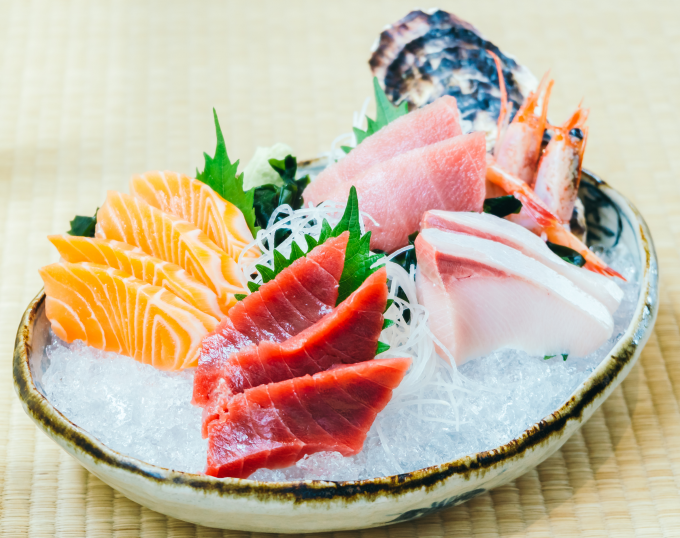

Raw foods, if not prepared hygienically, are at risk of being contaminated with parasitic larvae. Photo: Freepik
Blood pudding
Blood pudding is made from raw blood, without heat treatment, so bacteria and parasites are not destroyed. Therefore, eating blood pudding has a high risk of parasitic infection and digestive diseases, especially blood from infected pigs, ducks, goats...
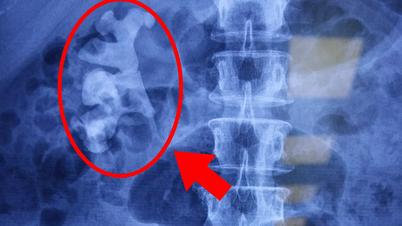
According to Dr. Khanh, there are many cases where people who eat raw blood are infected with worms. They migrate to the brain, nest in the brain causing meningitis or the worms nest compresses the brain, causing the patient to have severe headaches and convulsions that are easily mistaken for stroke. In this case, if not treated promptly, the patient may suffer from hemiplegia and many other sequelae such as reduced vision, epilepsy...
Rare meat
The habit of eating undercooked goat, buffalo, beef, pork... can introduce worms and parasites into the body. Poor meat quality, unclean processing, and undercooked cooking will not eliminate harmful parasites. After entering the body, the worm larvae will escape the cyst and adhere to the small intestine, penetrating through the intestinal wall and throughout the body. Animal meat must be thoroughly cooked before use to ensure that it does not transmit worms and parasites.
Pickled meat and fish
Fermented meat and fish dishes such as fermented pork rolls, sour meat, and sour salted fish are not cooked but are cooked using the fermentation of leaves (guava leaves, fig leaves, polyscias fruticosa leaves), rice bran, and some spices. If these dishes are not fermented enough, the eggs and larvae of worms in these foods will not be destroyed. People who eat these dishes may be infected with parasites. In addition, manual processing and storage that do not meet food safety and hygiene standards can easily put meat and fish at high risk of being infected with worm larvae.
Raw vegetables, aquatic vegetables
Vegetables and fruits grown underground or underwater are at high risk of parasitic infection. These foods, if watered with dirty water, fertilized with fresh manure or grown in dirty soil containing worm eggs. People who regularly drink fresh vegetable juice, eat raw vegetables or dip vegetables are at high risk of worm infection and other digestive diseases such as diarrhea, dysentery, and poisoning.
Dr. Khanh added that parasites are different from bacteria and viruses, their eggs or larvae that stick to the surface of vegetables can be washed away by rinsing directly under clean running water. To avoid parasitic infections, people should limit eating raw vegetables or wash raw vegetables thoroughly under clean running water (coriander, lettuce, pennywort, mustard greens...), aquatic vegetables (watercress, celery, lotus root, water spinach, water spinach, Vietnamese coriander) should be cooked thoroughly. Before processing vegetables into food, they need to be washed many times and soaked in salt water.
Animal organs
When parasitic worms enter the animal's body, they often parasitize the internal organs, which are very difficult to clean. If consumed, the possibility of parasitic infection is high.
Many people have the habit of drinking alcohol after eating raw or undercooked food to "kill" parasites. However, according to Dr. Khanh, the alcohol concentration in alcohol will be diluted when entering the stomach, so it will not be effective. Parasites can survive in the acidic environment of the stomach, so adding sour or spicy spices cannot kill them. However, parasites can die when heated to a temperature of about 60-70 degrees Celsius. The only way to completely kill them is to cook food and drinks at high temperatures. Depending on the type of food, the processing time is different.
To avoid cross-contamination, everyone needs to make sure to disinfect kitchen utensils after each use; avoid mixing raw and cooked foods; wear protective gloves when handling raw foods; and wash hands with soap before and after cooking.
Trinh Mai
Source link


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the meeting of the Subcommittee on Documents of the First National Assembly Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/72b19a73d94a4affab411fd8c87f4f8d)
![[Photo] General Secretary concludes visit to Azerbaijan, departs for visit to Russian Federation](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/7a135ad280314b66917ad278ce0e26fa)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam begins official visit to Russia and attends the 80th Anniversary of Victory over Fascism](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/5d2566d7f67d4a1e9b88bc677831ec9d)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with the Policy Advisory Council on Private Economic Development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/387da60b85cc489ab2aed8442fc3b14a)

![[Photo] President Luong Cuong presents the decision to appoint Deputy Head of the Office of the President](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/501f8ee192f3476ab9f7579c57b423ad)

























































![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh talks on the phone with Singaporean Prime Minister Lawrence Wong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/8/e2eab082d9bc4fc4a360b28fa0ab94de)






























Comment (0)