Diabetic patients face the risk of foot damage due to complications caused by the disease.
A typical case is Ms. NTK (64 years old, Binh Duong) who has had diabetes for more than 10 years and often has numb feet. 10 days ago, she discovered that her left ring toe was red and swollen but did not feel any pain.
After buying antibiotics to take herself, the red and swollen wound spread to her entire foot, her ring toe turned black and oozed pus. Her family took her to the hospital in the hope of saving her left foot.
Through examination, doctors said that Ms. K. had diabetic neuropathy causing loss of sensation in her feet leading to toe infection.
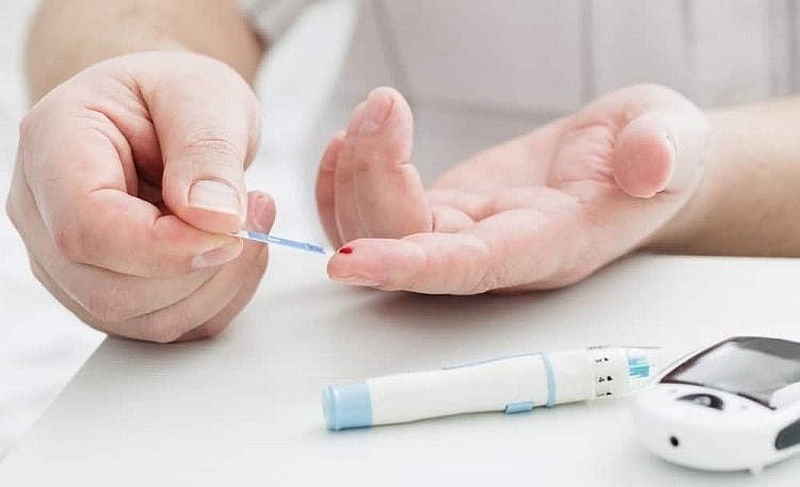 |
| Illustration |
A normal person with a wound like Mrs. K's would be in unbearable pain and not be able to sleep, but Mrs. K did not feel any pain at all.
Ms. K. faced the risk of having her toe amputated due to severe necrosis. After examination and evaluation, the doctor decided to remove the necrotic tissue and care for the patient's foot to keep it intact.
Another case is Ms. NTM (57 years old, Soc Trang) with type 2 diabetes had to have 2 toes amputated due to a severe infection.
Before that, she was stabbed by a small piece of glass but did not feel any pain so she did not go to the doctor to get the wound treated. After 1 week, her foot became infected and 2 toes became gangrenous.
According to statistics from the health sector, Vietnam has about 7 million people with diabetes, of which more than 55% of patients have complications.
The World Health Organization (WHO) lists diabetic neuropathy among the top 10 neurological diseases causing health decline in 2021.
According to Dr. Truong Thi Vanh Khuyen, Department of Endocrinology - Diabetes, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, among patients hospitalized for foot infections, nearly 50% of cases have reduced or lost sensation in the feet.
Neurological complications in diabetic patients reduce or lose sensation in the feet, so when stepping on thorns, bones, pieces of glass, hot coals, or being scratched or bitten by insects, etc., the patient does not feel it immediately, leading to late detection of the wound and late treatment.
Furthermore, because the pain sensation is reduced, the patient will not be aware of the severity of the wound, delaying hospitalization. These factors increase the risk of severe infection, gangrene, and the risk of amputation.
Diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy is the most typical and common form of peripheral nerve complication in diabetics, and the incidence increases with the duration of the disease.
Statistics show that 10%-15% of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetics have peripheral neuropathy and this rate can exceed 50% in patients with diabetes for more than 10 years. Pain, numbness and paresthesia of both limbs are the most common clinical manifestations in patients with peripheral neuropathy, severe cases can lead to foot ulcers and even amputation.
The cause and pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy remain unclear, but hyperglycemia, lipid metabolism disorders, and abnormalities in nerve signal transmission are now considered to be the initiating factors for a series of pathophysiological changes in peripheral neuropathy.
When metabolic factors are abnormal, the normal structure and function of the entire peripheral nervous system, including myelinated and unmyelinated nerve axons, vascular neurons, and glial cells, are disrupted. In addition, abnormalities in nerve signaling pathways inhibit axon repair and promote apoptosis of damaged cells.
There have been many recent advances in the study of peripheral neuropathy mechanisms, including oxidative stress pathways, microvascular injury mechanisms, neuronal signaling pathway injury mechanisms, and other potential mechanisms involving neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cellular oxidative damage.
Severe diabetic neuropathy not only causes loss of sensation in the feet, but also causes foot deformities, calluses, foot ulcers, foot necrosis, and increases the risk of foot amputation.
Patients can recognize early diabetic neuropathy complications in the feet such as: numbness, tingling, and itching in the feet; pain when walking and pain relief when resting; slipping off shoes without realizing it, muscle atrophy in the legs and arms, muscle weakness, etc.
To prevent diabetic neuropathy, in addition to good blood sugar control, patients should listen to their bodies to detect early signs of abnormalities in order to get early examination and treatment.
At the same time, diabetics should proactively see an endocrinologist - diabetes specialist to be screened for diabetic foot complications regularly at least twice a year to detect the disease and receive early treatment, preventing unfortunate complications from occurring.
Patients with diabetic foot complications need to follow the doctor's instructions for monitoring, examination and treatment.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/bien-chung-ban-chan-cua-benh-nhan-tieu-duong-d223591.html


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh starts construction of vital highway through Thai Binh and Nam Dinh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/12/52d98584ccea4c8dbf7c7f7484433af5)



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Swedish Minister of International Development Cooperation and Foreign Trade](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/12/ae50d0bb57584fd1bbe1cd77d9ad6d97)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh works with the Standing Committee of Thai Binh Provincial Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/12/f514ab990c544e05a446f77bba59c7d1)























































































Comment (0)