Acute pancreatitis is not only a dangerous disease but also easily recurs, and if not treated promptly, can lead to death.
Having just escaped the critical condition after many days of treatment for acute pancreatitis, Mr. NTH ( Hanoi ) shook his head and refused all invitations to drink at the end of the year. The doctor's advice about the increase in cases of acute pancreatitis and alcohol poisoning at the end of the year made him even more determined not to repeat the offense. This is also a warning for many people during the Tet holiday season, when the need to eat, drink and drink alcohol increases dramatically.
Dangerous diseases from drinking habits
Mr. NTH still cannot forget the emergency treatment at the hospital for acute pancreatitis, which seemed like a “one-way trip”. Before being admitted to the hospital, he felt severe abdominal pain, could not eat or drink, and the pain spread to his chest, sides and back. When he was admitted to the hospital, the plasma taken from his body was milky, due to high blood fat, severe acute pancreatitis, threatening his life.
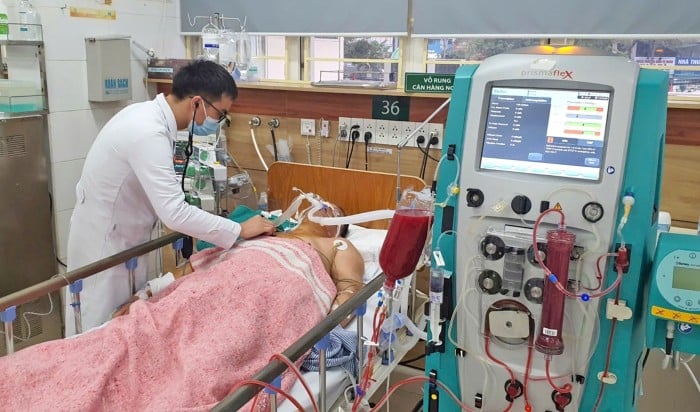 |
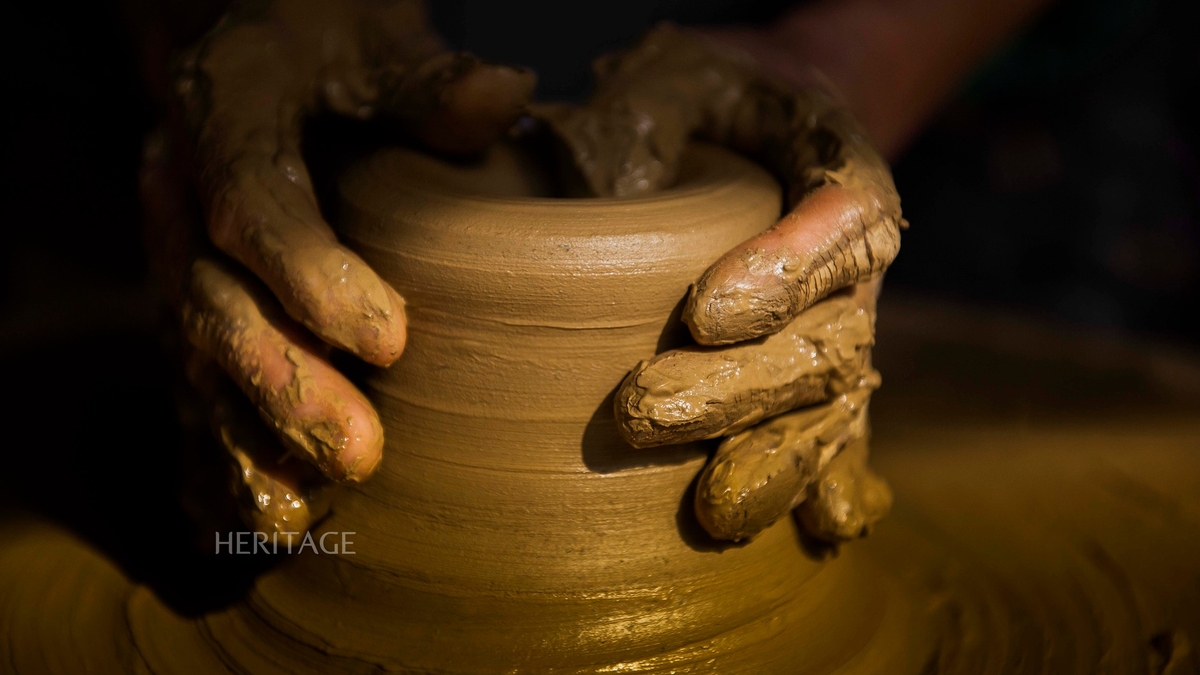
| The habit of drinking alcohol and beer every day causes many people to suffer from acute pancreatitis. Illustrative photo |
He said the cause of the above condition was the habit of drinking beer every day, especially at year-end parties. Drinking alcohol continuously caused him to suffer from acute pancreatitis, a dangerous disease that can lead to death if not treated promptly.
According to doctors, acute pancreatitis is a condition in which the pancreas is suddenly inflamed. If not treated promptly, the disease can lead to multiple organ failure, pancreatic necrosis and infection, with a mortality rate ranging from 5-15%, up to 20% depending on the cause, severity and health status of the patient.
The habit of drinking a lot of beer and alcohol increases blood fat, narrows the pancreatic duct, causing digestive enzymes to not be secreted into the small intestine but stagnate in the pancreas, leading to inflammation. Especially during Tet, when the need to drink beer and alcohol increases, cases of acute pancreatitis often increase, with rapid and dangerous developments.
Acute pancreatitis is a disease that is not only dangerous but also prone to recurrence, and if not treated promptly, can lead to death. However, one of the major problems is that the symptoms of acute pancreatitis are easily confused with other diseases such as gastritis, cardiovascular problems or biliary tract disease. This makes many people subjective, self-medicate without going to the hospital, making the condition more serious.
When experiencing symptoms such as continuous upper abdominal pain, increased pain after eating foods high in protein or fat, or after drinking alcohol, the patient should go to the hospital for timely examination and treatment.
Also during the end of the year, hospitals often receive cases of serious alcohol poisoning, especially methanol poisoning. Nghe An General Hospital recently received many cases of alcohol poisoning in serious condition, deep coma, especially methanol poisoning.
A typical example is the case of Mr. LXĐ (48 years old, Vinh City) who was hospitalized with headache, blurred vision, and fatigue after drinking alcohol.
Test results showed that the methanol concentration in his blood was 63.85 mg/100 ml. He received intensive treatment and fortunately recovered, while a friend of his, who also drank the same wine, unfortunately died from severe poisoning.
According to Dr. Nguyen Trong Toan, Department of Poison Control, Nghe An General Hospital, in recent years, the department has received many patients with alcohol poisoning, most of them male and of different ages. In particular, many patients suffered from severe methanol poisoning, were in deep coma and had to be put on a ventilator.
At the Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital, alcohol poisoning during Tet is not uncommon. Doctor Nguyen Trung Nguyen, Director of the Center, said that methanol poisoning usually has two stages: the hidden stage (from the first few hours to 30 hours) and the stage with obvious symptoms. Initial symptoms are often mild and easily overlooked, making patients unaware of the danger level of the poisoning.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning include: headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, disorientation, bluish lips and fingernails, difficulty breathing, seizures, coma, and can lead to death if not treated promptly.
At the end of the year, when festivals and parties are taking place densely, people need to pay special attention to protecting their health. The habit of drinking alcohol not only increases the risk of acute pancreatitis but can also cause methanol poisoning, leading to serious complications.
When experiencing unusual symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, or nausea after drinking alcohol, the patient should quickly go to a medical facility for timely diagnosis and treatment. Remember, prevention and early detection of disease are always the most important factors to protect life during the Tet holiday season.
Connective tissue disease is rare but can easily lead to dangerous complications.
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is an uncommon autoimmune disease characterized by a cross-section of clinical features from several different autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, and polymyositis.
This disease is associated with the presence of antinuclear antibodies against the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) antigen, and although rare, can cause serious complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Recently, Medlatec General Hospital received patient NTH (30 years old) for examination because of unusual red rashes on both cheeks. Medical history showed that Ms. H. had suffered from thrombocytopenia of unknown cause for the past 10 years and was being treated with Medrol 2mg daily.
Through examination, the doctor discovered skin lesions with unclear red rash on both cheeks, the skin was tight and discolored, the surface was not scaly and there were no blisters.
Laboratory testing showed that the patient was positive for multiple autoimmune antibodies, including ANA (antinuclear antibody), Anti-nRNP/Sm, Anti-DsDNA, and several others.
Based on clinical and paraclinical results, Ms. H. was diagnosed with mixed connective tissue disease. The patient was prescribed a personalized treatment regimen and advised to avoid direct exposure to sunlight to reduce the risk of aggravating the disease.
According to Master, Doctor Tran Thi Thu, Dermatology specialist, Medlatec General Hospital, mixed connective tissue disease is 9 times more common in women than in men, and most patients develop the disease in adulthood.
MCTD is characterized by a cross-reactivity between symptoms of other autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Although the exact cause of the disease is unknown, risk factors have been noted. Genetic factors play an important role; people with relatives with autoimmune diseases are at increased risk of developing MCTD.
Certain genes such as HLA-DR and HLA-DQ, if altered, can cause the immune system to mistakenly identify the body's normal tissues as "enemies", leading to the immune system attacking its own body.
In addition to genetic factors, environmental factors such as viral infections (EBV, CMV), exposure to toxic chemicals (silica dust, pesticides), and ultraviolet (UV) rays can also trigger an abnormal immune response. The hormone estrogen can also affect the functioning of the immune system and increase the risk of developing autoimmune diseases in women.
The symptoms of MCTD are varied and can vary from patient to patient. The early stages of the disease often have nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, joint pain and low-grade fever.
However, one of the hallmark signs of MCTD is Raynaud's syndrome, which involves fingers becoming pale, cold, and then turning blue-purple when exposed to cold or emotional disturbances.
If not detected and treated promptly, the disease can cause damage to many organs in the body and lead to serious complications such as myocarditis, mitral valve prolapse, interstitial pneumonia, pulmonary hypertension, autoimmune hepatitis, nephrotic syndrome, glomerulonephritis, aseptic meningitis, and cauda equina syndrome.
Symptoms can progress over time, seriously affecting quality of life and even becoming life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
To reduce the risk of disease and control it effectively, Dr. Thu recommends that patients should see a specialist when experiencing unusual symptoms and have regular health check-ups to detect complications early.
Additionally, patients should avoid direct sunlight, use sunscreen, not smoke, and keep warm in cold weather. A balanced diet, omega-3 supplements, light exercise, and stress management through relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga are also helpful.
MCTD is a complex autoimmune disease and difficult to diagnose because its symptoms overlap with those of other autoimmune diseases. Differentiating MCTD from overlap syndromes and differentiated autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, or dermatomyositis is a major clinical challenge.
Because MCTD can progress to differentiated autoimmune diseases over many years, accurate diagnosis and monitoring are important to help patients receive effective treatment and prevent dangerous complications.
Endometriosis and the Breakthrough Treatment of Radiofrequency Ablation
Endometriosis is a fairly common disease in women of reproductive age, seriously affecting the patient's quality of life.
In the past, surgery was often used as the only solution to treat endometriosis, but now, the minimally invasive radiofrequency ablation (RFA) method is bringing new hope to many women, helping to eliminate tumors and effectively reduce pain.
Ms. HPH (43 years old, Bac Giang) is one of the lucky patients who was successfully treated with high-frequency radio wave ablation. Returning to the hospital for a follow-up examination after choosing this method to treat endometriosis in the abdominal wall muscles, Ms. H. was happy because the results were very positive. The MRI scan results showed that the tumor had completely disappeared, and she no longer felt the pain in her abdominal wall like before.
Ms. H. shared, “Immediately after the radiofrequency ablation, my pain symptoms were significantly reduced. One month after the treatment, I no longer had to endure the pain during my menstrual period.” Ms. H.’s quality of life has improved significantly, making her and her family extremely happy.
Similarly, Ms. NTL (38 years old, Hanoi) also had to have two cesarean sections. However, in the past year, she has been constantly experiencing abdominal pain and has discovered a growing tumor in the old surgical scar area every time her period is near.
Worried, Ms. L. went to Hanoi Medical University Hospital for a check-up and was diagnosed with endometriosis in the abdominal wall muscles. After being treated with radiofrequency ablation, Ms. L. no longer felt pain and could no longer feel the tumor in her abdomen.
Sharing about the high-frequency wave ablation method, Dr. Nguyen Thai Binh, Center for Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Radiology, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, said that this is a new technique for treating endometriosis in the abdominal wall muscles, not yet popular in the world and is being implemented for the first time in Vietnam.
This method uses high frequency waves to destroy lesions and tumors without surgery, helping patients recover quickly.
By making a small needle puncture into the abdominal wall, the doctor will use radiofrequency waves to burn off each point of the tumor until it disappears completely.
This is a minimally invasive, non-surgical method that helps reduce pain and complications, while allowing patients to recover quickly. After the procedure, patients will be in good health immediately and will not experience any complications, and can resume normal activities and work the following day.
Doctor Thai Binh added that before applying this method, patients often had to undergo surgery, even cutting the rectus abdominis muscle, causing pain and a long recovery time.
The rate of remaining lesions and requiring reoperation is also quite high. However, with the radiofrequency ablation method, patients only need anesthesia, no anesthesia, and can go home immediately after the procedure or stay in the hospital for only one day.
Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrial cells migrate, forming masses outside the uterine lining, which can appear in locations such as the pelvic peritoneum, ovaries or abdominal wall, especially in areas of old surgical scars.
The disease can cause severe pain, especially during the menstrual cycle, seriously affecting the patient's daily activities. According to statistics, one in 10 women suffer from this disease.
Pain is the most common and recognizable symptom of endometriosis, however, the disease can also cause menstrual disorders and even infertility. Depending on the location and extent of the damage, pain symptoms can vary, affecting each patient differently.
To control the disease and prevent serious complications, doctors recommend that women of reproductive age should have regular check-ups and proactively seek medical attention immediately when experiencing unusual symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, menstrual disorders, or difficulty conceiving. Early detection and timely treatment can help patients avoid dangerous complications and protect reproductive health.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is now proving to be an effective and minimally invasive solution for women with endometriosis, especially in cases where the tumor causes pain and discomfort. With the development of medicine, women have more and more safe treatment options, helping to improve the quality of life and protect reproductive health.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/tin-moi-y-te-ngay-131-nguy-co-mat-mang-vi-ruou-bia-cuoi-nam-d240418.html







![[Photo] Closing ceremony of the 18th Congress of Hanoi Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/17/1760704850107_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)
























![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper launches “Fatherland in the Heart: The Concert Film”](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760622132545_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-36-png.webp)













































































Comment (0)